I2773-4.4 en
141
Somat eDAQ
lite
7.2.9 Damage Equivalent Load
The Damage Equivalent Load channel generates an accumulated equivalent load
range value as a function of the user-defined damage slope parameter and the
associated accumulated rainflow cycle count for the selected input channel.
NOTE
The Damage Equivalent Load channel has two outputs, load and cycle, each of which
has its own name, description, type, units, full-scale min and max, and data type fields.
The eDAQ
lite
processes the input channel through a rainflow cycle counter using the
user-defined hysteresis value for peak picking. For each closed cycle, the eDAQ
lite
computes a load damage parameter as (closed cycle range ^ damage slope) and
adds it to the running sum that accumulates load damage on a cycle-by-cycle basis.
For each output sample, the eDAQ
lite
processes the residual peak-valley sequence
through the rainflow cycle counter to account for the additional accumulated load
damage and accumulated closed cycle counts. The Damage Equivalent Load output
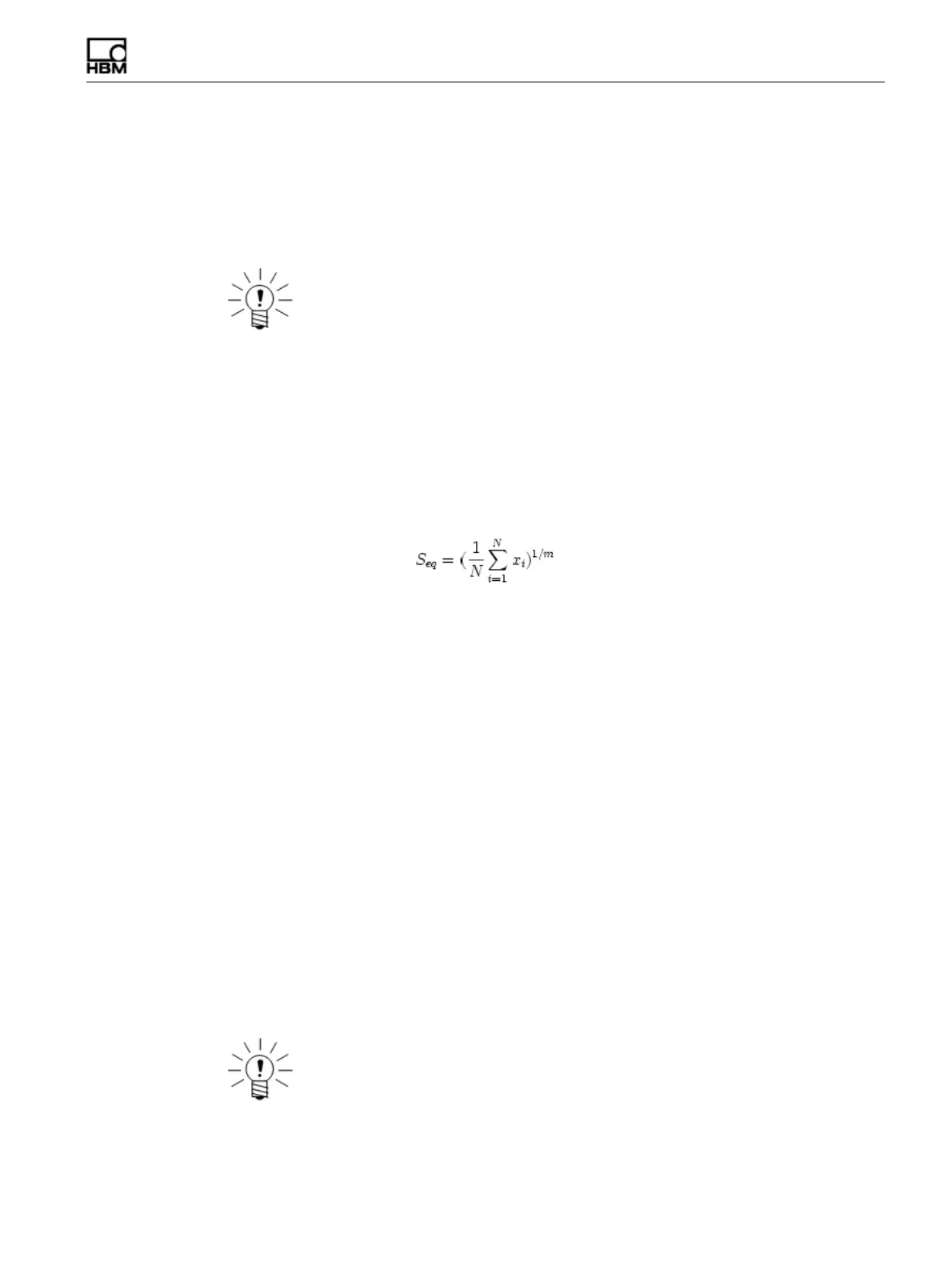
value (
S
eq
) is computed using the following equation:
where,
x
i
is the load damage for each closed cycle,
N
is the number of closed cycles
and
m
is the damage slope.
For more information on the data processing algorithms used, see “Data Processing
Algorithms” on page 221.
Input Channel
The input channel data type must be 32-bit float.
Output Data Type
Both output channel data types are 32-bit float.
Hysteresis
Set the desired hysteresis level for the peak valley processing algorithm.
Damage Slope
Set the damage slope used in the processing algorithm as described above. This can
be any value from 1.0 to 20.0.
Window Samples
Specify the number of input samples used to generate one output sample. This sets
the analysis window size and associated output sample rate. Specify any positive
integer value greater than one.
NOTE
There can be fairly significant computational overhead in generating each output
sample, particularly when the residual peak-valley sequence is relatively long (i.e., 100
residual peak-valleys or more). Consider the computational overhead when specifying
the window samples.
HBM: public
 Loading...
Loading...