3.8 Confirming Faulty Measurements
39
3
Measurement Fault Detection Order
Out-of-Range Detection Function
Examples of Out-of-Range Faults
Current Monitor Function
The instrument supplies constant measurement current through the DUT via the H
CUR
and L
CUR
probes. A
current monitor fault occurs if constant current cannot be attained. If the contact check and voltage level mon-
itor results are normal, the out-of-range and comparator result displays indicate “Hi”.
Example of Current Monitor Fault
• Broken DUT (open work)
•H
CUR
or L
CUR
probe contact fault
•H
CUR
or L
CUR
cable break
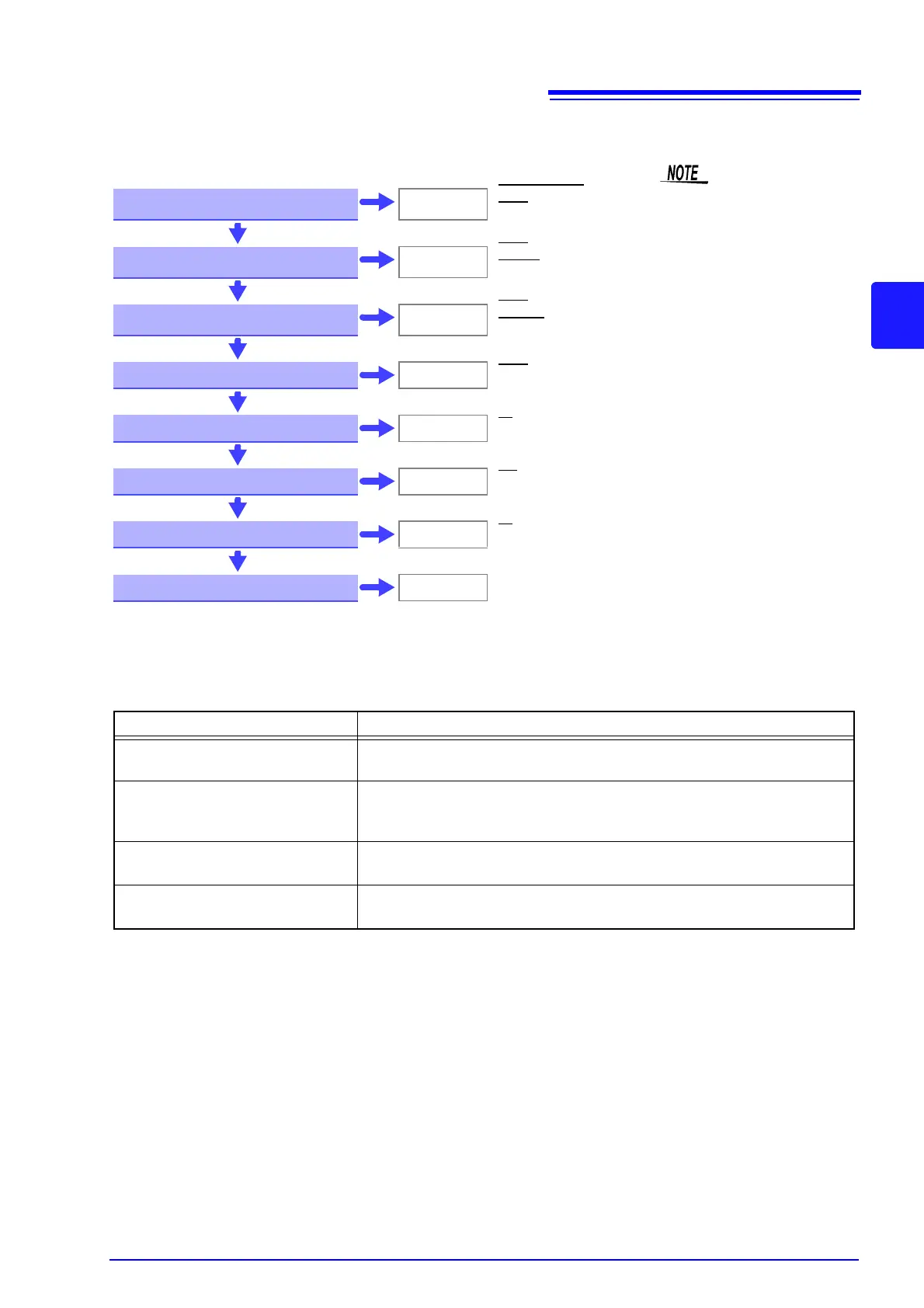
Measurement Fault Detection Display EXT I/O signal
Measurement fault detection
proceeds in the order shown at
the left, ending with display of
the first detected error.
Corresponding measurement
fault signals are also output at
the EXT I/O connector.
Probe Short Circuit
ERR: 021
PRB_SHORT output,
ERR output
Yes
Hi Wiring Contact Error
C.E. Hi
ERR output,
CE_HI output
Yes
Lo Wiring Contact Error
C.E. Lo
ERR output,
CE_LO
output
Yes
Voltage Level Monitor Error
C.E. Volt
ERR output
Yes
Constant-Current Error
+OvrRng
HI output
Yes
Below Lower Limit
-OvrRng
LO output
Yes
Above Upper Limit
+OvrRng
HI output
Yes
No Measurement Data
- - - - - - - -
Out-of-Range Detection Measurement Example
The measured value is outside of the
measurement range.
Attempting to measure 13 k with the 10 k range selected
The relative tolerance (%) display of
the measured value exceeds the dis-
play range (999.999%).
Measuring 500 (+2400%) with a reference value of 20
The zero-adjusted value is outside of
the display range.
In the 1 range with 0.5 zero-adjustment in effect, measuring 0.1 provides
a zero-adjusted value of -0.4 , which is outside of the display range.
While measuring, input voltage ex-
ceed the A/D converter input range.
Measuring a large resistance value in an electrically noisy environment
 Loading...
Loading...