ASYMMETRIC BINOCULAR TRACING
The two rims are traced as if they have different shapes; the perimeters and the shapes are kept.
BOXING DIMENSIONS
The boxing system is a standard method for indicating the dimensions of frame contours (or gauges). This
operation consists of fitting the frame into a rectangle whose dimensions are indicated.
• Boxing center: geometric center of the rectangle
• Boxing axis: horizontal axis of the frame passing through the boxing center
• A-dimension: length of the rectangle
• B-dimension: height of the rectangle
• E-dimension: the longest radius starting from the boxing center
• Boxing height: calculated from the tangent line at the bottom of the frame
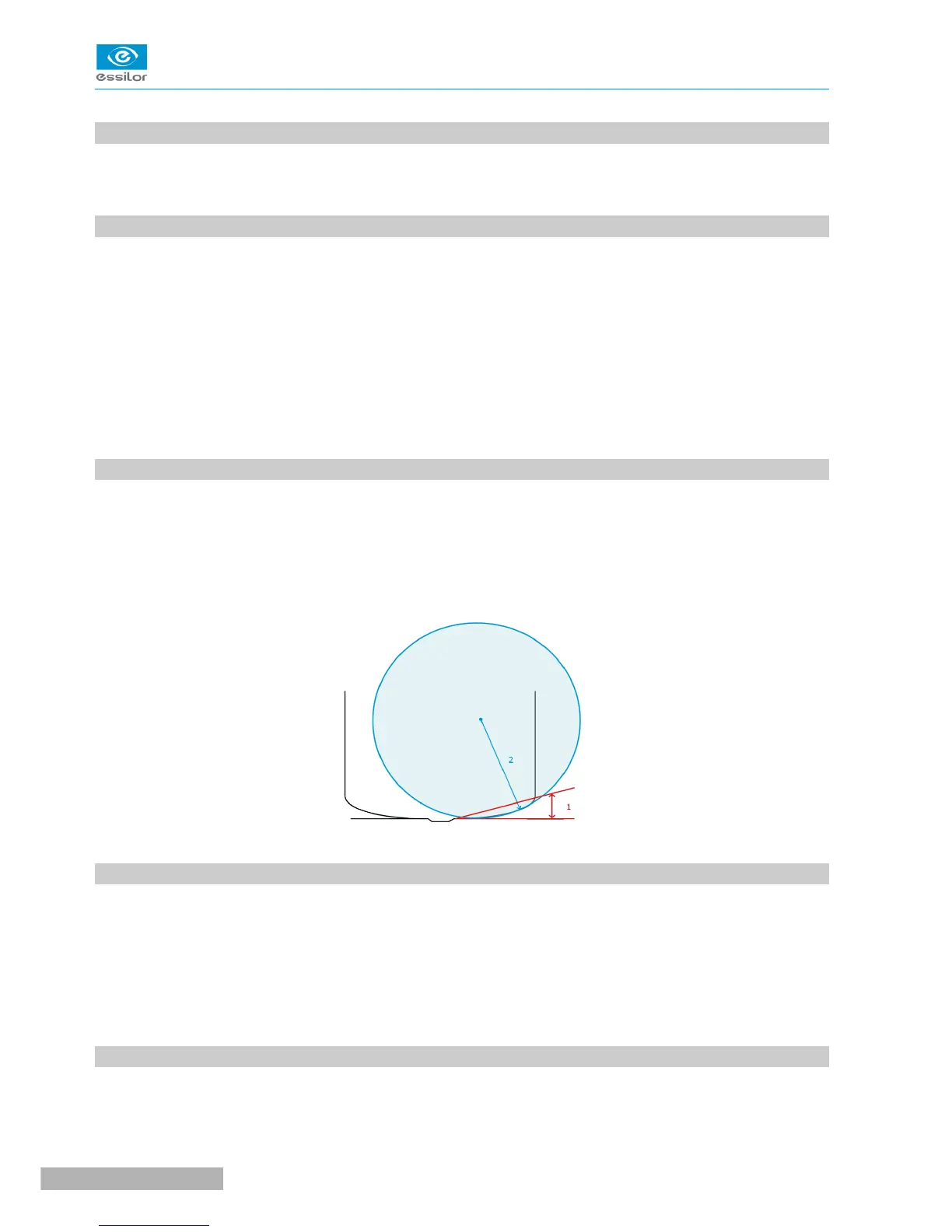
CURVE ANGLE AND FRAME BASE
1. Curve angle: relative parameter formed between the median plane of each frame rim and the general
plane of the frame. It is used to compute the decentration necessary for curved corrective lenses. The
curve angle is expressed in degrees.
2. Frame base: parameter corresponding to the radius of the sphere going through the maximum
number of points traced on the circle. It allows a better correspondence between lens bases (bevel)
and the frame. The frame base is expressed in diopters.
EXECUTIVE LENS
Type of bifocal lens with two full fields: one which corrects far vision defects and one which corrects near
vision defects. They are available in two models:
• separation line present on the front surface of the lens
• separation line present on the rear surface of the lens
• Example of lenses of this type: Telex lenses
TM
ID
The job identifier, or ID, consists of alphanumeric characters. It is unique.

 Loading...
Loading...