442 Appendix A: Functions and Instructions
8992APPA.DOC TI-89 / TI-92 Plus: Appendix A (US English) Susan Gullord Revised: 02/23/01 1:48 PM Printed: 02/23/01 2:21 PM Page 442 of 132
e
^(squareMatrix1)
⇒
squareMatrix
Returns the matrix exponential of
squareMatrix1
. This is
not
the same as
calculating
e
raised to the power of each
element. For information about the
calculation method, refer to
cos()
.
squareMatrix1
must be diagonalizable. The
result always contains floating-point
numbers.
e
^([1,5,3;4,2,1;6,
ë
2,1])
¸
782.209 559.617 456.509
680.546 488.795 396.521
524.929 371.222 307.879
eigVc()
MATH/Matrix menu
eigVc(squareMatrix)
⇒
matrix
Returns a matrix containing the eigenvectors
for a real or complex
squareMatrix
, where
each column in the result corresponds to an
eigenvalue. Note that an eigenvector is not
unique; it may be scaled by any constant
factor. The eigenvectors are normalized,
meaning that if V = [x
1
, x
2
, … , x
n
], then:
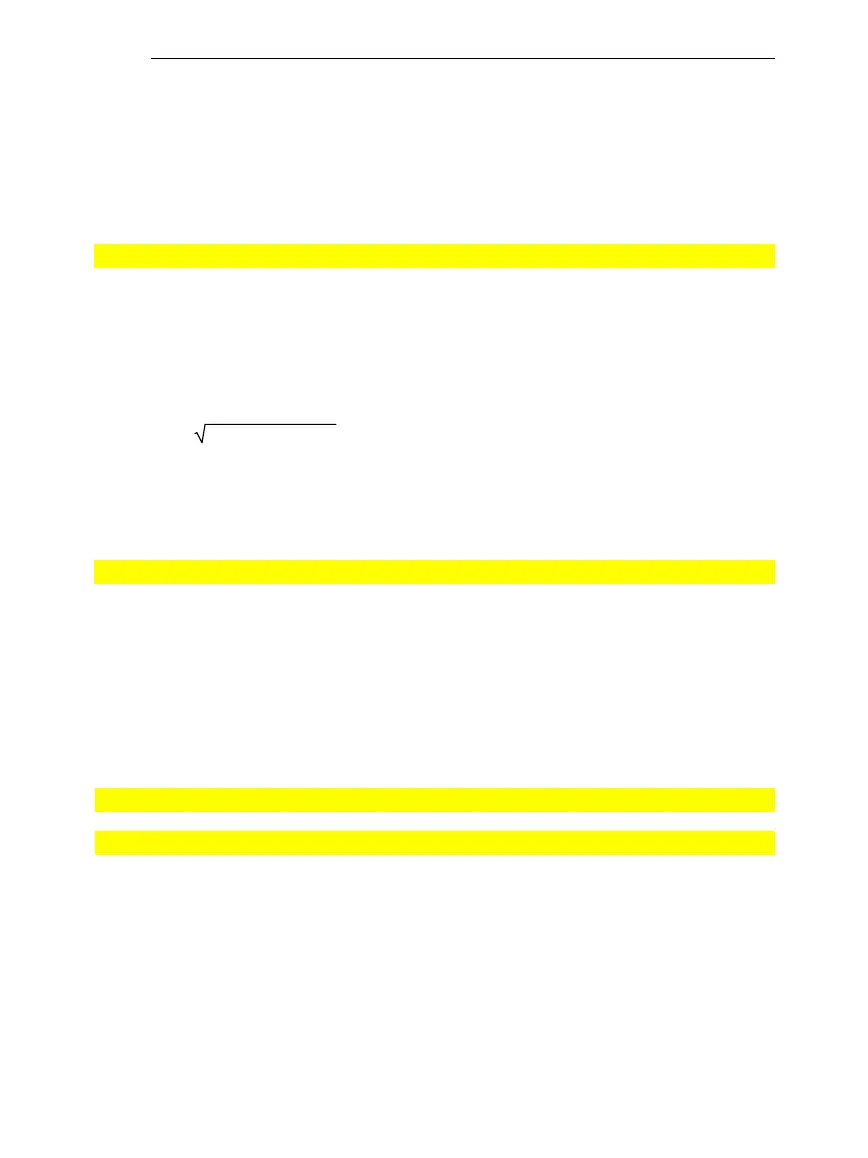
x
1
2
+ x
2
2
+ … + x
n
2
= 1
squareMatrix
is first balanced with similarity
transformations until the row and column
norms are as close to the same value as
possible. The
squareMatrix
is then reduced to
upper Hessenberg form and the eigenvectors
are computed via a Schur factorization.
In Rectangular complex format mode:
[L1,2,5;3,L6,9;2,L5,7]
!
m1
¸
ë
1 2 5
3
ë
6 9
2
ë
5 7
eigVc(m1)
¸
ë
.800… .767…
.767…
.484… .573…+.052…
ø
i
.573…
ì
.052…
ø
i
.352… .262…+.096…
ø
i
.262…
ì
.096…
ø
i
eigVl()
MATH/Matrix menu
eigVl(squareMatrix)
⇒
list
Returns a list of the eigenvalues of a real or
complex
squareMatrix
.
squareMatrix
is first balanced with similarity
transformations until the row and column
norms are as close to the same value as
possible. The
squareMatrix
is then reduced to
upper Hessenberg form and the eigenvalues
are computed from the upper Hessenberg
matrix.
In Rectangular complex format mode:
[L1,2,5;3,L6,9;2,L5,7]
!
m1
¸
ë
1 2 5
3
ë
6 9
2
ë
5 7
eigVl(m1)
¸
{
ë
4.409… 2.204…+.763…
ø
i
2.204…
ì
.763…
ø
i
}
Else
See
If
, page 456.
ElseIf
CATALOG
See also
If
, page 456.
If Boolean expression1 Then
block1
ElseIf Boolean expression2 Then
block2
©
ElseIf Boolean expressionN Then
blockN
EndIf
©
ElseIf
can be used as a program instruction
for program branching.
Program segment:
©
:If c
oice=
T
en
: Goto option
: E
seIf c
oice=2 T
en
: Goto option2
: E
seIf c
oice=3 T
en
: Goto option3
: E
seIf c
oice=4 T
en
: Disp "Exiting Program"
: Return
:En
If
©

 Loading...
Loading...


















