Static Virtual LANs (VLANs)
Special VLAN Types
Hubs dedicated to connecting management stations to the Management VLAN
can also be included in the above topology. Note that any device connected
to a hub in the Management VLAN will also have Management VLAN access.
3. Configure the Management VLAN on the selected switch ports.
4. Test the management VLAN from all of the management stations autho-
rized to use the Management VLAN, including any SNMP-based network
management stations. Ensure that you include testing any Management
VLAN links between switches.
Note If you configure a Management VLAN on a switch by using a Telnet connection
through a port that is not in the Management VLAN, then you will lose
management contact with the switch if you log off your Telnet connection or
execute write memory and reboot the switch.
Configuration
Syntax: [no] management-vlan < vlan-id | vlan-name >
Configures an existing VLAN as the management VLAN. The no
form disables the management VLAN and returns the switch to its
default management operation. Default: Disabled. In this case, the
VLAN returns to standard VLAN operation.
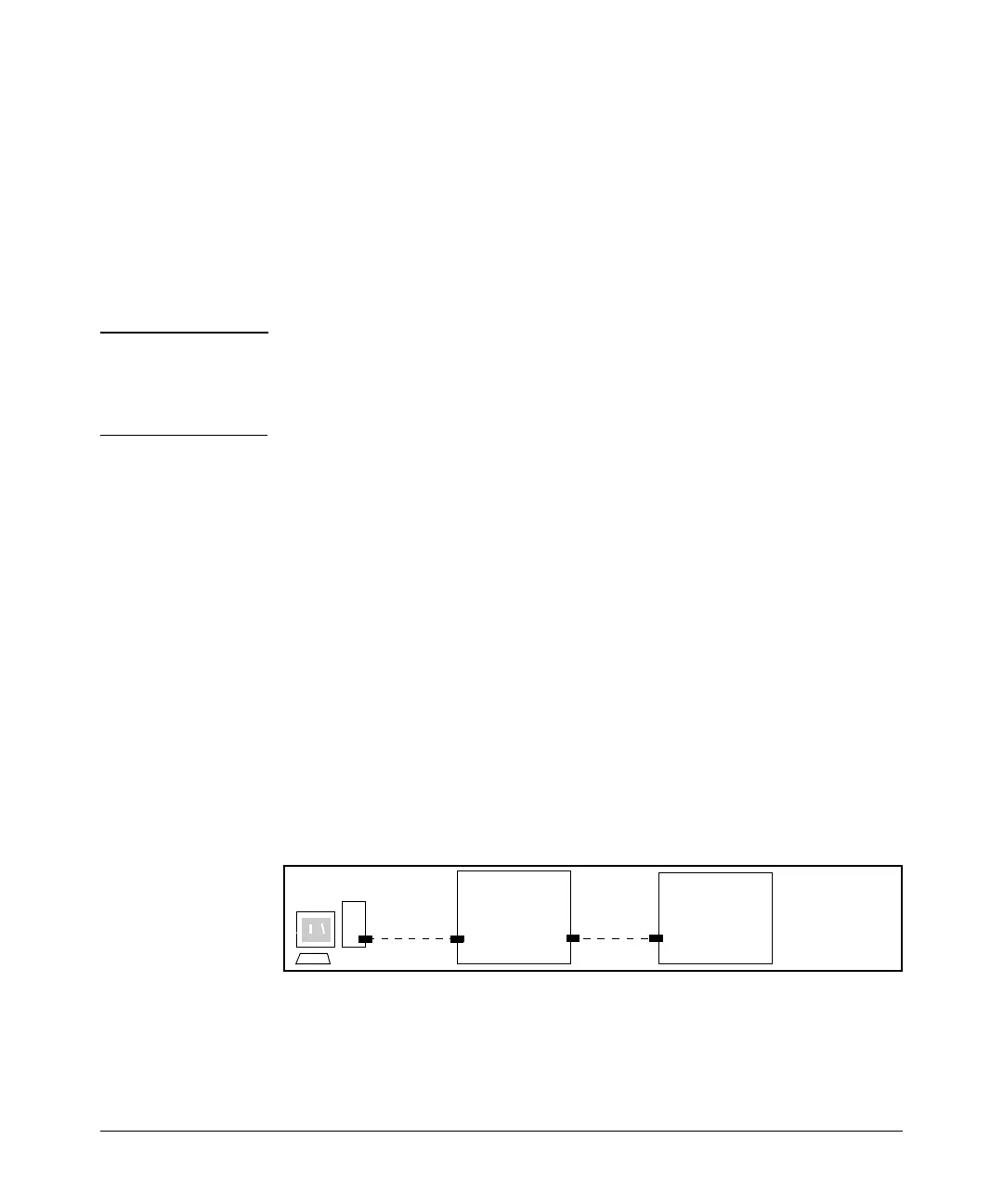
For example, suppose you have already configured a VLAN named My_VLAN
with a VID of 100. Now you want to configure the switch to do the following:
■ Use My_VLAN as a Management VLAN (tagged, in this case) to connect
port A1 on switch “A” to a management station. (The management station
includes a network interface card with 802.1Q tagged VLAN capability.)
■ Use port A2 to extend the Management VLAN to port B1 (which is already
configured as a tagged member of My_VLAN) on an adjacent HP Procurve
switch that supports the Management VLAN feature.
Switch
“
B”
Switch
“A”
A1
B1
A2
Figure 2-29. Illustration of Configuration Example
HPswitch (config)# management-vlan 100
HPswitch (config)# vlan 100 tagged a1
HPswitch (config)# vlan 100 tagged a2
2-47
 Loading...
Loading...











