13-7
Cisco ME 3800X and 3600X Switch Software Configuration Guide
OL-23400-01
Chapter 13 Configuring STP
Understanding Spanning-Tree Features
How a Switch or Port Becomes the Root Switch or Root Port
If all switches in a network are enabled with default spanning-tree settings, the switch with the lowest
MAC address becomes the root switch. In Figure 13-2, Switch A is elected as the root switch because
the switch priority of all the switches is set to the default (32768) and Switch A has the lowest MAC
address. However, because of traffic patterns, number of forwarding interfaces, or link types, Switch A
might not be the ideal root switch. By increasing the priority (lowering the numerical value) of the ideal
switch so that it becomes the root switch, you force a spanning-tree recalculation to form a new topology
with the ideal switch as the root.
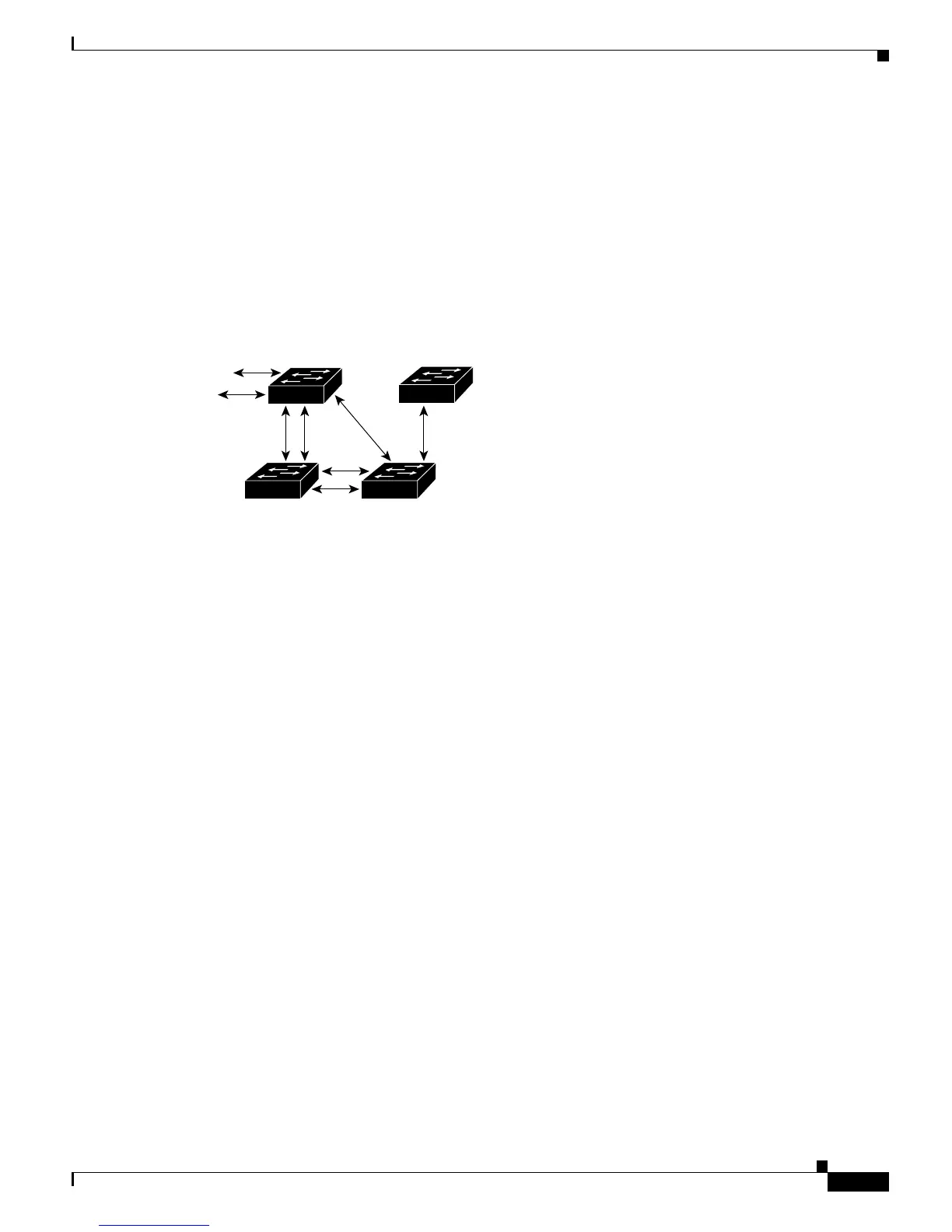
Figure 13-2 Spanning-Tree Topology
When the spanning-tree topology is calculated based on default parameters, the path between source and
destination end stations in a switched network might not be ideal. For instance, connecting higher-speed
links to an interface that has a higher number than the root port can cause a root-port change. The goal
is to make the fastest link the root port.
For example, assume that one port on Switch B is a Gigabit Ethernet link and that another port on
Switch B (a 10/100 link) is the root port. Network traffic might be more efficient over the Gigabit
Ethernet link. By changing the spanning-tree port priority on the Gigabit Ethernet port to a higher
priority (lower numerical value) than the root port, the Gigabit Ethernet port becomes the new root port.
Spanning Tree and Redundant Connectivity
You can create a redundant backbone with spanning tree by connecting two switch interfaces that are
participating in spanning tree to another device or to two different devices, as shown in Figure 13-3.
Spanning tree automatically disables one interface but enables it if the other one fails. If one link is
high-speed and the other is low-speed, the low-speed link is always disabled. If the speeds are the same,
the port priority and port ID are added together, and spanning tree disables the link with the lowest value.

 Loading...
Loading...











