1-15
Cisco ASA Series CLI Configuration Guide
Chapter 1 Configuring QoS
Configuring QoS
• You cannot configure traffic shaping in the global policy.
Detailed Steps
Examples
The following example enables traffic shaping on the outside interface, and limits traffic to 2 Mbps;
priority queuing is enabled for VoIP traffic that is tagged with DSCP EF and AF13 and for IKE traffic:
hostname(config)# access-list ike permit udp any any eq 500
hostname(config)# class-map ike
hostname(config-cmap)# match access-list ike
hostname(config-cmap)# class-map voice_traffic
hostname(config-cmap)# match dscp EF AF13
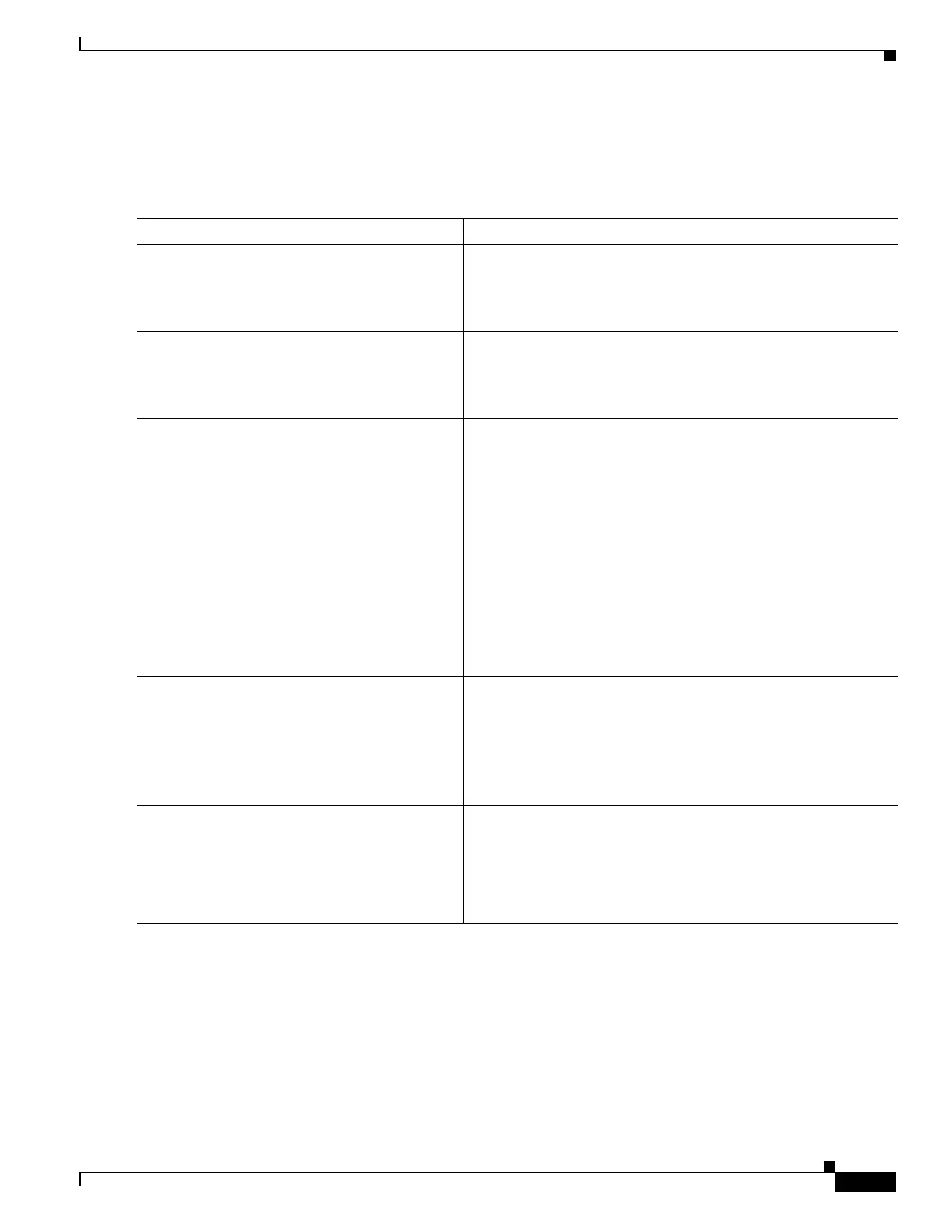
Command Purpose
Step 1
policy-map name
Example:
hostname(config)# policy-map shape_policy
Adds or edits a policy map. This policy map must be different
from the hierarchical priority-queuing map.
Step 2
class class-default
Example:
hostname(config-pmap)# class class-default
Identifies all traffic for traffic shaping; you can only use the
class-default class map, which is defined as match any, because
the ASA requires all traffic to be matched for traffic shaping.
Step 3
shape average rate [burst_size]
Example:
hostname(config-pmap-c)# shape average
70000 4000
Enables traffic shaping, where the average rate argument sets the
average rate of traffic in bits per second over a given fixed time
period, between 64000 and 154400000. Specify a value that is a
multiple of 8000. See the “Information About Traffic Shaping”
section on page 1-4 for more information about how the time
period is calculated.
The burst_size argument sets the average burst size in bits that can
be transmitted over a given fixed time period, between 2048 and
154400000. Specify a value that is a multiple of 128. If you do not
specify the burst_size, the default value is equivalent to
4-milliseconds of traffic at the specified average rate. For
example, if the average rate is 1000000 bits per second, 4 ms
worth = 1000000 * 4/1000 = 4000.
Step 4
(Optional)
service-policy priority_policy_map_name
Example:
hostname(config-pmap-c)# service-policy
priority-sub-policy
Configures hierarchical priority queuing, where the
priority_policy_map_name is the policy map you created for
prioritized traffic in the “(Optional) Configuring the Hierarchical
Priority Queuing Policy” section on page 1-13.
Step 5
service-policy policymap_name interface
interface_name
Example:
hostname(config)# service-policy
shape-policy interface inside
Activates the shaping policy map on an interface.

 Loading...
Loading...











