4. Configuration
72
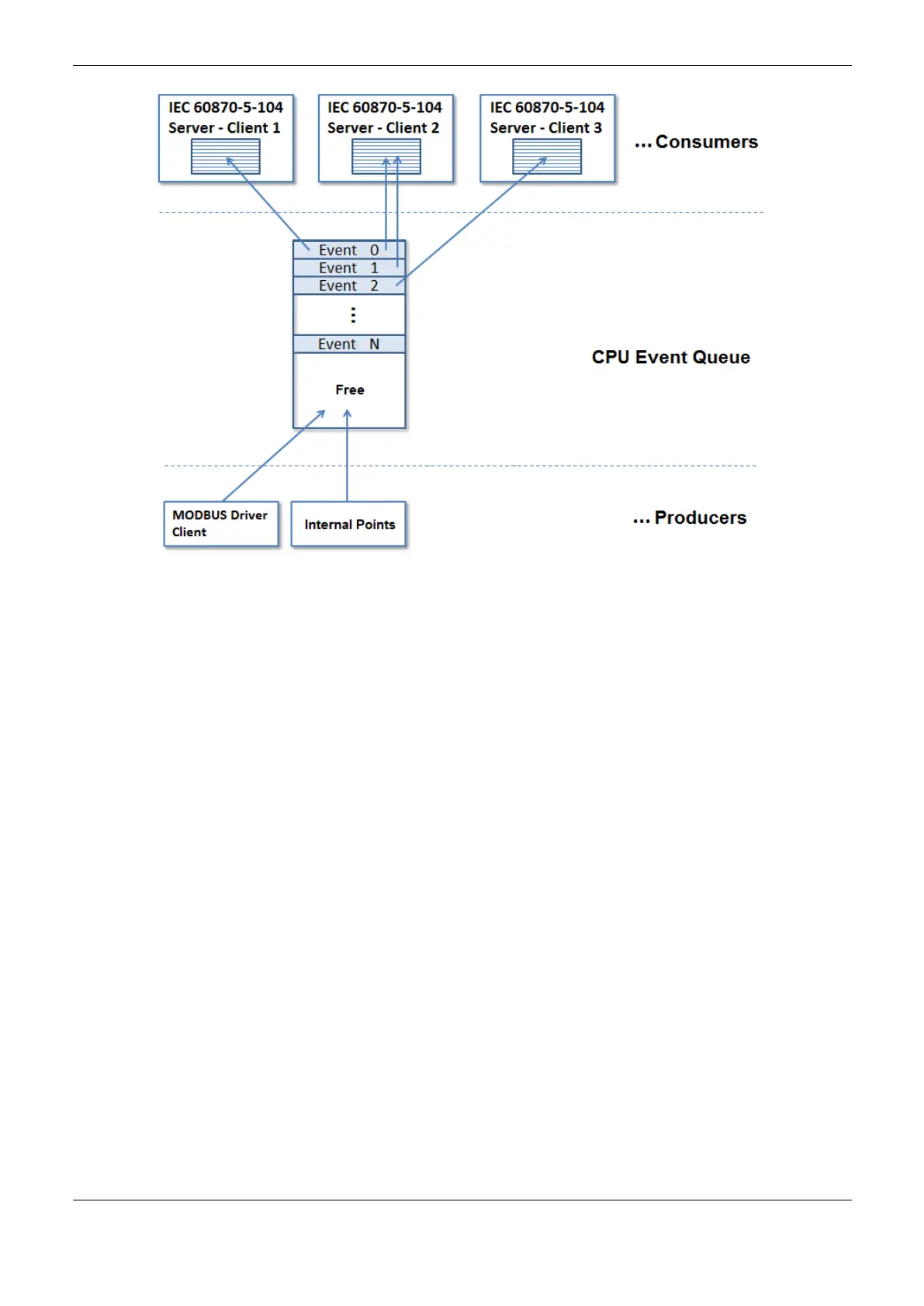
Figure 4-13. CPU’s Event Queue
Cosumers
The consumers are typically communication drivers that that will communicate with SCADA or
HMI. After been stored in CPU’s queue, the cosumers receive the events related to communication
points mapped in its configuration. These events are then stored in a consumer’s own events queue,
which the size and working is described on the communication driver specific section .
Queue Functioning Principles
Once stored in CPU’s queue, each event is transmited to the consumer that has that communication
point in its data base. On the figure above, the Event 0 is reffered to a communication point mapped
to two control centers IEC 60870-5-104 (Client 1 and 2). Thus the Event 1 is reffered to a
communication point mapped only to one control center IEC 60870-5-104 (Client 2). By its time, the
Event 2 is reffered to a communication point mapped to another control center IEC 60870-5-104
(Client 3).
The events remain stored in the CPU’s queue until all its consumers acknowledge its receiving. The
criteria used to confirm the receive is specific of each consumer. In case of the Server IEC 60870-5-
104, the acknowledge occurs when the event is transmited to the client IEC 60870-5-104.
In Nexto Series case, there are no diagnostics available to watch the CPU’s events queue occupation,
not even information about the queue overflow. However the consumers have a diagnostics group
reffered to its events queue. Further informations can be found at the specific driver communication
section.
Overflow Sing
The overflow sign to the consumers events queue occurs in two sittuations:
When the consumer events queue is out of space to store new events.

 Loading...
Loading...