The sensor resistance and the input resistance are in parallel which means: R =
If the temperature sensor is used on the single-ended analog input of Circulo then R = R because R >> R
.
The input voltage is = 5 V ·
To evaluate the accuracy, the amount of ticks for the measured temperature range needs to be considered:
Temperature range / Amount of ticks for the temperature range = Temperature measured / tick
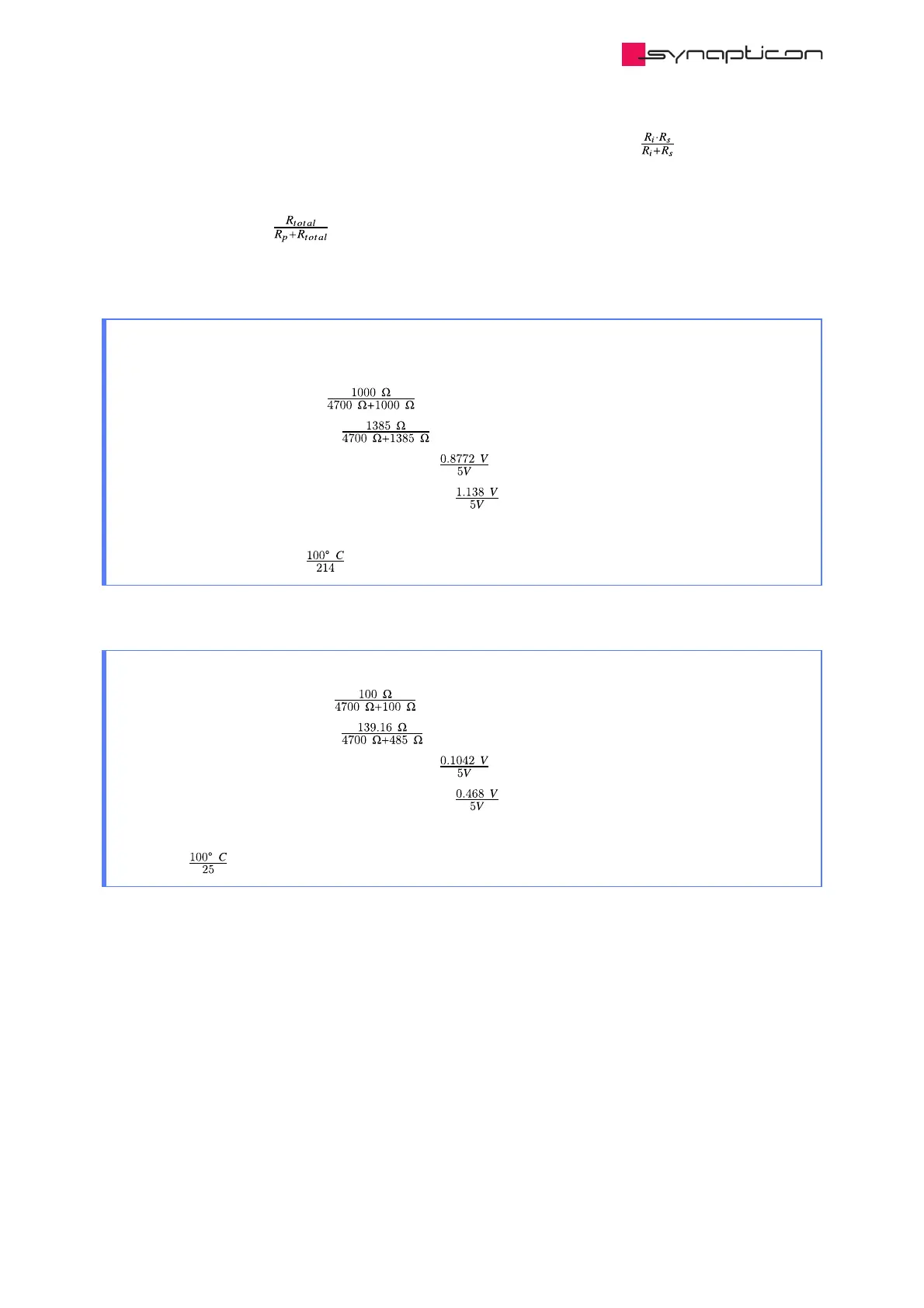
Example: ADC output on Circulo for a PT1000 temperature sensor
R = 4.7 kΩ, R be neglected because R >> R
ADC input voltage for 0° = 5 V · = 0.8772 V
ADC input voltage for 100° = 5 V · = 1.138 V
The converted value (ADC ticks) for 0° is = 4095 · = 718
The converted value (ADC ticks) for 100° is = 4095 · = 932
Temperature range in ticks: 932 - 718 = 214 ticks for 100° C.
This leads to an accuracy of ≈ 0.5° for measuring the temperature.
Now the accuracy of a PT100 with an R of 4.7 kΩ can be calculated for comparison:
Example: ADC output on Circulo for a PT100 temperature sensor.
ADC input voltage for 0° = 55 V · = 0.1042 V
ADC input voltage for 100° = 5 V · = 0.134 V
The converted value (ADC ticks) for 0° is = 4095 · = 85
The converted value (ADC ticks) for 100° is = 4095 · = 110
Temperature range in ticks: 110 - 85 = 25 for 100°C
Accuracy: = 4° for measuring the temperature.
total
s total i
s
p i i s
p
 Loading...
Loading...