IP Routing Features
Overview of IP Routing
IP Route Exchange Protocols
The switch supports the following IP route exchange protocols:
■ Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
■ Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
These protocols provide routes to the IP route table. You can use one or more
of these protocols, in any combination. The protocols are disabled by default.
For configuration information, see the following:
■ “Configuring RIP” on page 11-21
■ “Configuring OSPF” on page 11-34
IP Global Parameters for Routing Switches
The following table lists the IP global parameters and the page where you can
find more information about each parameter.
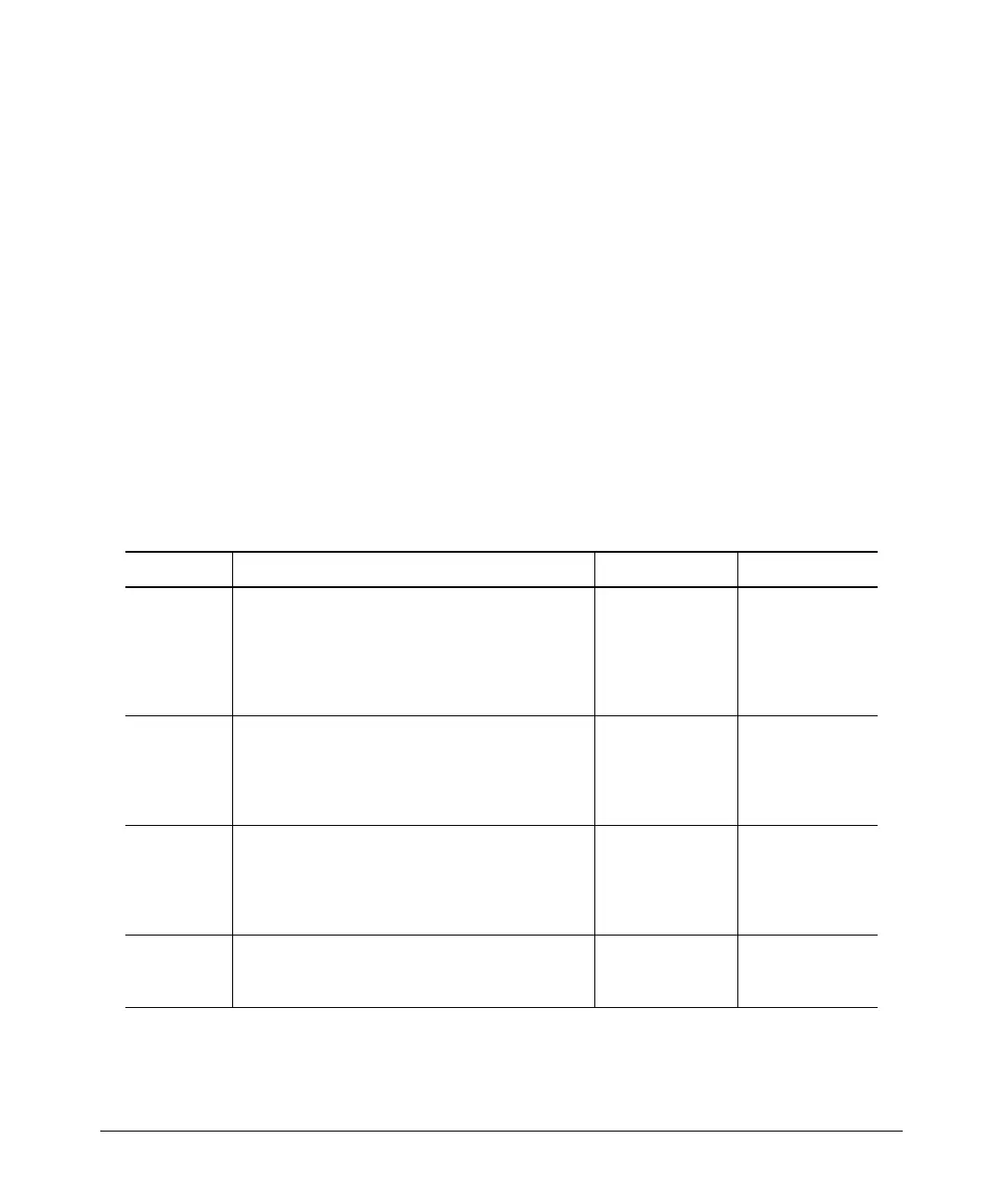
Table 11-1. IP Global Parameters for Routing Switches
Parameter Description Default See page
Router ID The value that routers use to identify themselves to
other routers when exchanging route information.
OSPF uses the router ID to identify routers. RIP does
not use the router ID.
The lowest-
numbered IP
address
configured on the
lowest-numbered
routing interface.
11-10
Address
Resolution
Protocol
(ARP)
A standard IP mechanism that routers use to learn
the Media Access Control (MAC) address of a
device on the network. The router sends the IP
address of a device in the ARP request and receives
the device’s MAC address in an ARP reply.
Enabled 11-11
ARP age The amount of time the device keeps a MAC address
learned through ARP in the device’s ARP cache. The
device resets the timer to zero each time the ARP
entry is refreshed and removes the entry if the timer
reaches the ARP age.
Five minutes not configurable
Proxy ARP An IP mechanism a router can use to answer an ARP
request on behalf of a host, by replying with the
router’s own MAC address instead of the host’s.
Disabled 11-13
11-7

 Loading...
Loading...











