Using the FFT
3–38
TDS 340A, TDS 360 & TDS 380 User Manual
H Filter the input to bandwidth limit it to frequencies below that of the Nyquist
frequency.
H Recognize and ignore the aliased frequencies.
If you think you have aliased frequencies in your FFT, select the source channel
and adjust the horizontal scale to increase the sample rate. Since you increase the
Nyquist frequency as you increase the sample rate, the alias signals should
“unfold” and appear at their proper frequency.
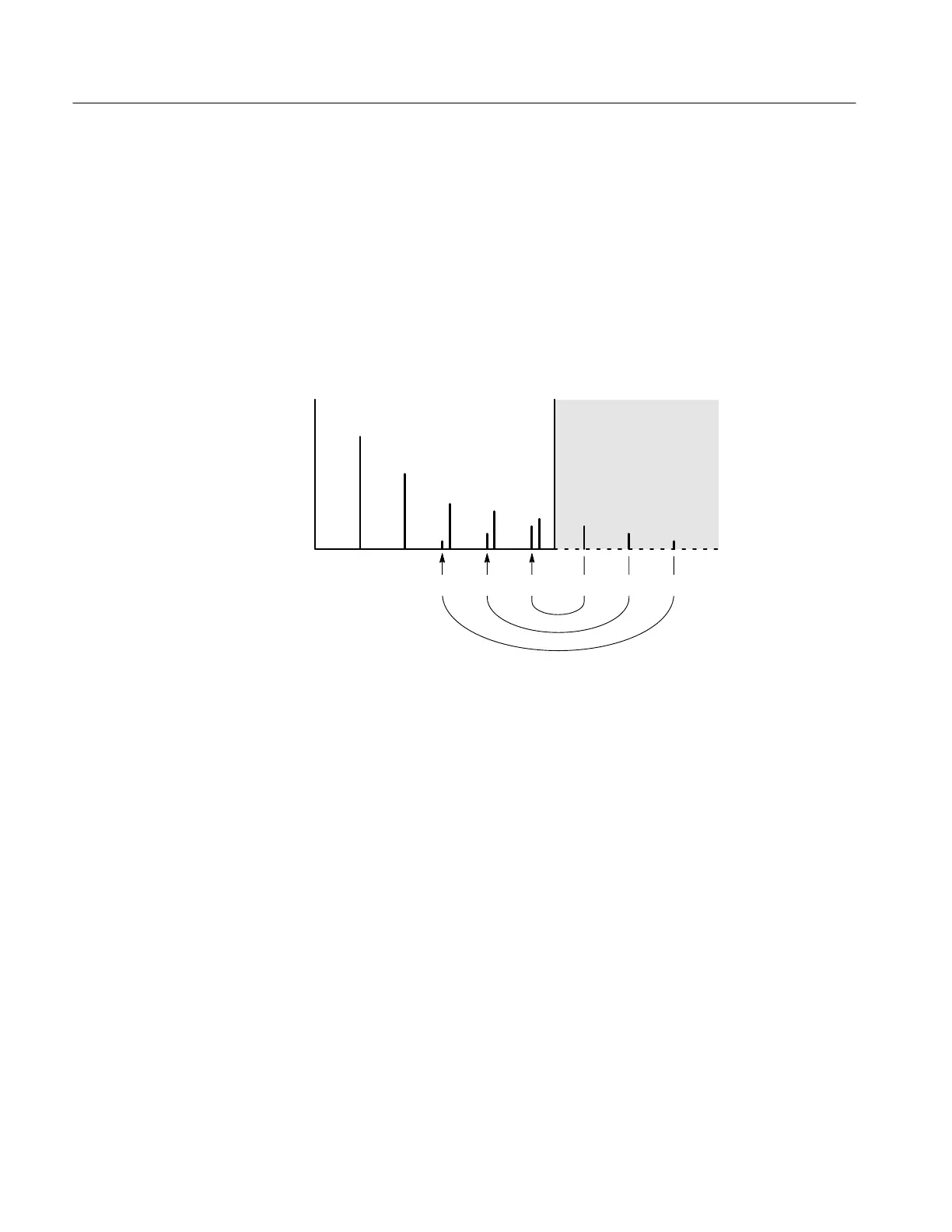
Nyquist frequency
point
Frequency
Amplitude
Aliased frequencies Actual frequencies
Figure 3–25: How aliased frequencies appear in an FFT
The oscilloscope multiplies the FFT time domain record by a Hanning window
before it inputs the record to the FFT function. Figure 3–26 shows how the time
domain record is processed.
The FFT windowing acts like a bandpass filter between the FFT time domain
record and the FFT frequency domain record. The shape of the window controls
the ability of the FFT to resolve (separate) the frequencies and to accurately
measure the amplitude of those frequencies. The Hanning window is optimized
for low leakage and good amplitude measurement accuracy on the different
frequency components of the signal.
If possible, adjust the trigger position so that the most interesting parts of the
signal in the time domain record are positioned in the center region of the
window so that the tapering does not cause severe errors.
FFT Windows

 Loading...
Loading...











