Redundancy and Availability Features
Service Availability Features ▀
Cisco ASR 5000 Series Product Overview ▄
Hardware
Failure
Scenario
Effect on
Accounting
Data
Effect on the
Flow of User
Data Packets
Effect on User
Control
Transactions
Effect on
Management
Traffic
Standby SMC takes
control of all system
& management
processes as SPIO
remains active.
Standby SPIO takes
over, using active
SMC.
After applying a soft
busy-out to the
system, performs a
soft boot after the
last session
disconnects.
Service
interrupt for the
duration of
system boot
(~4 min)
Service
interrupt for
the duration
of system
boot (~4 min)
Service
interrupt for
the duration
of system
boot (~4
min)
Service interrupt
for the duration
of system boot
(~4 min)
Service interrupt
for the duration
of system boot
(~4 min)
Important: When an SMC or SPIO failover occurs, the standby SMC or SPIO automatically becomes active.
However, should the failed card's error condition be corrected (by replacement or configuration change), the state of the
repaired SMC or SPIO does not automatically return to the active state. This migration must occur through manual
intervention by a system administrative user.
With the ability of performing on-line process migration, supporting 1:1 SMC and SPIO redundancy, and utilizing the
fully redundant switching fabric and control bus, single points of failure are eliminated from the switch fabric and
system management capabilities.
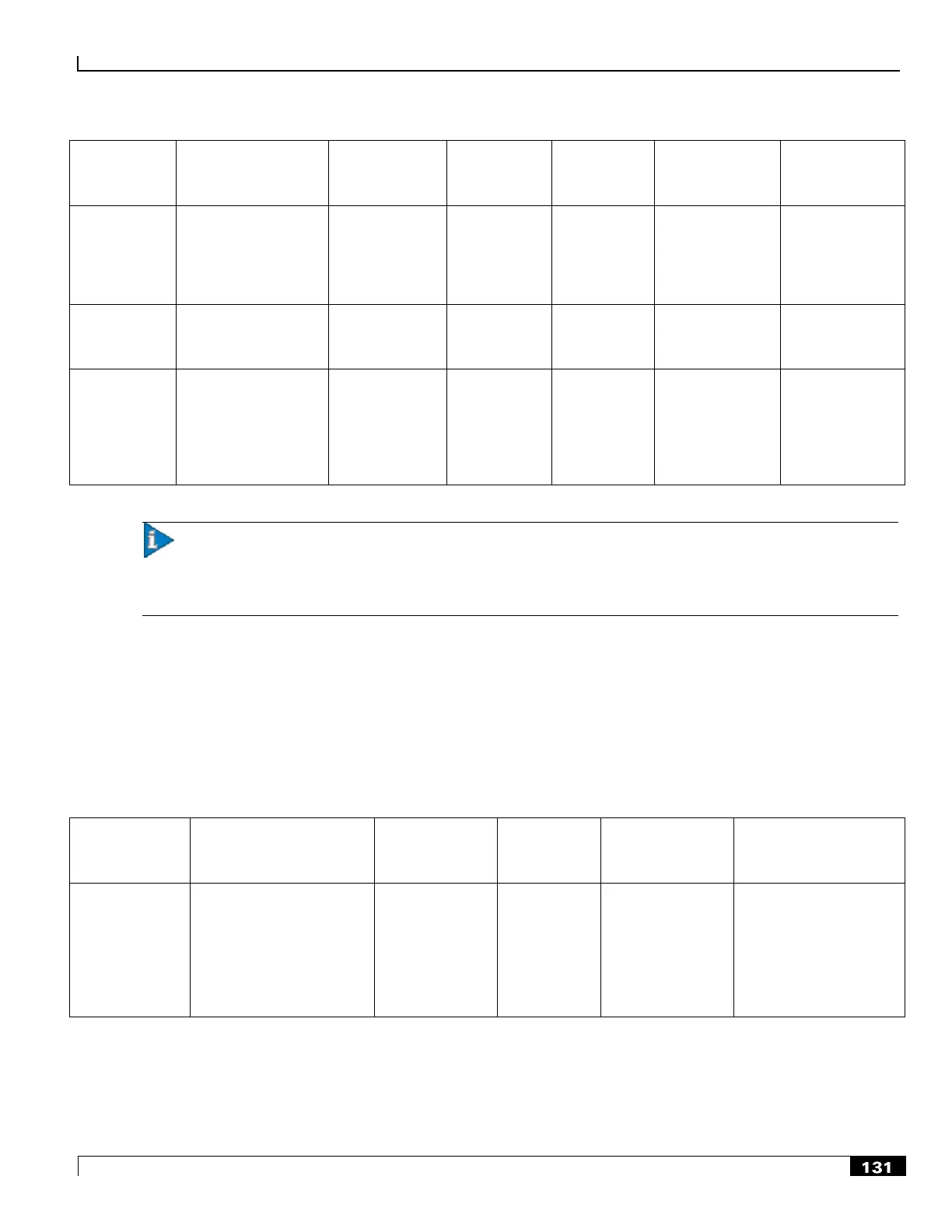
The following table shows various maintenance and failure situations involving the processing cards (PSC, PSC2, PPC),
Line Cards (LCs), and RCC cards; and explains how each situation is resolved. Note that LCs are not needed behind the
standby processing cards that provide redundancy.
Table 23. Service Assurance Features for Processing and Line Cards
Hardware
Failure Scenario
Effect on
Accounting Data
Effect on the flow
of Data Packets
Effect on Control
Transactions
Processing Card
Planned
maintenance
Session managers are
migrated to standby
processing card. Other
tasks are restarted on
standby card. Network
connection is maintained
on existing LC via RCC.
< 2 sec. interrupt
to user traffic on
affected
processing card
(user application
will retransmit
data)
< 2 sec. interrupt to new
call setups (PCF/SGSN
and mobile nodes will
retransmit requests)

 Loading...
Loading...



