AW00089317000 Color Creation and Enhancement
Basler ace GigE 187
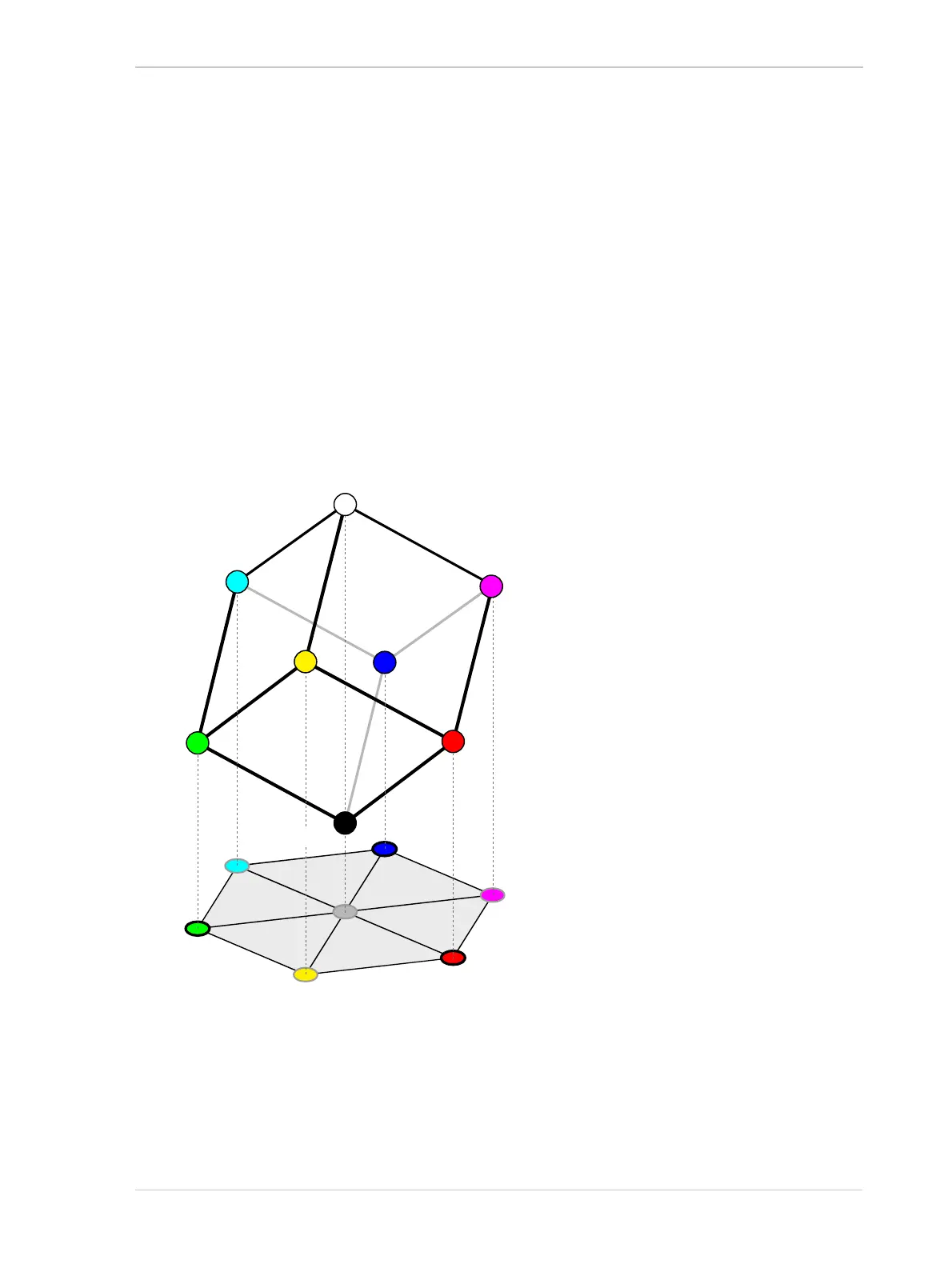
The color space can be represented as a color cube (see Figure 90 on page 187) where the primary
colors R, G, B, the secondary colors C, M, Y, and black and white define the corners. All shades of
gray are represented by the line connecting the black and the white corner.
For ease of imagination, the color cube can be projected onto a plane (as shown in Figure 90) such
that a color hexagon is formed. The primary and secondary colors define the corners of the color
hexagon in an alternating fashion. The edges of the color hexagon represent the colors resulting
from mixing the primary and secondary colors. The center of the color hexagon represents all
shades of gray including black and white.
The representation of any arbitrary color of the RGB color space will lie within the color hexagon.
The color will be characterized by its hue and saturation:
Hue specifies the kind of coloration, for example, whether the color is red, yellow, orange etc.
Saturation expresses the colorfulness of a color. At maximum saturation, no shade of gray is
present. At minimum saturation, no "color" but only some shade of gray (including black and
white) is present.
C
R
Black
White
R
C
M
B
G
Y
M
B
G
Y
Fig. 90: RGB Color Cube With YCM Secondary Colors, Black, and White, Projected On a Plane

 Loading...
Loading...







