152 Functional Description CG Drives & Automation, 01-5326-01r5
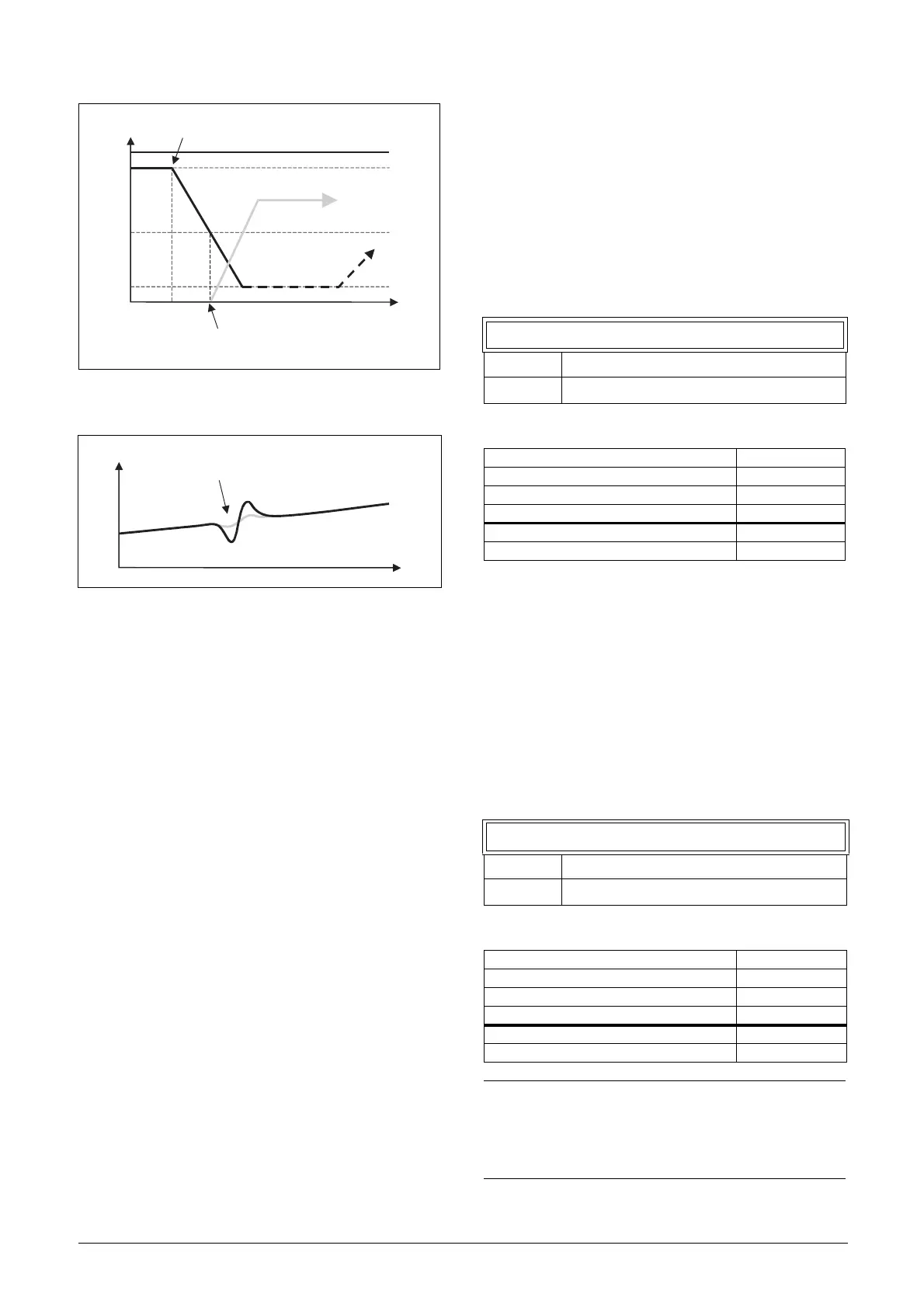
Fig. 119 Transition speed start
Fig. 120 Effect of transition speed
Settle Time Stop [39F]
The settle stop allows the process to settle after a pump is
switched off before the pump control continues. If an
additional pump is stopped D.O.L. (Direct On Line) or Y/
,
the flow or pressure can still fluctuate due to the 'rough'
start/stop method. This could cause unnecessary starting
and stopping of additional pumps.
During the Settle stop:
• PID controller is off.
• the speed is kept at a fixed level after stopping a pump
Communication information
Transition Speed Stop [39G]
The transition speed stop is used to minimize a flow/
pressure overshoot when shutting down an additional pump.
The setting depends on the dynamics of both the master
drive and the additional drives.
In general:
• If the additional pump has 'slow' start/stop dynamics,
then a higher transition speed should be used.
• If the additional pump has 'fast' start/stop dynamics,
then a lower transition speed should be used.
Communication information
Speed
Actual
Trans
Min
Switch on
procedure starts
Additional pump
Master pump
Flow/Pressure
Actual start
command of next
pump (RELAY)
Flow/Pressure
Transition speed
decreases overshoot
Time
39F Settle Stop
Default: 0 s
Range: 0–999 s
Modbus Instance no/DeviceNet no: 43175
Profibus slot/index 169/79
EtherCAT and CANopen index (hex) 4c67
Profinet IO index 19559
Fieldbus format Long, 1=1 s
Modbus format EInt
39G TransS Stop
Default: 60%
Range: 0-100% of total min speed to max speed
Modbus Instance no/DeviceNet no: 43176
Profibus slot/index 169/80
EtherCAT and CANopen index (hex) 4c68
Profinet IO index 19560
Fieldbus format Long, 1=1%
Modbus format EInt
NOTE: If set to 0 %, the transition speed when
stopping pumps, is ignored and no speed adaption is
made.
I.e. the slave pump is stopped directly and speed of
the master pump is continued.

 Loading...
Loading...