Static Virtual LANs (VLANs)
Special VLAN Types
Switch
A
3
Port A1
Port A3
Port A6
Port A7
4
1
Switch
B
Port B2
Port B4
Port B5
Port B9
Switch
C
Port C2
Port C3
Port C6
Port C8
Server
Server
Server
2
Links with Ports
Configured as Members of
the Management VLAN
and other VLANs
Links Not Belonging to the
Management VLAN
System
Management
Workstation
Marketing
Shipping
System Server
(on the
DEFAULT_VLAN)
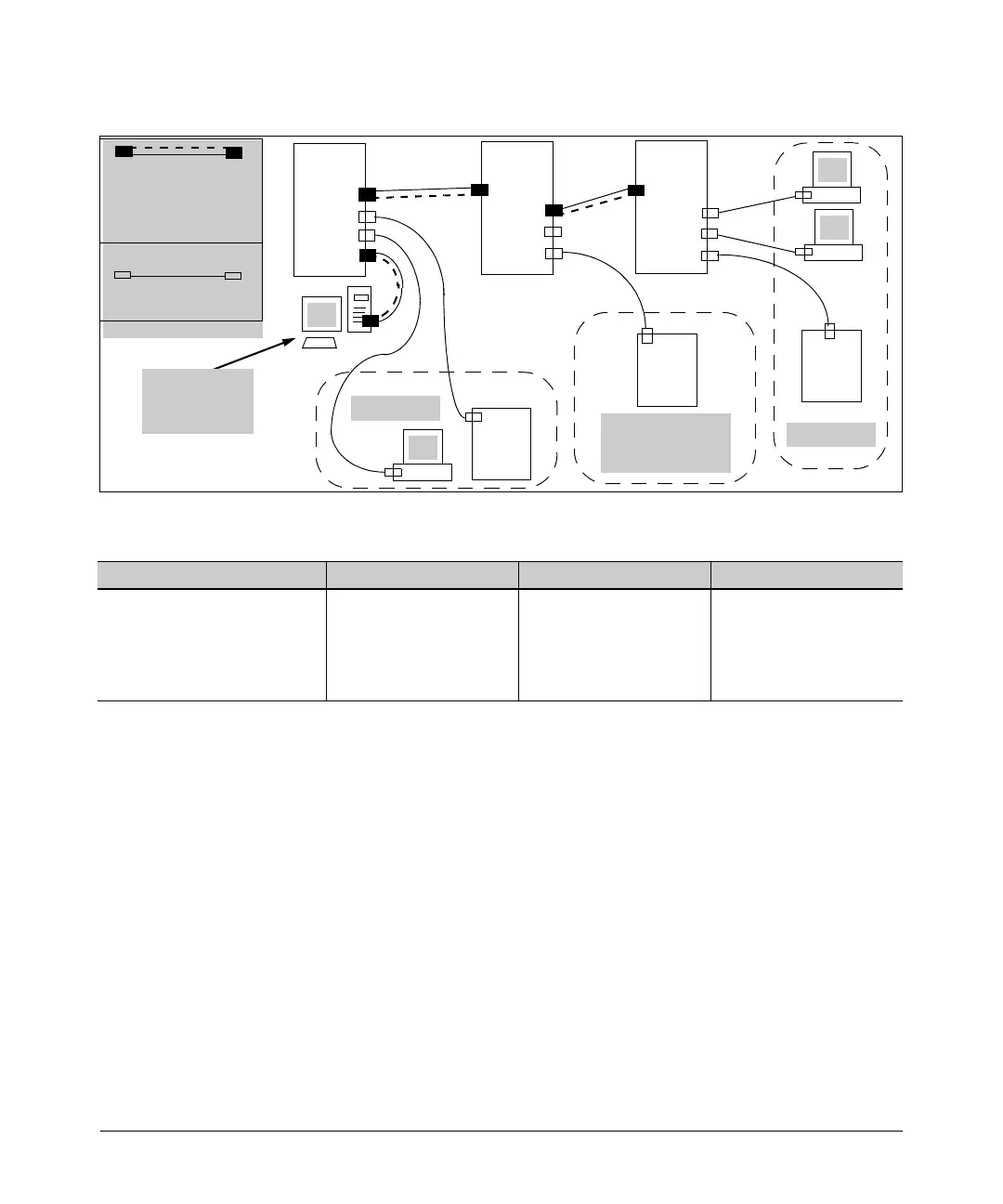
Figure 2-28. Example of Management VLAN Control in a LAN
Table 2-7. VLAN Membership in Figure
2-28
Switch A1 A3 A6 A7 B2 B4 B5 B9 C2 C3 C6 C8
Management VLAN (VID = 7) Y N Y N Y N
Marketing VLAN (VID = 12) N N N Y Y
Shipping Dept. VLAN (VID = 20) N Y N N N
DEFAULT-VLAN (VID = 1) Y Y Y Y
N Y Y N N N
N N N N N N Y
Y N N N N N N
Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
Preparation
1. Determine a VID and VLAN name suitable for your Management VLAN.
(You must manually configure the IP addressing for the Management
VLAN. The switch does not allow the Management VLAN to acquire an IP
address through DHCP/Bootp.)
2. Plan your Management VLAN topology to use HP ProCurve switches that
support this feature. (Refer to page 2-44.) The ports belonging to the
Management VLAN should be only the following:
• Ports to which you will connect authorized management stations
(such as Port A7 in figure 2-28.)
• Ports on one switch that you will use to extend the Management VLAN
to ports on other HP ProCurve switches (such as ports A1 and B2 or
B4 and C2 in figure
2-28 on page 2-46.).
2-46
 Loading...
Loading...











