Manage Python applications
Digi TransPort User Guide 703
Manage Python applications
About Python programming for Digi TransPort devices
Some of the Digi TransPort routers support the Python scripting language. Python allows users to
extend and enhance the basic functionality of the router through programming. The routers
contain a Python interpreter which may be invoked from the command line. This can be useful
for developing scripts. The more usual way to use Python is to write a script to implement a
required function and to run this script autonomously. It is common practice for Python scripts to
use the file extension .py, such as myscript.py. A Python script is a text file containing Python
commands and may be created using a normal plain text editor. Python is a powerful language
and obtains some of its power from the many modules that are available for it. A description of
the Python language is outside the scope of this manual. For more information on Python
programming see the Digi Python Programmer’s Guide on www.digi.com.
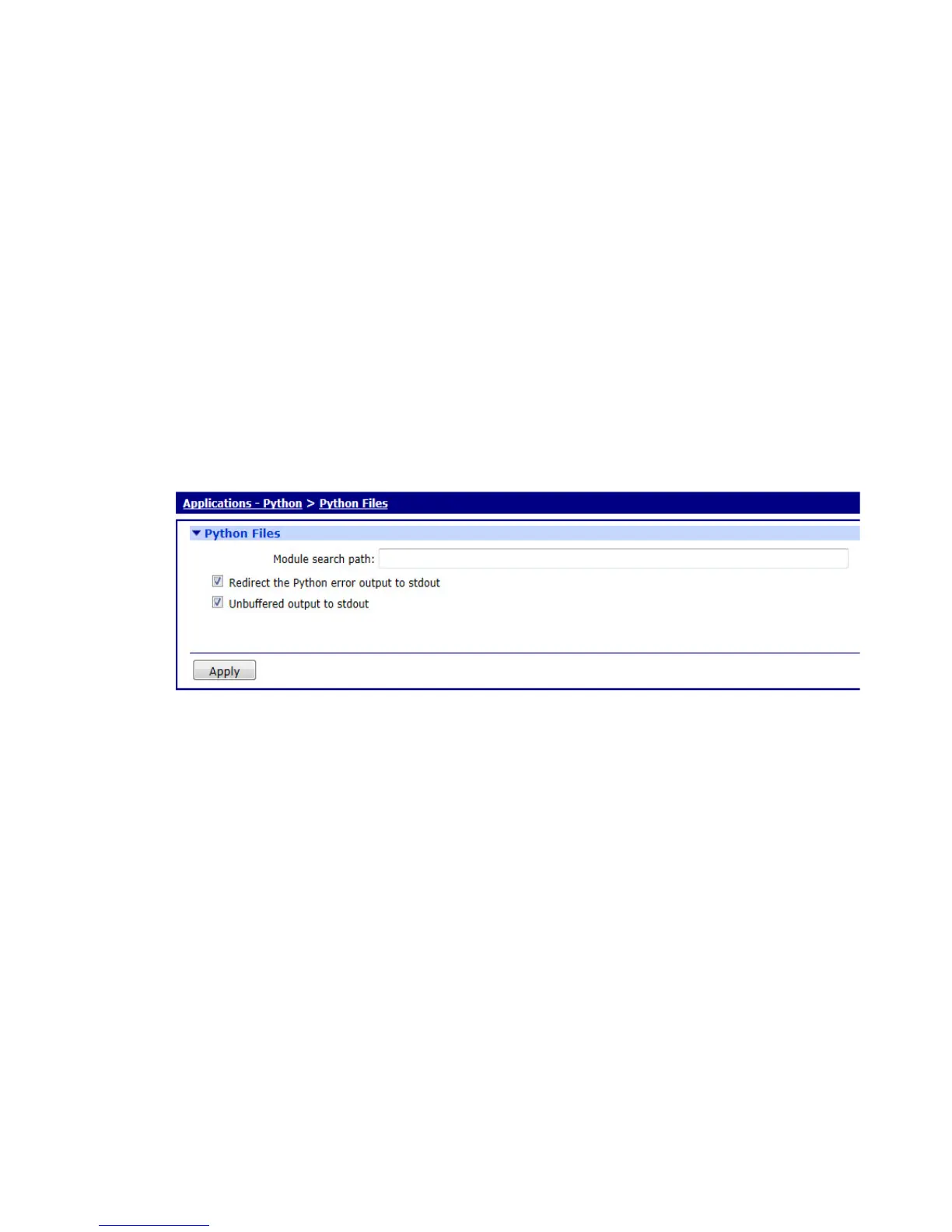
Python Files page
To manage Python application files, go to Applications > Python > Python Files.
This page has the following settings:
Module search path
Sets the search path for Python modules that are not in the default search path. Multiple
locations may be specified by separating pathnames with colons, such as
pymod1.zip:python21.zip. This causes the interpreter to search for the two compressed files
pymod1.zip and python21.zip. Note that TransPort routers have a flat filing system structure
that does not support subdirectories.
Redirect the Python output to debug
When checked, this checkbox allows the redirection of the stdout file handle to the debug
output (stderr) file handle. The default state of this parameter is Off. The easiest way to see
this in action is to issue the command to start the Python interpreter from a debug/CLI
terminal, and note that the screen remains blank. Stop the interpreter (using the exit()
command), set this parameter to On, and re-issue the command to start the interpreter. This
time, the familiar Python welcome message and prompt should appear on the console.
Unbuffered output to stdout
When checked, this checkbox allows redirection of unbuffered output to file handle to the
debug output (stderr) file handle.

 Loading...
Loading...











