E6582062
5. [Fundamental operation] How to use parameters 5-56
4
5
9
3) Adjusting PID control gain level
Adjust the PID control gain level according to the set values, the feedback signals, and the
object to be controlled.
<F362: PID1 proportional gain>
This parameter adjusts the proportional gain level of PID control. A correction value proportional
to the particular deviation (the difference between the set value and the feedback value) is
obtained by multiplying this deviation by the parameter setting.
A larger P-gain adjustment value gives faster response. Too large an adjustment value,
however, results in an unstable event such as hunting.
<F363: PID1 integral gain>
This parameter adjusts the integral gain level of PID control. Any remaining deviations (residual
deviation offset) during proportional action are cleared to zero.
A larger I-gain adjustment value reduces residual deviations. Too large an adjustment value,
however, results in an unstable event such as hunting.
Memo
• PID control can be temporarily turned off with an external signal. Assign "36: PID control OFF"
to an input terminal.
• PID control should be OFF when very low speed drive is needed.
• If speed PID is selected, motor is possibly rotating forward and reverse. If you don't want to
rotate reverse, set <F311: Reverse inhibited> or select process PID (<F359>=1, or 11).
Title Parameter name Adjustment range Unit
Default
setting
F362 PID1 proportional gain 0.01 - 100.0 - 0.30
F363 PID1 integral gain 0.01 - 100.0
s
-1
0.20
F366 PID1 differential gain 0.00 - 2.55 s 0.00
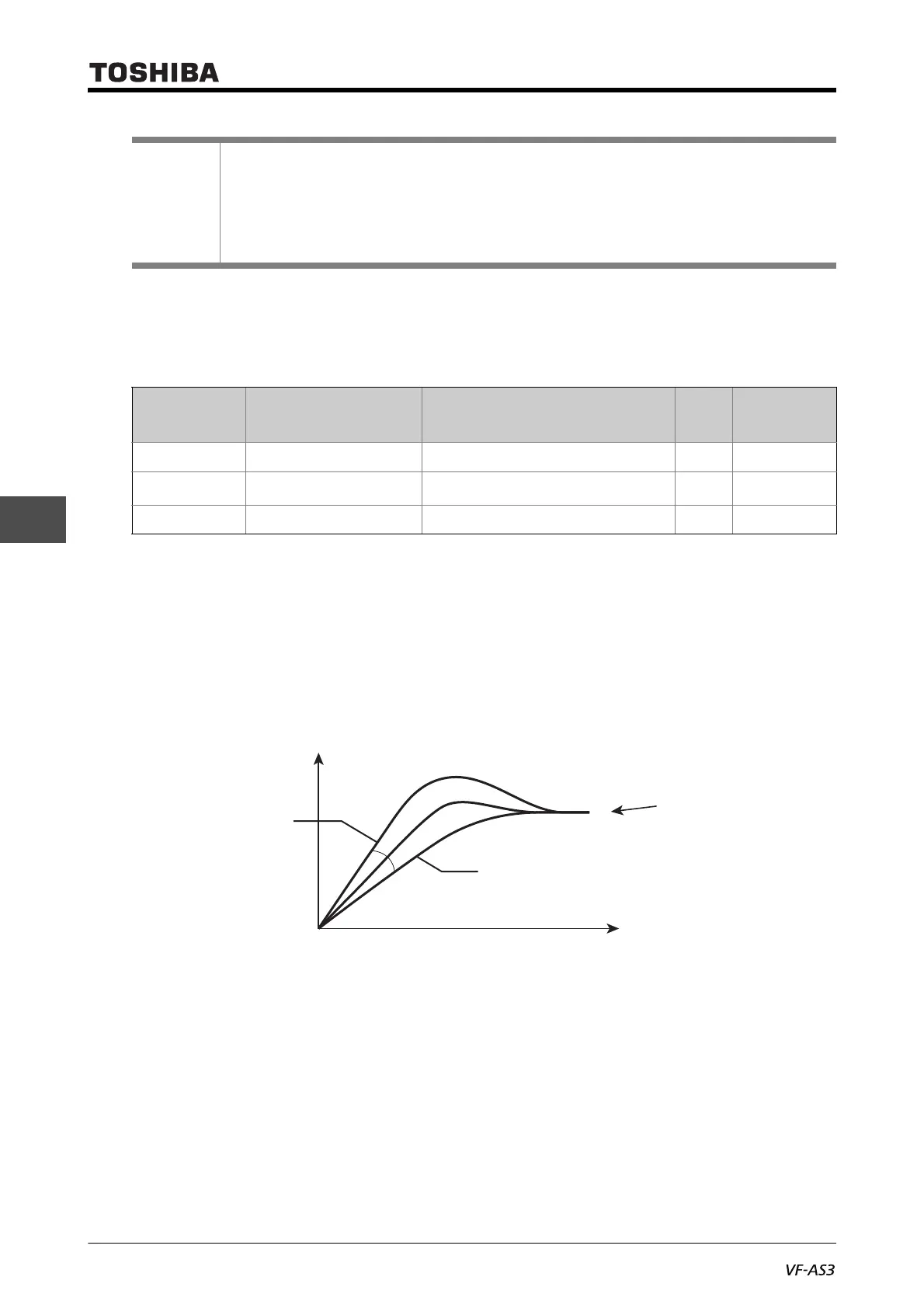
PID set value
Output frequency
Fast response
Large
Slow response
Time
Small
<F362>
<F362>

 Loading...
Loading...
















