1.6 Precautions for Using Inverters
1-26
Precautions for connection of peripheral equipment
(1) Phase-advancing capacitors for power factor correction
Do not mount a phase-advancing capacitor for power factor correction in the inverter's input (primary)
circuit. Mounting it in the input (primary) circuit takes no effect. To correct the inverter power factor,
use an optional DC reactor (DCR). Do not mount a phase-advancing capacitor for power factor
correction in the inverter's output (secondary) circuit. Mounting it in the output (secondary) circuit
causes an overcurrent trip, disabling operation.
An overvoltage trip that occurs when the inverter is stopped or running with a light load is assumed to
be due to surge current generated by open/close of phase-advancing capacitors in the power system.
An optional DC/AC reactor (DCR/ACR) is recommended as a measure to be taken at the inverter
side.
Input current to an inverter contains a harmonic component that may affect other motors and
phase-advancing capacitors on the same power supply line. If the harmonic component causes any
problems, connect an optional DCR/ACR to the inverter.
In some cases, it is necessary to insert a reactor in series with the phase-advancing capacitors.
(2) Power supply lines (Application of a DC/AC reactor)
Use an optional DC reactor (DCR) when the capacity of the power supply transformer is 500 kVA or
more and is 10 times or more the inverter rated capacity or when there are thyristor-driven loads on
the same power supply line. If no DCR is used, the percentage-reactance of the power supply
decreases, and harmonic components and their peak levels increase. These factors may break
rectifiers or smoothing capacitors in the converter section of the inverter, or decrease the
capacitance of the capacitors.
If the input voltage unbalance rate is 2% to 3%, use an optional AC reactor (ACR).
Voltage unbalance (%) = [Max voltage (V) - Min voltage (V)] / [Three-phase average voltage (V)] x 67
(IEC61800- 3)
(3) DC reactor (DCR) for correcting the inverter input power factor (for suppressing harmonics)
To correct the inverter input power factor (to suppress harmonics), use an optional DCR. Using a
DCR increases the reactance of inverter’s power source so as to decrease harmonic components on
the power source lines and correct the power factor of the inverter.
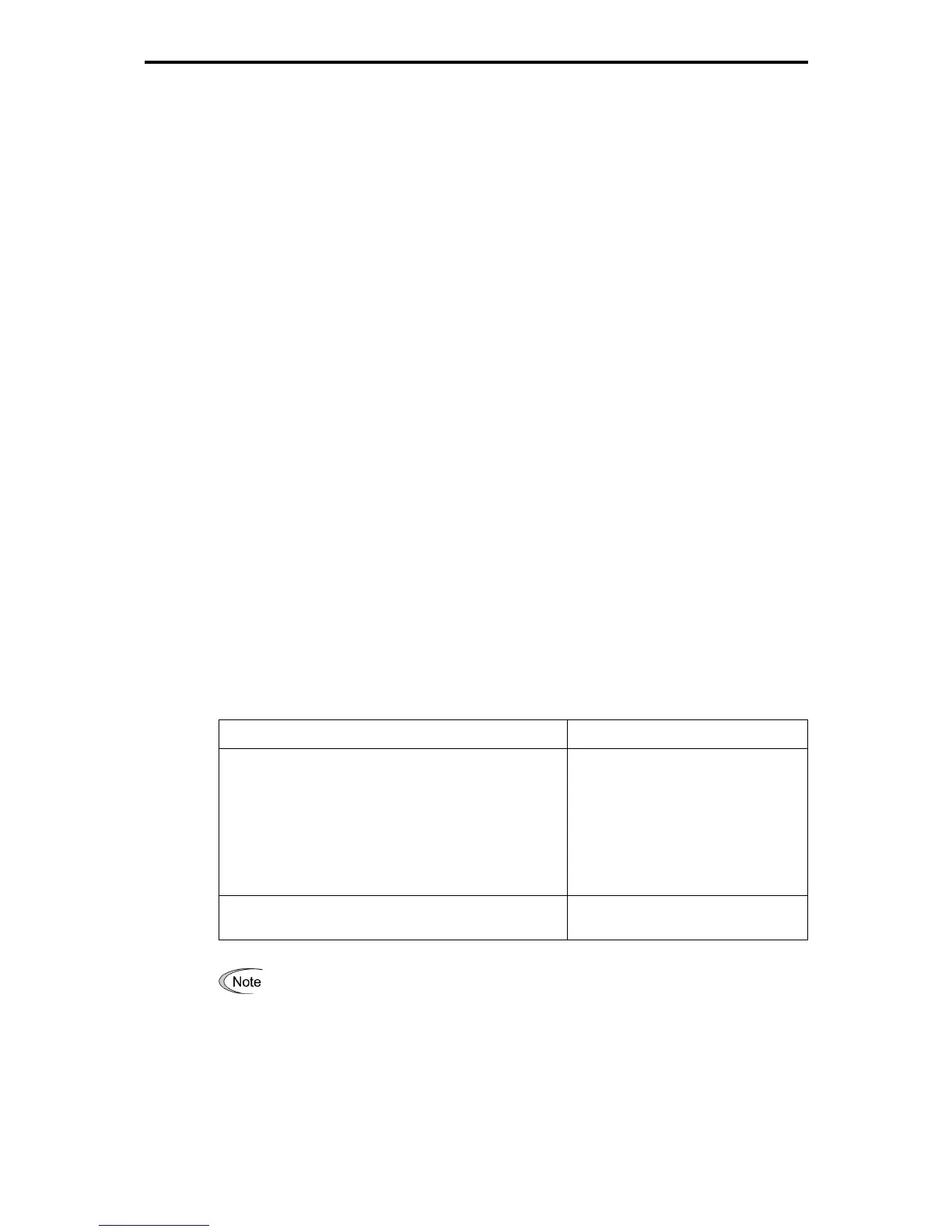
Table 1.6-6
DC reactor type Remarks
Input power factor of DCR2/4-/A/B: Approx.
90 to 95%
Compliant with the Public Construction Works Standard
Specifications (Electrical Equipment Works), Edition
2010, supervised by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure,
Transport and Tourism. (Based on Edition 2010, the
input power factor calculated with the power factor for
the fundamental wave as 1 stands at 94% or higher.)
The last letter identifies the
capacitance.
Input power factor of DCR2/4-C: Approx. 86 to 90%
Exclusively designed for nominal
applied motor of 37 kW or above.
Select a DCR matching not the inverter but the nominal applied motor. Therefore, for
HD-mode inverters, arrange a DCR with the same capacity as the inverter; for LD-mode
inverters, arrange a DCR with one rank higher capacity than the inverter.
(4) PWM converter for correcting the inverter input power factor
Using a PWM converter (High power-factor, regenerative PWM converter, RHC series) corrects the
inverter power factor up to nearly 100%.
When combining an inverter with a PWM converter, disable the main power loss detection by setting
the function code H72 to "0." If the main power loss detection is enabled (H72 = 1, factory default),
the inverter interprets the main power as being shut down, ignoring an entry of a run command.

 Loading...
Loading...











