Operating Basics
TDS5000B Series Quick Start User Manual
27
Acquisition Concepts
Acquisition Hardware
Before a signal can be displayed, it must pass through the input channel where it is scaled and digitized. Each
channel has a dedicated input amplifier and digitizer. Each channel produces a stream of digital data from which
the instrument extracts waveform records.
Sampling Process
Acquisition is the process of sampling
an analog signal, converting it into
digital data, and assembling it into a
waveform record, which is then stored
in acquisition memory.
Input signal Sampled points Digital values
+5.0 V
-5.0 V
+5.0 V
0V 0V 0V
-5.0 V
0V
Real-time Sampling
In real-time sampling, the instrume nt
digitizes all of t he points it acquires
using one trigger event. Always use
real-time sampling to capture single-
shot or transient events.
Sampling rate
Record points
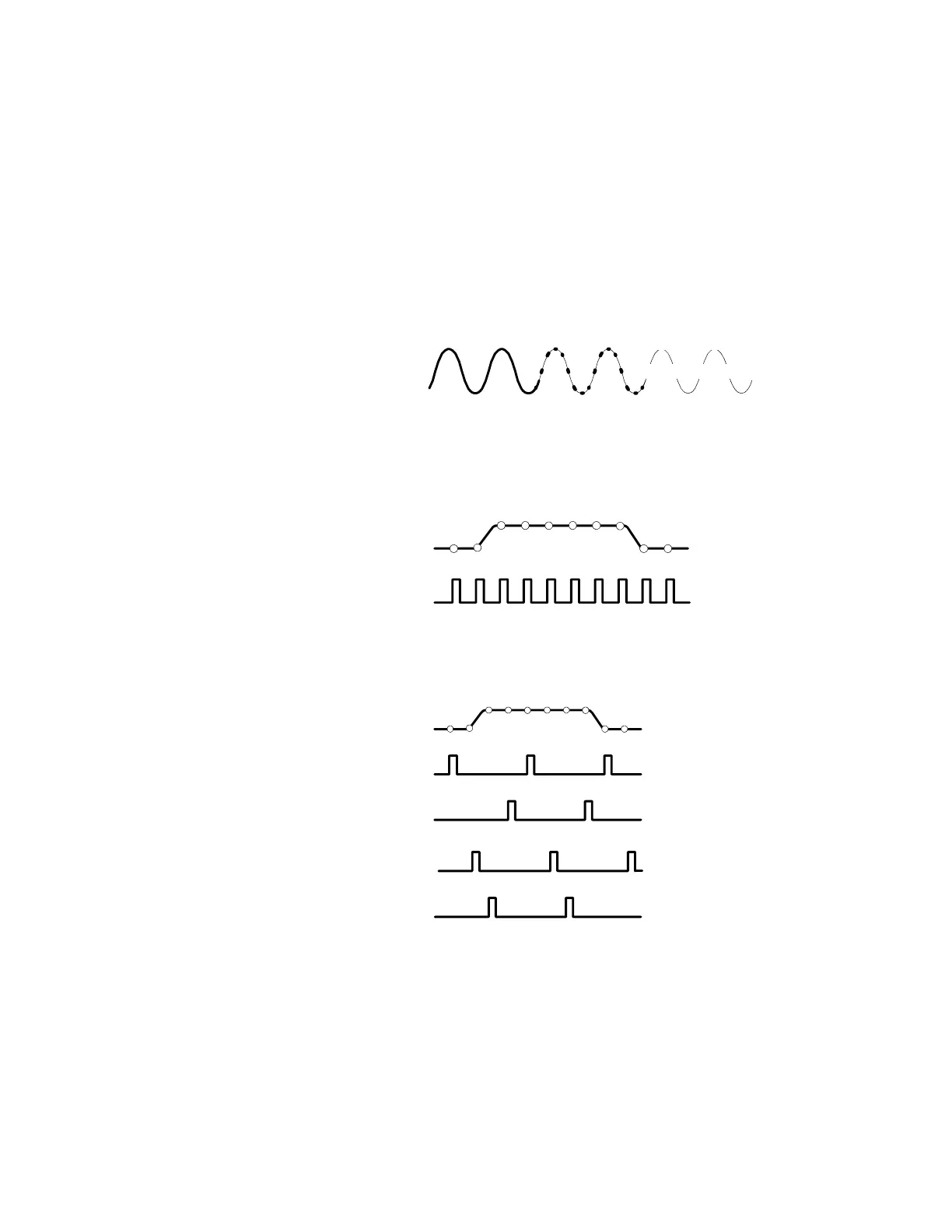
Equivalent-time Sampling
The instrument uses equivalent-time
sampling to extend its sample rate
beyond its real-time maximum
sampling rate. Equivalent-time
sampling is only used if Equivalent
Time is selected and the time base is
set to a sampling rate that is too fast
to create a waveform record using
real-time sampling.
The instrument makes multiple
acquisitions of a repetitive waveform
to obt ain the sample density required
for one complete waveform record.
Thus, equivalent time sampling should
only be used with repe titive signals.
1st acquisition cycle
3rd acquisition cycle
nth acquisition cycle
2nd acquisition cycle
Record points

 Loading...
Loading...

















