5. Initial Programming
229
5. Initial Programming
The main goal of this chapter is to help in the programming and configuration of Nexto Series CPUs
so that the user will be able to take the first steps before starting a controller programming.
Nexto Series CPU uses the standard IEC 61131-3 for language programming, which are: IL, ST, LD,
SFC and FBD, and besides these, an extra language, CFC. These languages can be separated in text
and graphic. IL and ST are text languages and are similar to Assembly and C, respectively. LD, SFC,
FBD and CFC are graphic languages. LD uses the relay block representation and it is similar to relay
diagrams. SFC uses the sequence diagram representation, allowing an easy way to see the event
sequence. FBD and CFC use a group of function blocks, allowing a clear vision of the functions
executed by each action.
The programming is made through the MasterTool IEC XE (IDE) development interface. The
MasterTool IEC XE allows the use of the six languages in the same project, so the user can apply the
best features offered by each language, resulting in more efficient applications development, for easy
documentation and future maintenance.
For further information regarding programming, see User Manual MasterTool IEC XE - MU299609,
Programming Manual MasterTool IEC XE - MU399609 or IEC 61131-3 standard.
Memory Organization and Access
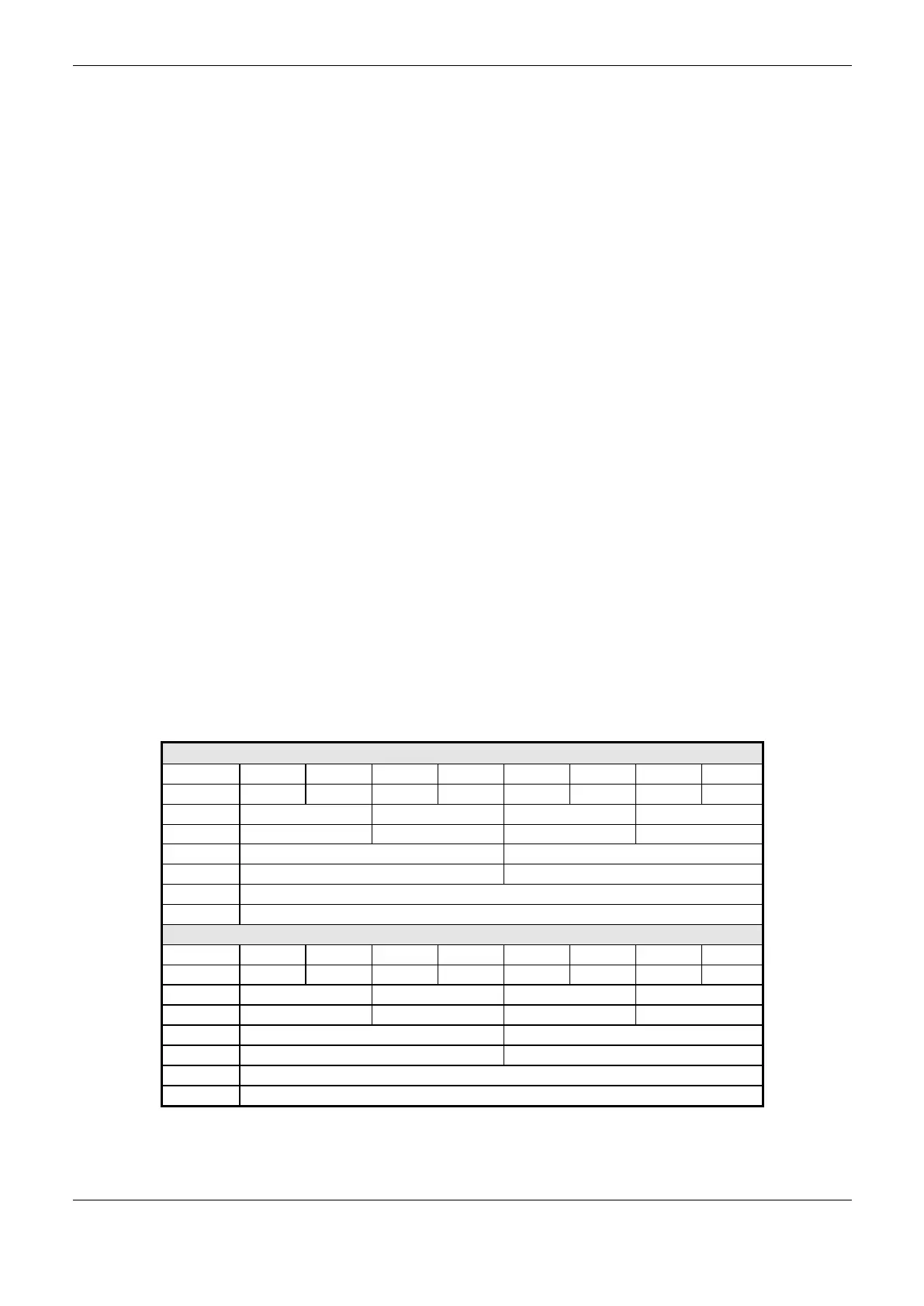
Nexto Series uses an innovative memory organization and access feature called big-endian, where the
most significant byte is stored first and will always be the smallest address (e.g. %QB0 will always
be more significant than %QB1, as in Table 5-1, where, for CPUNEXTO string, the letter U is byte 0
and the letter O is the byte 7).
Besides this, the memory access must be done carefully as the variables with higher number of bits
(WORD, DWORD, LONG), use as index the most significant byte, in other words, the %QD4 will
always have as most significant byte the %QB4. Therefore it will not be necessary to make calculus
to discover which DWORD correspond to defined bytes. The Table 5-1, shows little and big endian
organization.
MSB Little-endian (Traditional) LSB
HSB <– Big-endian (NEXTO) –> LSB
Table 5-1. Example
 Loading...
Loading...