Comparator (COMP) RM0440
780/2126 RM0440 Rev 4
24.3.4 COMP LOCK mechanism
The comparators can be used for safety purposes, such as over-current or thermal
protection. For applications having specific functional safety requirements, it is necessary to
insure that the comparator programming cannot be altered in case of spurious register
access or program counter corruption.
For this purpose, the comparator control and status registers can be write-protected (read-
only).
Once the programming is completed, the COMPx LOCK bit can be set. This causes the
whole register to become read-only, including the COMPx LOCK bit.
The write protection can only be removed by an MCU reset.
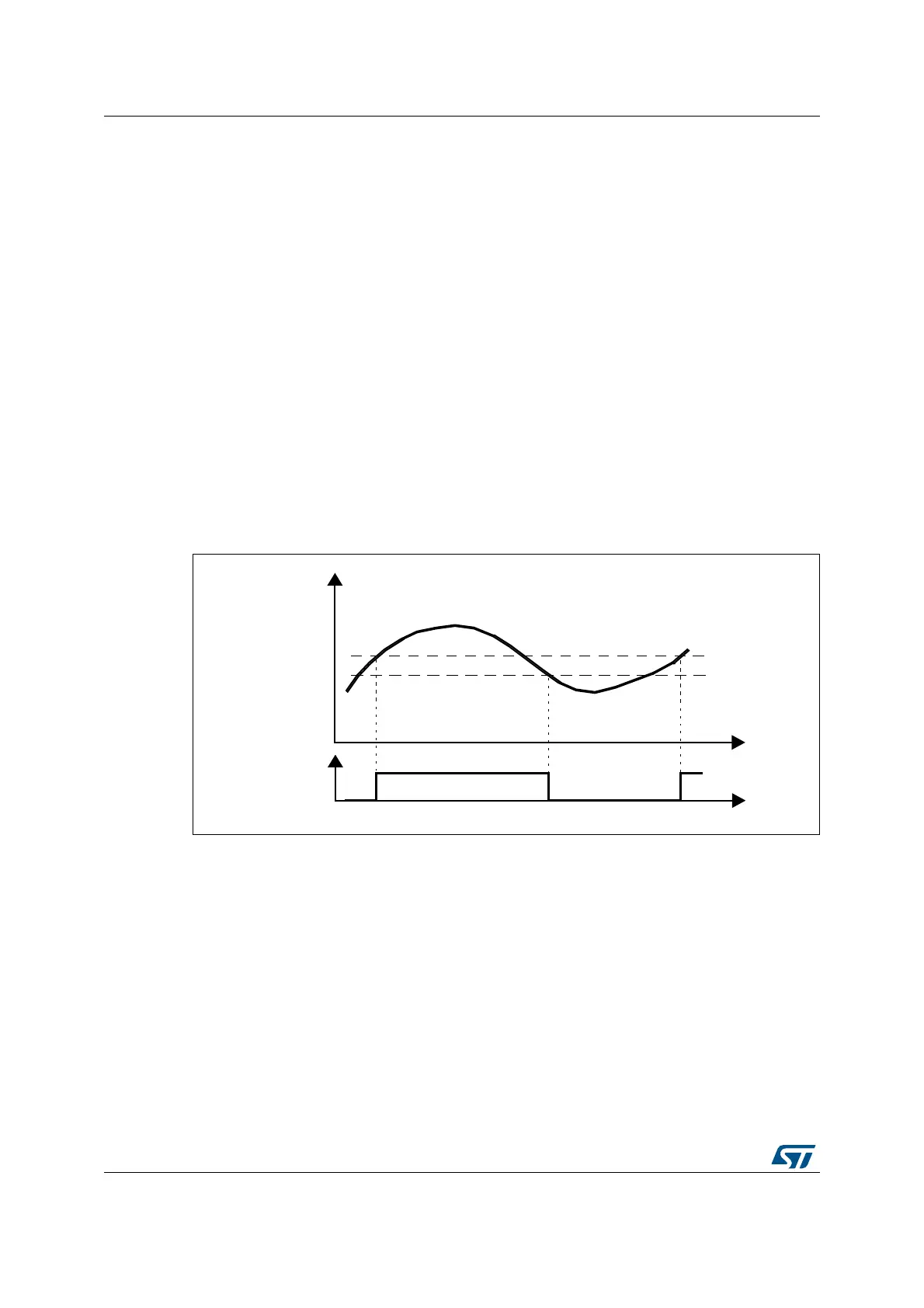
24.3.5 COMP hysteresis
The comparator includes a programmable hysteresis to avoid spurious output transitions
with noisy input signals. It is non-symmetrical and only acting to falling edge of the
comparator output. The internal hysteresis function can be disabled so as to set the amount
of hysteresis with external components, which can be useful for example when exiting a
low-power mode.
Figure 169. Comparator hysteresis
24.3.6 COMP output blanking
The purpose of the blanking function is to prevent the current regulation from tripping upon
short current spikes at the beginning of PWM period (typically the recovery current in power
switch anti-parallel diodes). This goes through setting a dead window defined with a timer
output compare signal. The blanking source is selected individually per comparator channel
by software through BLANKSEL[2:0] bitfield of corresponding COMP_CxCSR register, as
shown in Table 197: Blanking sources. The inverted blanking signal is logical AND-ed with
the comparator stage output to produce the comparator channel x output. See the example
provided in the following figure.
MS19984V1
INP
INM
INM - V
hyst
COMP_OUT
 Loading...
Loading...