F28x CPU + FPU + VCU and CLA
1 - 8 C2000 Microcontroller Workshop - Architecture Overview
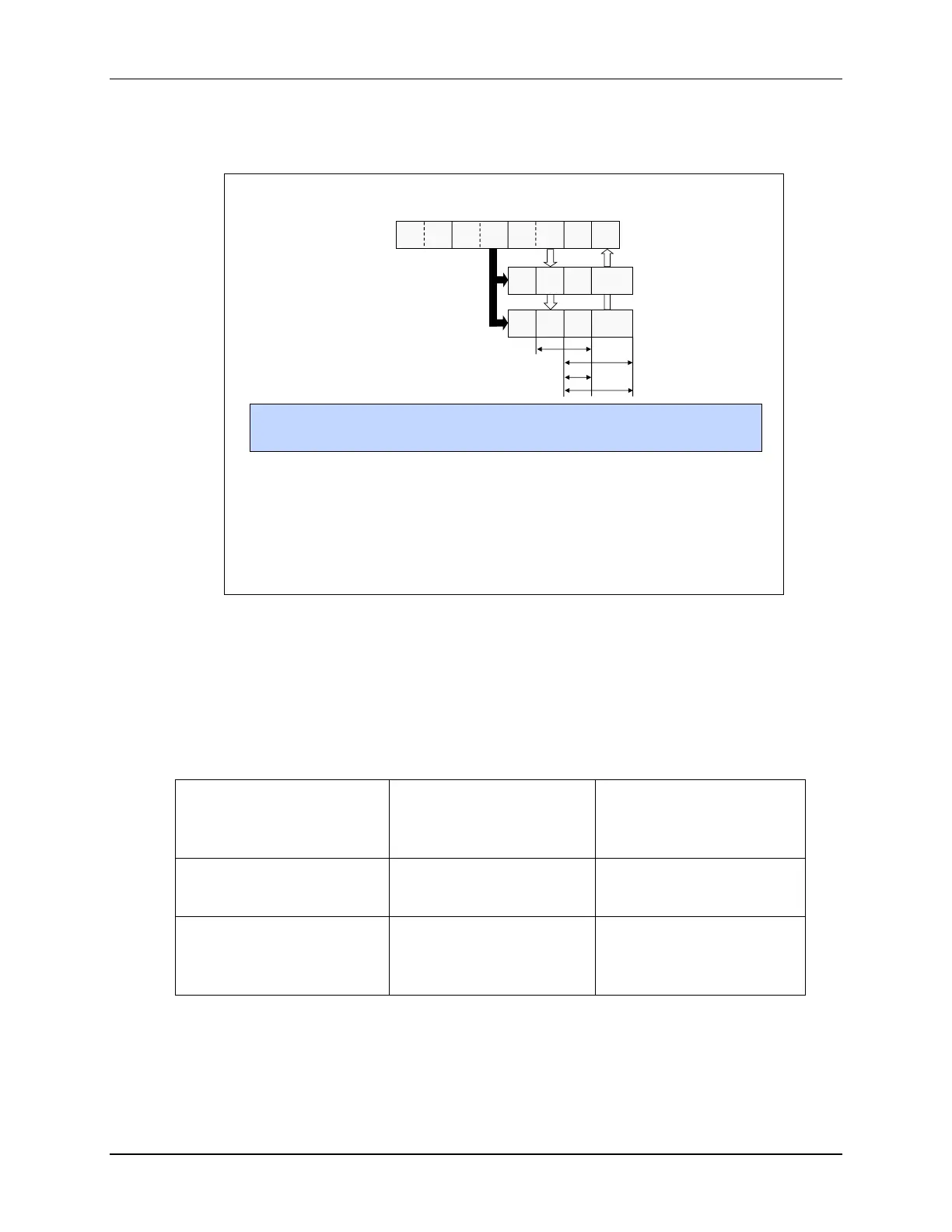
F28x CPU + FPU + VCU Pipeline
F28x CPU + FPU + VCU Pipeline
Floating Point Unit and VCU has an unprotected pipeline
i.e. FPU/VCU can issue an instruction before previous instruction has
written results
Compiler prevents pipeline conflicts
Assembler detects pipeline conflicts
Performance improvement by placing non-conflicting
instructions in floating-point pipeline delay slots
F
1
F
2
D
1
D
2
R
1
R
2
E
W
F28x Pipeline
Fetch Decode Read Exe Write
Floating-point math operations, conversions between integer and floating-
point formats, and complex MPY/MAC require 1 delay slot – everything else
does not require a delay slot
(load, store, max, min, absolute, negative, etc.)
Load
Store
0 delay slot instruction
1 delay slot instruction
D R E
1
E
2
/W
VCU Instruction
D R E
1
E
2
/W
FPU Instruction
Floating-point and VCU operations are not pipeline protected. Some instructions require delay
slots for the operation to complete. This can be accomplished by insert NOPs or other non-
conflicting instructions between operations.
In the user’s guide, instructions requiring delay slots have a ‘p’ after their cycle count. The 2p
stands for 2 pipelined cycles. A new instruction can be started on each cycle. The result is valid
only 2 instructions later.
Three general guideslines for the FPU/VCU pipeline are:
Math MPYF32, ADDF32,
SUBF32, MACF32,
VCMPY
2p cycles
One delay slot
Conversion I16TOF32, F32TOI16,
F32TOI16R, etc…
2p cycles
One delay slot
Everything else* Load, Store, Compare,
Min, Max, Absolute and
Negative value
Single cycle
No delay slot
* Note: MOV32 between FPU and CPU registers is a special case.
 Loading...
Loading...