Enhanced Charging Service Overview
Cisco ASR 5000 Series Product Overview ▄
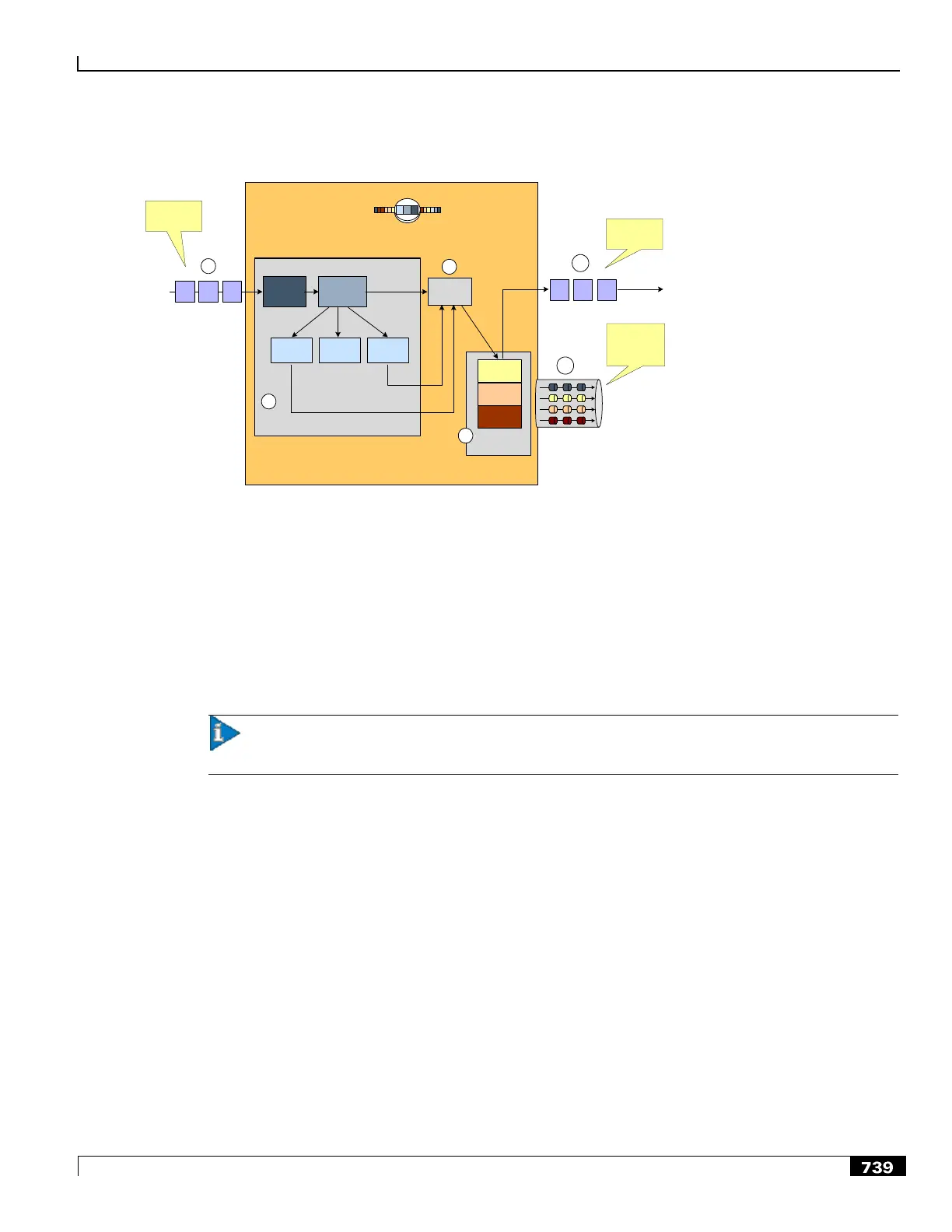
Figure 180. Routing Ruledefs and Packet Inspection
Protocol
Analyzer Stack
Shallow Inspection
Bearer
Anlayzer
IP
Analyzer
TCP
Analyzer
UDP
Analyzer
ICMP
Analyzer
Routing
Ruledefs
data flows,
states, and
statistics
1
2
3
Other
Analyzers
Deep
Inspection
4
5a
Outgoing
packets
Incoming
packets
5b
Step 1 The packet is redirected to ECS based on the ACLs in the subscriber‘s template /APN and packets enter ECS through
the Protocol Analyzer Stack.
Step 2 Packets entering Protocol Analyzer Stack first go through a shallow inspection by passing through the following
analyzers in the listed order:
Step a Bearer Analyzer
Step b IP Analyzer
Step c ICMP, TCP, or UDP Analyzer as appropriate
Important: In the current release traffic routes to the ICMP, TCP, and UDP analyzers by default.
Therefore, defining routing ruledefs for these analyzers is not required.
Step 3 The fields and states found in the shallow inspection are compared to the fields and states defined in the routing ruledefs
in the subscriber‘s rulebase.
The ruledefs‘ priority determines the order in which the ruledefs are compared against packets.
Step 4 When the protocol fields and states found during the shallow inspection match those defined in a routing ruledef, the
packet is routed to the appropriate layer 7or 7+ analyzer for deep-packet inspection.
Step 5 After the packet has been inspected and analyzed by the Protocol Analyzer Stack:
Step a The packet resumes normal flow and through the rest of the ECS subsystem.
Step b The output of that analysis flows into the Charging Engine, where an action can be applied.
Applied actions include redirection, charge value, and billing record emission.
 Loading...
Loading...



