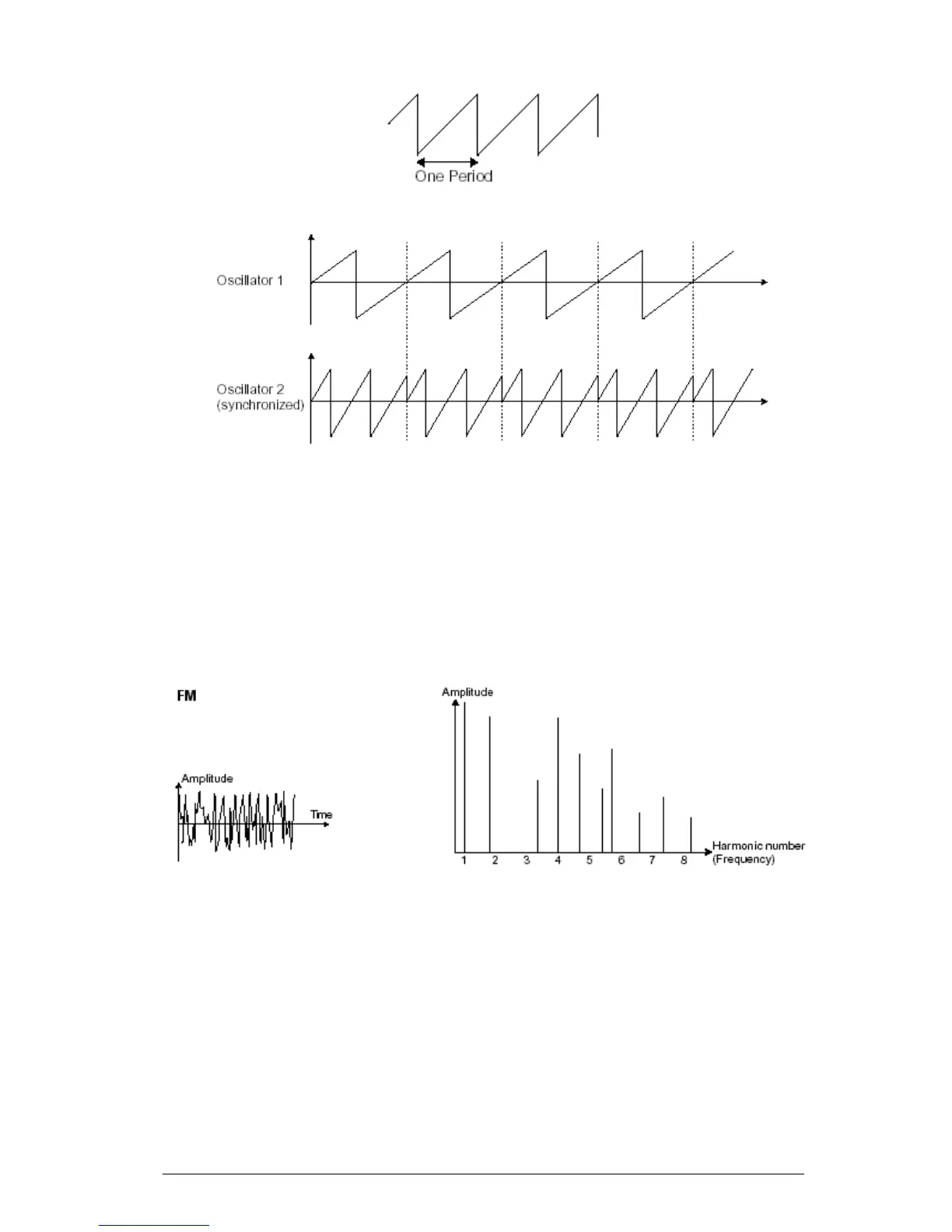
In the above image, oscillator2 is synchronized with the first and tuned to double the tonality. The
resulting waveform is unique in that it cannot be created by standard synthesis techniques such as
layering or filtering.
6.1.1.6 Frequency modulation
A frequency modulation (FM) can be created between 2 oscillators by connecting the
audio output from a first sinusoidal oscillator to the modulation input of a second
oscillator. On the Mini V, if you turn the modulation rate ring, you will obtain a sound
richer in harmonics. If you introduce a square or sawtooth signal, the result can be
quickly distorted… but interesting for inharmonic sonorities like bell sounds or special
effects for example.
Time and spectral representations of a frequency modulation
6.1.2 The noise module
The noise signal spectrum has all frequencies at an equal volume level, often referred to
as “white noise”. For this reason, the noise module is used to create different noises like
the imitation of wind or special effects. White noise is the richest of noises. Pink noise is
also regularly present on synthesizers. It is less rich in the high frequencies than white
noise.
Also note that the audio output of noise can also be used as a modulation signal
(especially when strongly filtered) to create random cyclic variations.
 Loading...
Loading...











