AC Induction Motor Example
C2000 Microcontroller Workshop - Numerical Concepts 8 - 29
AC Induction Motor Example
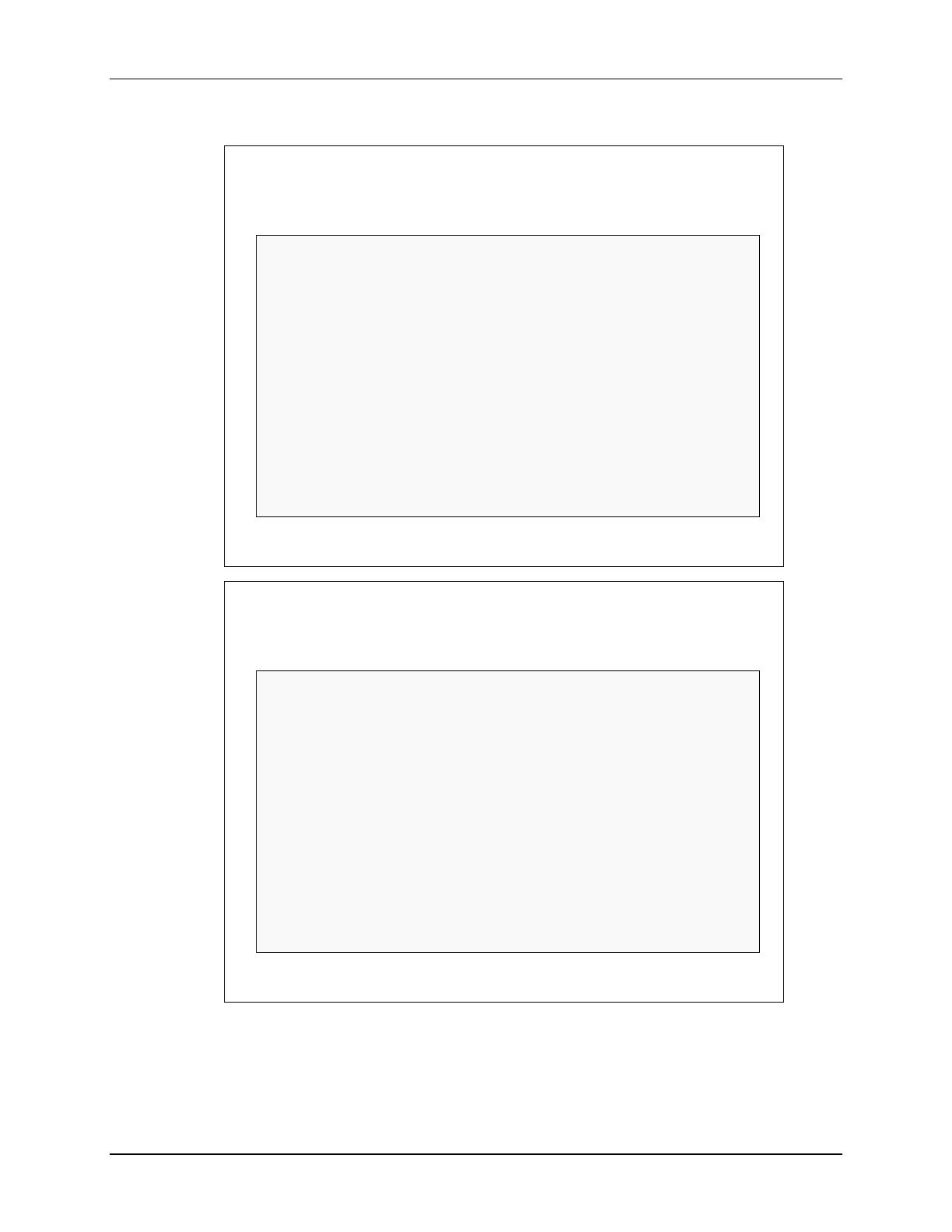
Park Transform – floating-point C code
#include “math.h”
#define TWO_PI 6.28318530717959
void park_calc(PARK *v)
{
float cos_ang , sin_ang;
sin_ang = sin(TWO_PI * v->ang);
cos_ang = cos(TWO_PI * v->ang);
v->de = (v->ds * cos_ang) + (v->qs * sin_ang);
v->qe = (v->qs * cos_ang) - (v->ds * sin_ang);
}
AC Induction Motor Example
Park Transform - converting to “IQmath” C code
#include “math.h”
#define TWO_PI 6.28318530717959
void park_calc(PARK *v)
{
float cos_ang , sin_ang;
sin_ang = sin(TWO_PI * v->ang);
cos_ang = cos(TWO_PI * v->ang);
v->de = (v->ds * cos_ang) + (v->qs * sin_ang);
v->qe = (v->qs * cos_ang) - (v->ds * sin_ang);
}
#include “IQmathLib.h”
_IQ(6.28318530717959)
_iq
_IQsin(_IQmpy(TWO_PI , v->ang));
_IQcos(_IQmpy(TWO_PI , v->ang));
_IQmpy(v->ds , cos_ang) + _IQmpy(v->qs , sin_ang);
_IQmpy(v->qs , cos_ang) - _IQmpy(v->ds , sin_ang);
The complete system was coded using "IQmath". Based on analysis of coefficients in the system,
the largest coefficient had a value of 33.3333. This indicated that a minimum dynamic range of 7
bits (+/-64 range) was required. Therefore, this translated to a GLOBAL_Q value of 32-7 = 25
(Q25). Just to be safe, the initial simulation runs were conducted with GLOBAL_Q = 24 (Q24)
 Loading...
Loading...