8
N
ETWORKING POSSIBILITIES
CHAPTER 2 SYSTEM OVERVIEW
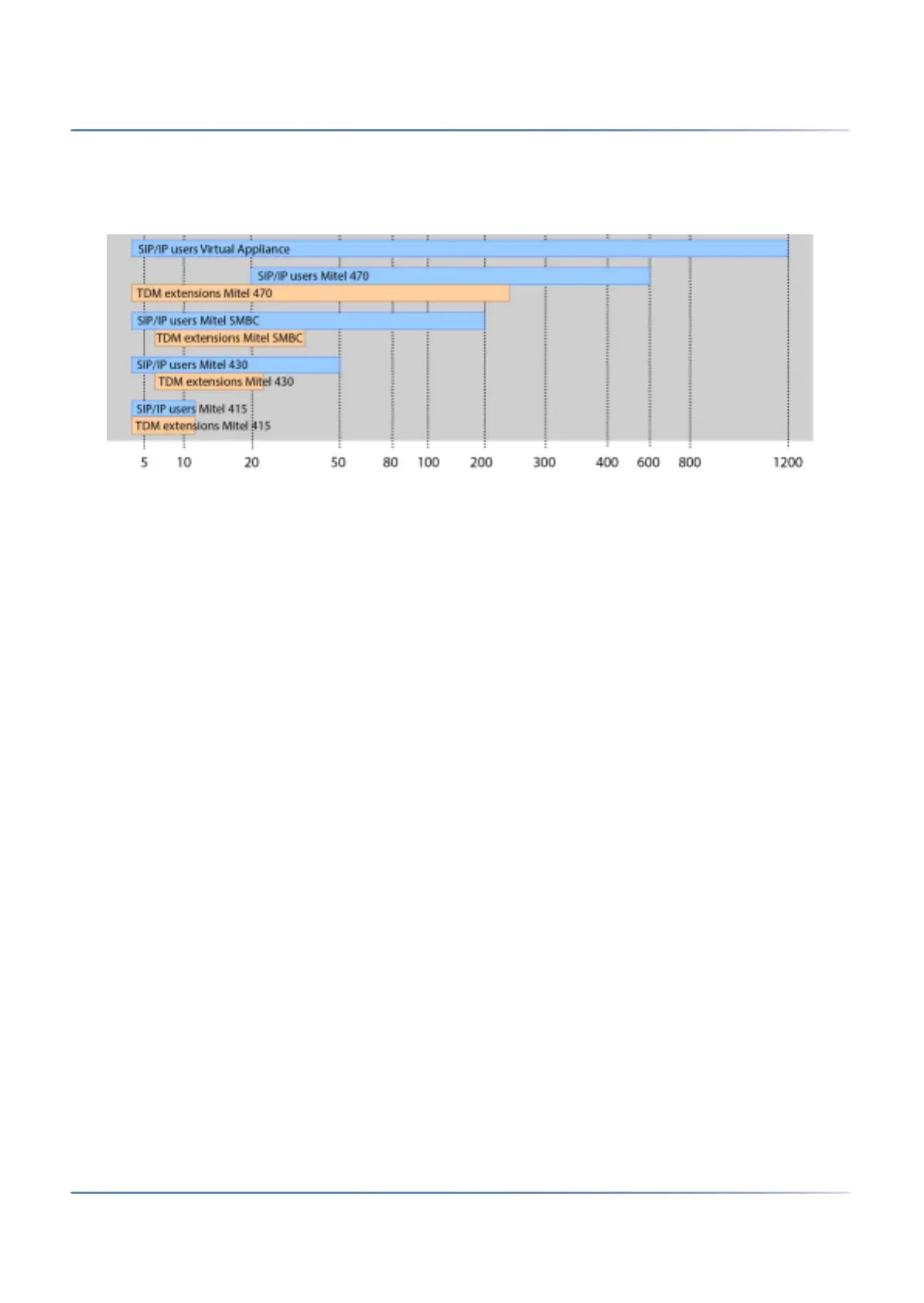
The diagram below shows the MiVoice Office 400 communication servers with their expansion capacity
for users with SIP/IP phones and TDM extensions (FXS, DSI, BRI-S).
Figure 2.3: Max. expansion capacity for users with SIP/IP phones and TDM extensions (FXS,
DSI, BRI-S)
Networking Possibilities
MiVoice Office 400 communication servers at different company locations, even beyond national borders,
can be linked together to form an enterprise-wide private communication network with a common
numbering plan. The following networking types are possible:
Mitel Advanced Intelligent Network (AIN)
In an AIN several communication servers of the MiVoice Office 400 series can be connected up to form
a homogeneous communication system. The single systems are connected with one another via the IP
network, thereby forming the nodes of the overall AIN system One node acts as the Master and controls
the other (satellite) nodes. All the features are then available at all the nodes.
No call charges are incurred as the internal voice traffic between locations is routed via the system’s own
data network. All the AIN nodes are configured and set up centrally via the Master.
If a node is isolated from the rest of the AIN by an interruption in the IP connection, it restarts with an emer-
gency configuration after a set amount of time. The connections are then routed to the public network via
local links, for example with ISDN or SIP connections, until contact with the AIN is restored.
For the Virtual Appliance communication server, AIN networking (Virtual Appliance as master) with at
least one satellite is mandatory.
SIP networking
Networking based on the open global SIP protocol is the universal way of connecting several systems
with one another via the private data network or the internet. MiVoice Office 400 communication platforms
can be used to network up to 100 other Mitel systems or SIP-compatible third-party systems. All the main
telephony features such as call number and name display, enquiry call, hold, brokering, call transfer and
conference circuits are supported. The transmission of DTMF signals and the T.38 protocol for Fax over
IP between the nodes is also possible.
Virtual and leased-line networking via BRI/PRI interfaces
With this type of connection the nodes are connected via basic rate interfaces (BRI) or primary rate inter-
faces (PRI).
 Loading...
Loading...