Clinical Guide
Smart532
™
A-10 UM-1151440EN, Rev. C, May 2016
In CW, the stimulus is a single square pulse of duration 10-500 msec. The
appropriate power is usually found by titration: the power is initially set to
a low level and then increased gradually until the desired tissue effect is
obtained. Table A-1 lists recommended clinical treatment parameters for
intended medical conditions using CW pulse:
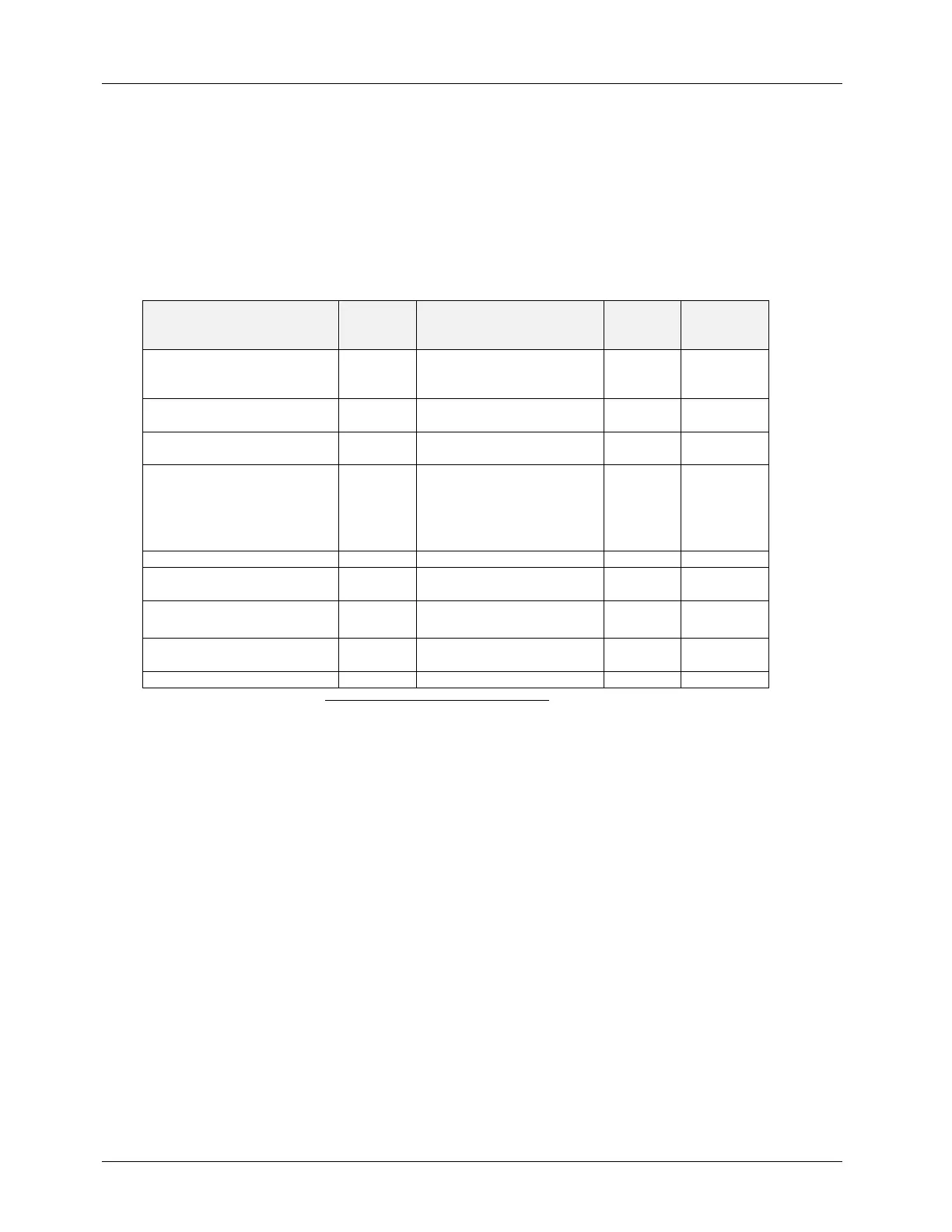
Table A-1: Recommended clinical treatment parameters in CW for intended medical conditions
Treatment
(Mode)
Power
(mW)
Required Tissue Reaction
duration
Spot size
(
m)
Diabetic Retinopathy including
Macular Edema or Proliferative
11
Proliferative Diabetic
Retinopathy (PDR)
12,13
Central Serous
ChorioRetinopathy (CSCR)
14
Macular Edema or Proliferative
Retinopathy associated with
Central Retinal Vein Occlusion
(CRVO) or Branch Retinal
12
Iridotomy for angle closure
(Stretch)
16
Stroma at the iridotomy site
becomes thin and tense
Iridotomy for angle closure
(Penetration)
16
Penetration , until a hole of
0.2 mm in the iris is formed
Trabeculoplasty for primary
open angle glaucoma
17
11
P. Romero-Aroca, J. Reyes-Torres, M. Baget-Bernaldiz and C. Blasco-Suñe, "Laser
treatment for diabetic macular edema in the 21st century,"
Curr. Diabetes Rev
., vol. 10, no.
2, pp. 100-12, 2014.
12
Y. Paulus and M. Blumenkranz, "Proliferative and nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy,"
One Network
, 2013.
13
C. Sanghvi, R. McLauchlan, C. Delgado, L. Young, S. Charles, G. Marcellino and P. Stanga,
"Initial experience with the Pascal photocoagulator: a pilot study of 75 procedures.,"
Br J
Ophthalmol
, vol. 92, no. 8, pp. 1061-4, 2008.
14
L. Ficker, G. Vafidis, A. While, P. Leaver, “Long-term follow-up of a prospective trial of
argon laser photocoagulation in the treatment of central serous retinopathy”,
Br J
Ophthalmol
, vol 72, pp. 829-34, 1988
15
M. Muqit, C. Sanghvi, R McLauchlan, C. Delgado, LB Young, SJ Charles, GR Marcellino and
PE. Stanga. “Study of clinical applications and safety for Pascal_ laser photocoagulation in
retinal vascular disorders”.
Acta Ophthalmologica
90:155-161, 2012
16
R. Harrad, K. Stannard and J. Shilling, "Argon laser iridotomy,"
Br J Ophthalmol
, vol. 69,
no. 5, pp. 368-72, 1985.
17
E. Rosenfeld, G. Shemesh and S. Kurtz, "The efficacy of selective laser trabeculoplasty
versus argon laser trabeculoplasty in pseudophakic glaucoma patients,"
Clin Ophthalmol
, vol.
6, pp. 1935-40, 2012.
18
L.V. Angioletti, P.J. Colquhoun, A.D. Kulik, E.H. Malpica , “Indirect photocoagulation of
subfoveal choroidal neovascularization in age-related macular degeneration”,
Bull N Y Acad
Med
, vol. 67(4), pp. 389-98, 1991
continuous
waveform (CW)
 Loading...
Loading...