11 Reference 133
1.2 Internal Pressure Changes of the WORK And MASTER
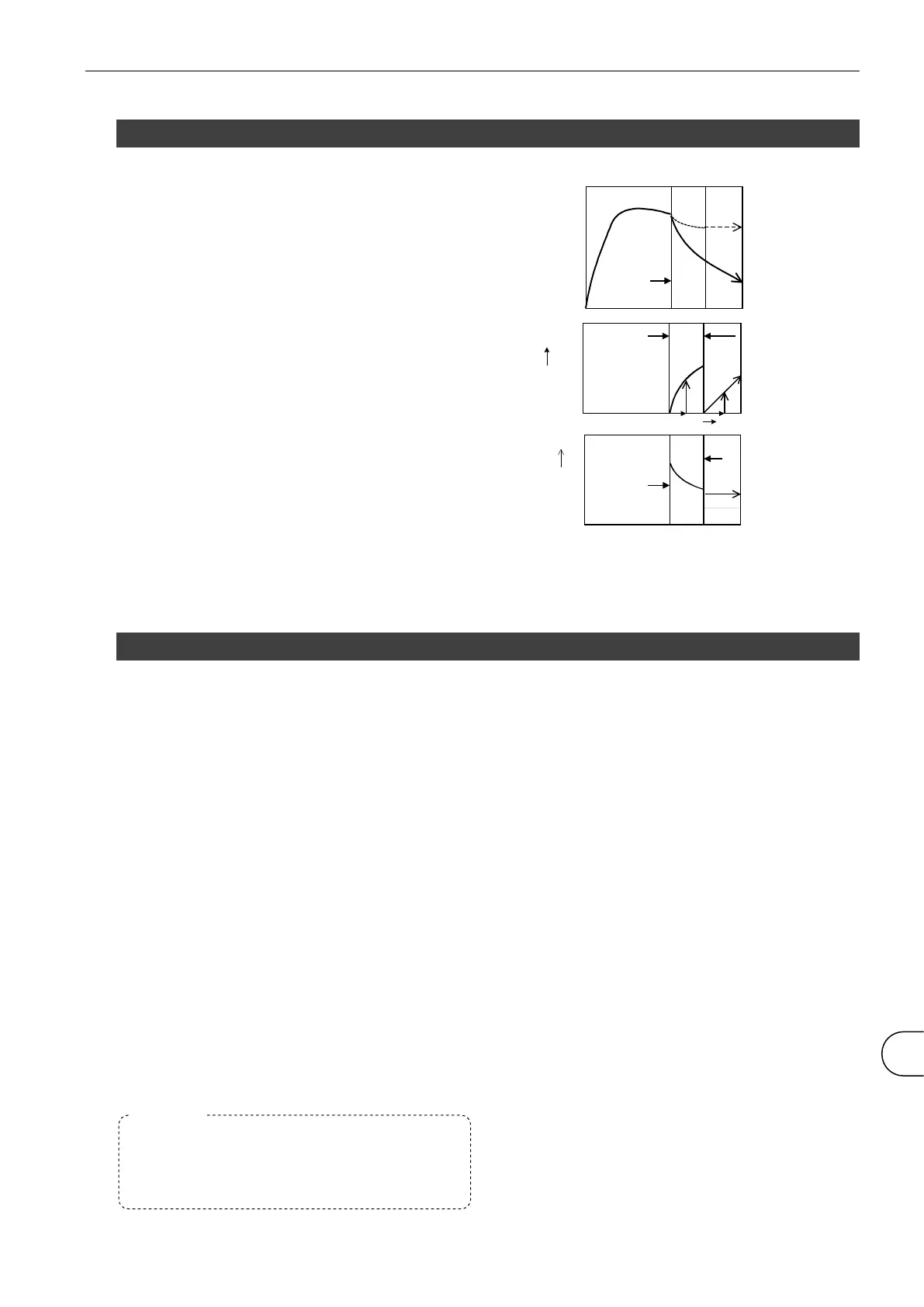
The figure on the right shows the pressure changes inside
the WORK and the MASTER.
In the BAL2 and the DET stages, the differential pressure
resulting from leaks rises at a constant rate with time. In
the DET stage, the differential pressure sensor (DPS)
output is zeroed through an automatic zero operation
before a differential pressure reading is produced.
Leak rate is calculated using the following equation:
Q = K · ΔP / ΔT
Where:
Q: Leak rate (mL/min)
K: Leak coefficient (equivalent internal volume)
ΔP: Differential pressure
ΔT: Time
1.3 Leak Rate Conversion
Detected differential pressure can be converted into leak rate (mL/min) using a conversion equation derived
from Boyle's Law. Using the unit's leak calibration facility makes calculations based on the conversion
equation unnecessary.
Pressure and Volume Relationship
The relationship between pressure and volume is stated in Boyle’s law, which establishes that, for an ideal
gas, pressure multiplied by volume is constant at a constant temperature. Boyle’s law can be represented
by the following equation:
PV = constant (where P is absolute pressure)
The amount of leakage to atmosphere is calculated and expressed by the following equation derived from
Boyle’s law.
Where:
∆V
L
: Leak [mL]
Ve: Equivalent internal volume [mL]
∆P: Pressure drop due to a leak [Pa]
Patm: Atmospheric pressure [Pa]
Differential pressure
change using
leaking part
P
T
Differential pressure
reading
Auto-zero
Auto-zero
P
Pressure change
using non-leaking
part and master
Pressure change
using leaking part
Internal pressure
Valve
closed
CHG and BAL1 BAL2 DET
Leak rate
Leak rate reading
Auto-zero
Auto-zero
Q
The definition of internal equivalent volume, Ve, is the
volume of air of the entire WORK-side pneumatic
circuit at a particular test pressure. Ve is used as
the leak coefficient K(Ve) in the leak rate calculation.
 Loading...
Loading...