AGC Designer’s Reference Handbook
DEIF A/S Page 129 of 168
The integrating function of the I regulator is increased, if the integral action coefficient, KI, is
increased. This means that the reset time gets smaller and a faster I regulation is achieved. If
the KI is adjusted to 0 (reset time endless), the I regulator is switched off.
Relay control
When the relay outputs are used for control purposes, the regulation works like this:
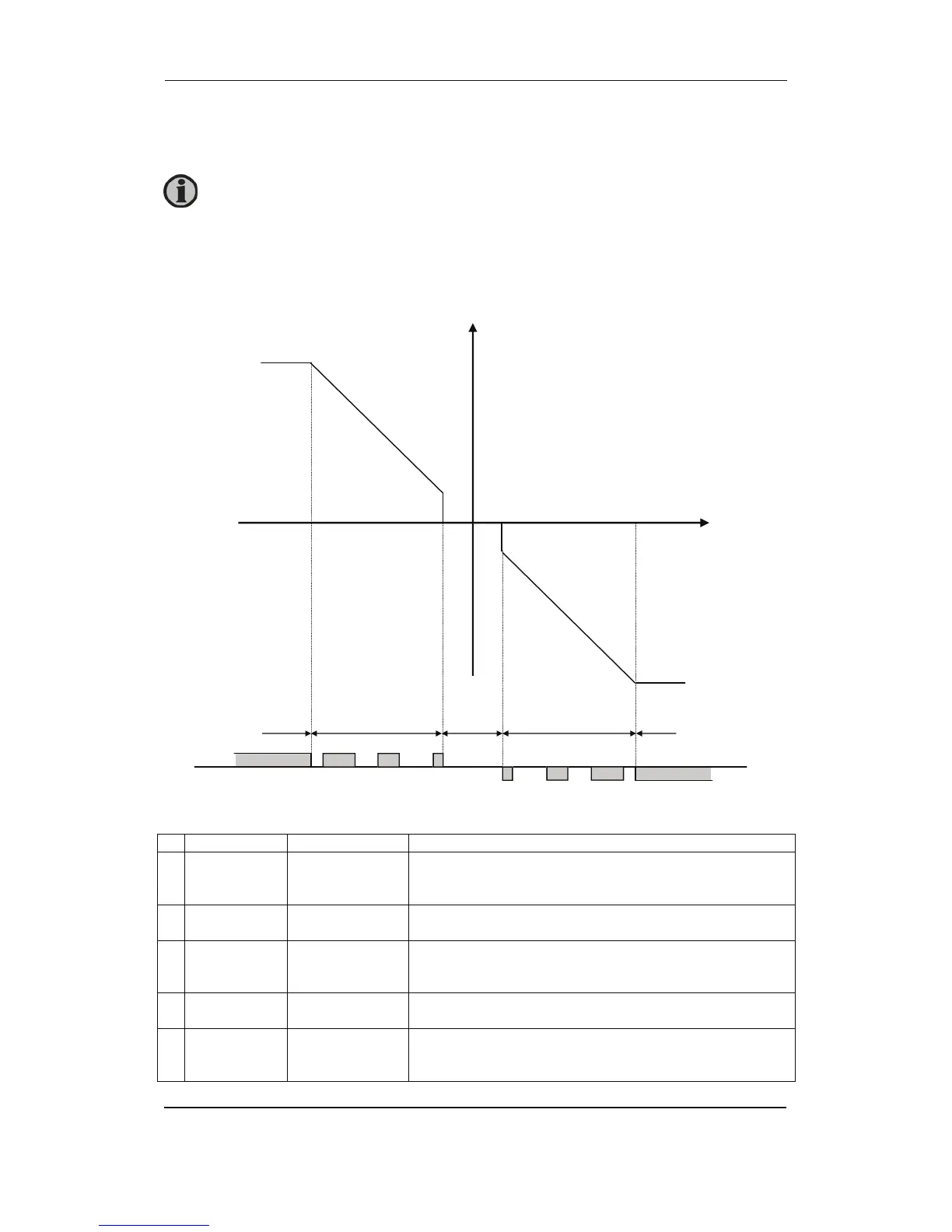
The regulation with relays can be split up into five steps.
# Range Description Comment
1 Static range Fix up signal The regulation is active, but the increase relay will be
constantly activated because of the size of the regulation
deviation.
2 Dynamic
range
Up pulse The regulation is active, and the increase relay will be
pulsing in order to eliminate the regulation deviation.
3 Dead band
area
No reg. In this particular range no regulation takes place.
The regulation accepts a predefined dead band area in
order to increase the lifetime of the relays.
4 Dynamic
range
Down pulse The regulation is active, and the decrease relay will be
pulsing in order to eliminate the regulation deviation.
5 Static range Fix down signal The regulation is active, but the decrease relay will be
constantly activated because of the size of the regulation
deviation.
55Hz
45Hz
50Hz
Regulator
output
Fix up signal Up pulse No reg. Fix down signal Down pulse
Hz
The integral action coefficient, KI, must not be too high. This will make the
regulation hunt similar to a too high proportional action factor, KP.
 Loading...
Loading...