9 Interfacing
Communication with GNSS Compass is possible on the following ports:
l
Ethernet
l
9.2 Serial Interface
l
CAN
l
1PPS Signal
Each port has different input and output capabilities.
9.1 Ethernet
The Ethernet interface offers a 100 MBit port for connection to a network, router or laptop/computer. The
interface offers a Web UI, as well as 4 (four) configurable data ports. Each Data Port
l
can be configured as a TCPServer, TCPClient or a UDPClient as detailed in 9.1.1 Ethernet Modes
l
can be configured with an Input and/or Output for a number of protocols as detailed in 9.1 Ethernet.
l
should only be used to establish a connection with a single remote computer/device at any one time.
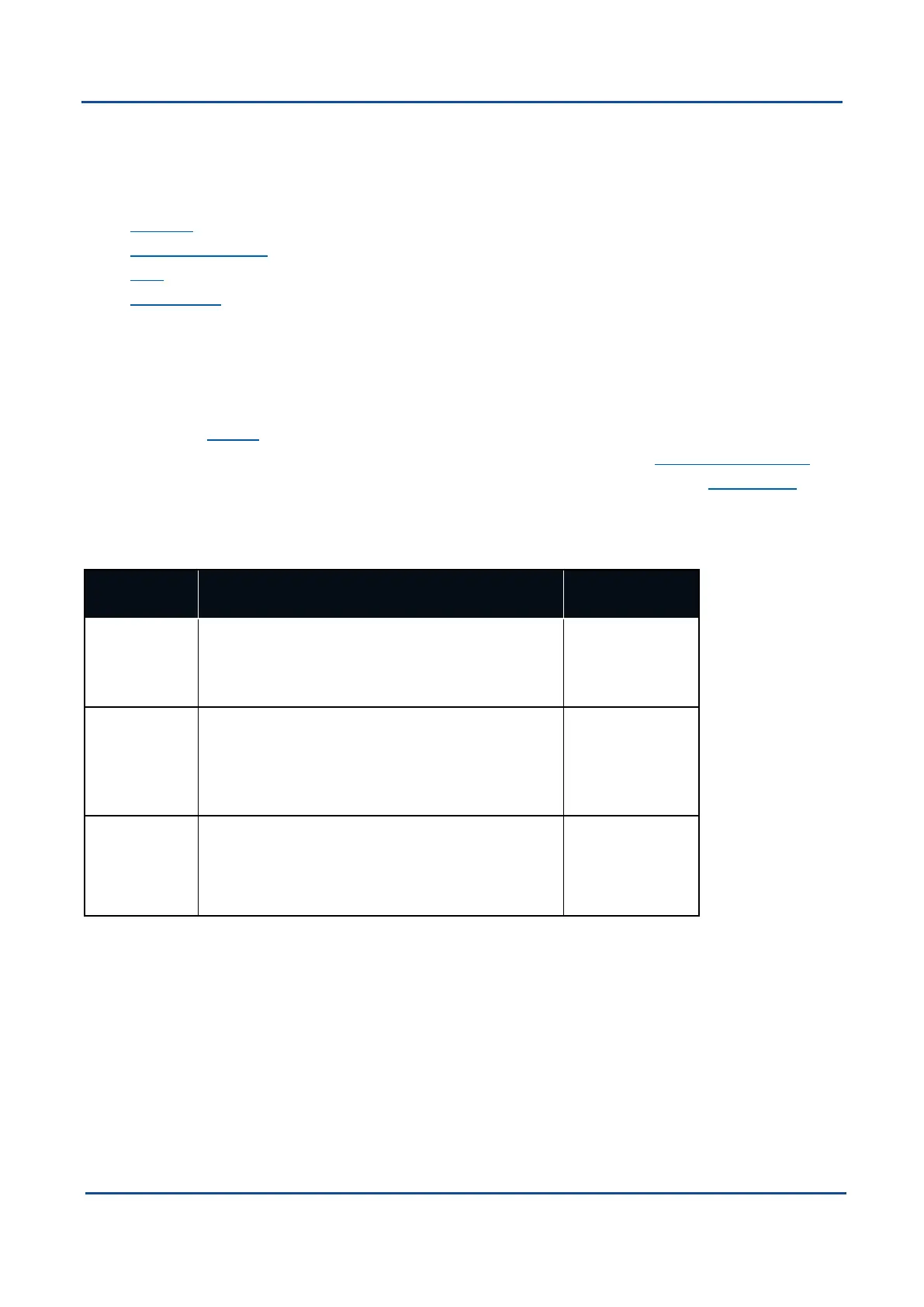
9.1.1 Ethernet Modes
Ethernet
Mode
Description Required Con-
figuration
TCPServer GNSS Compass will establish a TCPServer listen-
ing on the defined port. A connected client is able to
receive Output data and send Input data based on
the defined Input and Output functions.
Port
TCPClient GNSS Compass will continuously attempt to estab-
lish a TCPconnection to the defined Destination IP
and Port. Once established, a connected client is
able to receive Output data and send Input data
based on the defined Input and Output functions.
Client
Destination
IPaddress
Port
UDPClient GNSS Compass will send UDP Output data to the
defined Destination IP and Port. A client can also
send UDPInput data to GNSS Compass this same
Port.
Client
Destination
IPaddress
Port
Table 22: Ethernet Data Port Modes
v2.0 Page 65 04 Nov 2021
GNSS Compass Reference Manual • Interfacing

 Loading...
Loading...