5 Installation
5-46
CJ2 CPU Unit Hardware User’s Manual
Grounding has the following two purposes.
• Protective Grounding
Protective grounding is done to ensure safety. It is intended to prevent electrical shock by grounding
the electrical potential that is generated by factors such as leakage, induction, or failure.
• Functional Grounding
Functional grounding is done to protect device and system functions, including prevention of noise
from external sources, or prevention of noise from devices or equipment that could have harmful
effects on other devices or equipment.
Grounding requirements sometimes depend on the situation, based on experimentation. It is impor-
tant to sufficiently check the particular circumstances before grounding.
z Principles of One-point Grounding
For devices to operate properly, the reference potential between the devices must be stabilized. Use
one-point grounding so that noise current does not flow to ground lines between the devices.
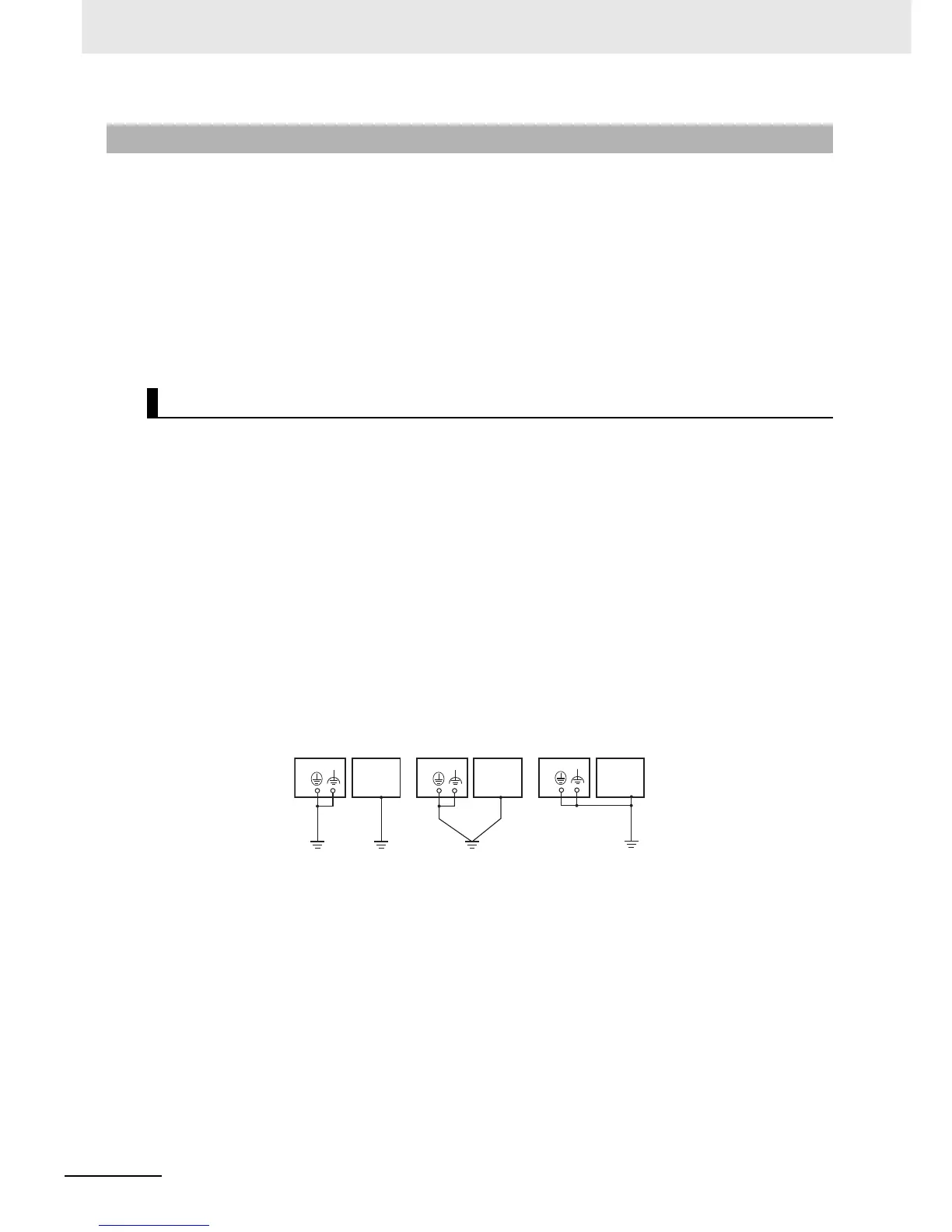
z Whenever possible, use an independent ground (with the ground pole
separated by a minimum of 10 m from any other ground pole).
• Ground to 100 Ω or less, and if possible use a separate ground from those of other devices. (Refer
to figure (a) in the diagram below.)
• If using an independent ground is not possible, then use a common ground as shown in figure (b).
Connect to the ground pole of the other device.
• Never connect to the same ground as a device that draws a large amount of power, such as a
motor or inverter. Ground the devices separately to avoid mutually adverse influences.
• To prevent electrical shock, do not connect to ground poles (especially steel frames) to which mul-
tiple devices are connected.
• Use a ground pole as close to the PLC as possible and keep the ground line as short as possible.
5-4-6 Grounding
Grounding Methods and Precautions
PLC
Other
device
Ground of
100 Ω or less
PLCPLC
Independent grounds:
Best
Common ground:
Acceptable
Common ground:
Incorrect
Grounding Methods
Other
device
Other
device
 Loading...
Loading...











