Introduction Ensemble Epaq Hardware Manual
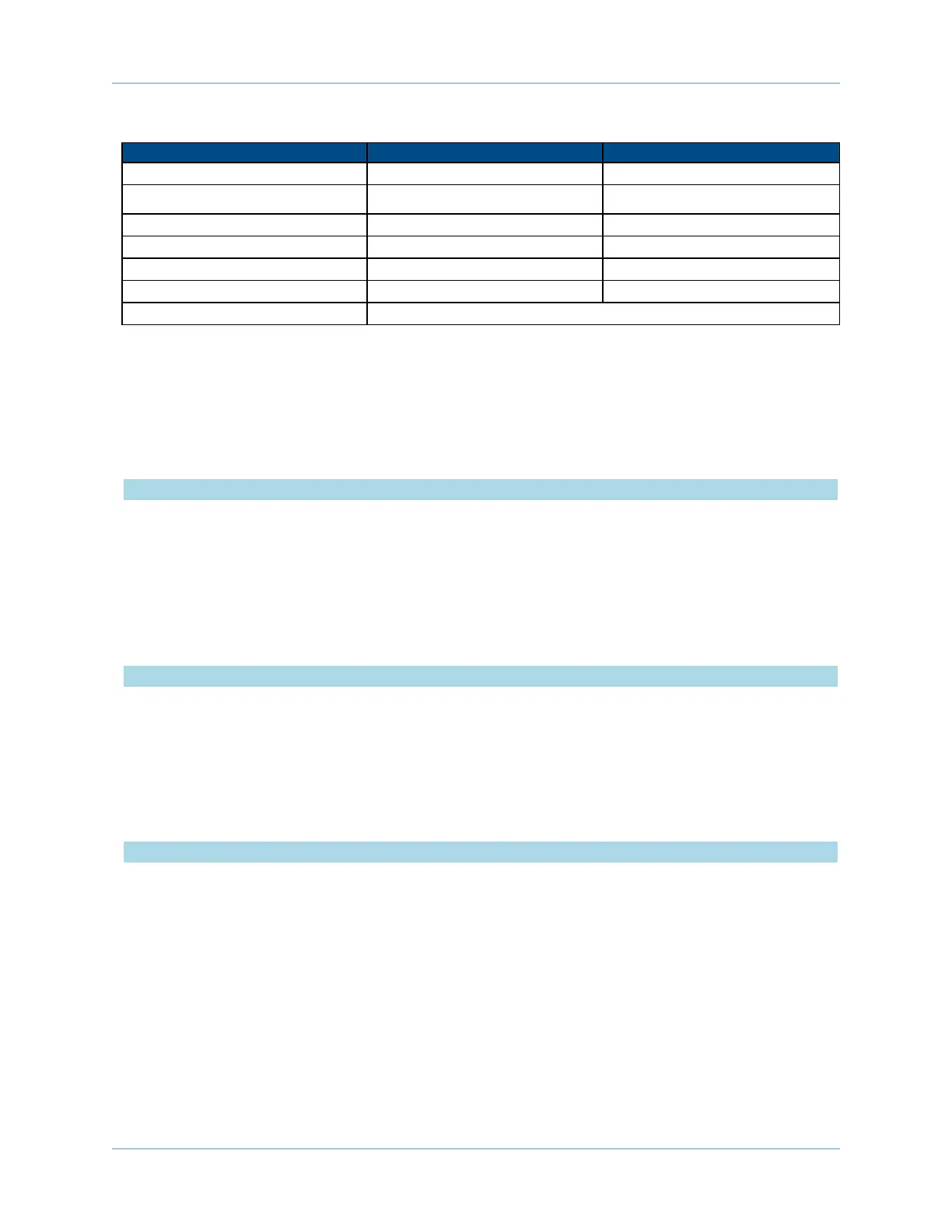
Table 1-4: Servo Amplifier Electrical Specifications
Description MP ML
Peak Bus Voltage 80 VDC 40 VDC
Peak Output Current 10 A
pk
10 A
pk
Continuous Output Current 5 A 5 A
PWMSwitching Frequency 20 kHz N/A
Power Amplifier Bandwidth Software Selectable Software Selectable
Minimum Load Inductance 0.1 mH@ 80 VDC N/A
Power Input 100 to 230 VACnominal input voltage(50/60 Hz)
The following equations can be used to determine total system power requirements. The actual power
required from the mains supply will be the combination of actual motor power (work), motor resistance
losses, and efficiency losses in the power electronics or power transformer.
For switching amplifier types:
An EfficiencyFactor of approximately 90% should be used in the following equations.
Brushless Motor
Output Power
Rotary Motors Pout [W] = Torque [N·m] * Angular velocity[rad/sec]
Linear Motors Pout [W] = Force [N] * Linear velocity[m/sec]
Rotary or Linear Motors Pout [W] = Bemf [V] * I(rms) * 3
Ploss = 3 * I(rms)^2 * R(line-line)/2
Pin = SUM (Pout + Ploss ) / EfficiencyFactor
DC Brush Motor
Pout [W] = Torque [N·m] * Angular velocity[rad/sec]
Ploss = I(rms)^2 * R
Pin = SUM (Pout + Ploss ) / EfficiencyFactor
For linear amplifier types:
An EfficiencyFactor of approximately 50% should be used in the following equations.
Linear Motor
Pdiss[W] = MotorCurrentPeak[A] * TotalBusVoltage[V] * 3 / 2
Pin = SUM (Pdiss ) / EfficiencyFactor
www.aerotech.com Chapter 1 9

 Loading...
Loading...