1.6 Precautions for Using Inverters
1-28
Noise reduction
If noise generated from the inverter affects other devices, or that generated from peripheral equipment
causes the inverter to malfunction, follow the basic measures outlined below.
(1) If noise generated from the inverter affects the other devices through power wires or grounding wires:
• Isolate the grounding terminals of the inverter from those of the other devices.
• Connect a noise filter to the inverter power wires.
• Isolate the power system of the other devices from that of the inverter with an insulated
transformer.
• Decrease the inverter's carrier frequency (F26).
(2) If induction or radio noise generated from the inverter affects other devices:
• Isolate the main circuit wires from the control circuit wires and other device wires.
• Put the main circuit wires through a metal conduit pipe, and connect the pipe to the ground near
the inverter.
• Install the inverter into the metal panel and connect the whole panel to the ground.
• Connect a noise filter to the inverter power wires.
• Decrease the inverter's carrier frequency (F26).
(3) When implementing measures against noise generated from peripheral equipment:
• For inverter's control signal wires, use twisted or shielded-twisted wires.
When using shielded-twisted wires, connect the shield of the shielded wires to the common
terminals of the control circuit.
• Connect a surge absorber in parallel with magnetic contactor's coils or other solenoids.
Leakage current
A high frequency current component generated by insulated gate bipolar transistors (IGBTs) switching
on/off inside the inverter becomes leakage current through stray capacitance of inverter input and output
wires or a motor. If any of the problems listed below occurs, take an appropriate measure against them.
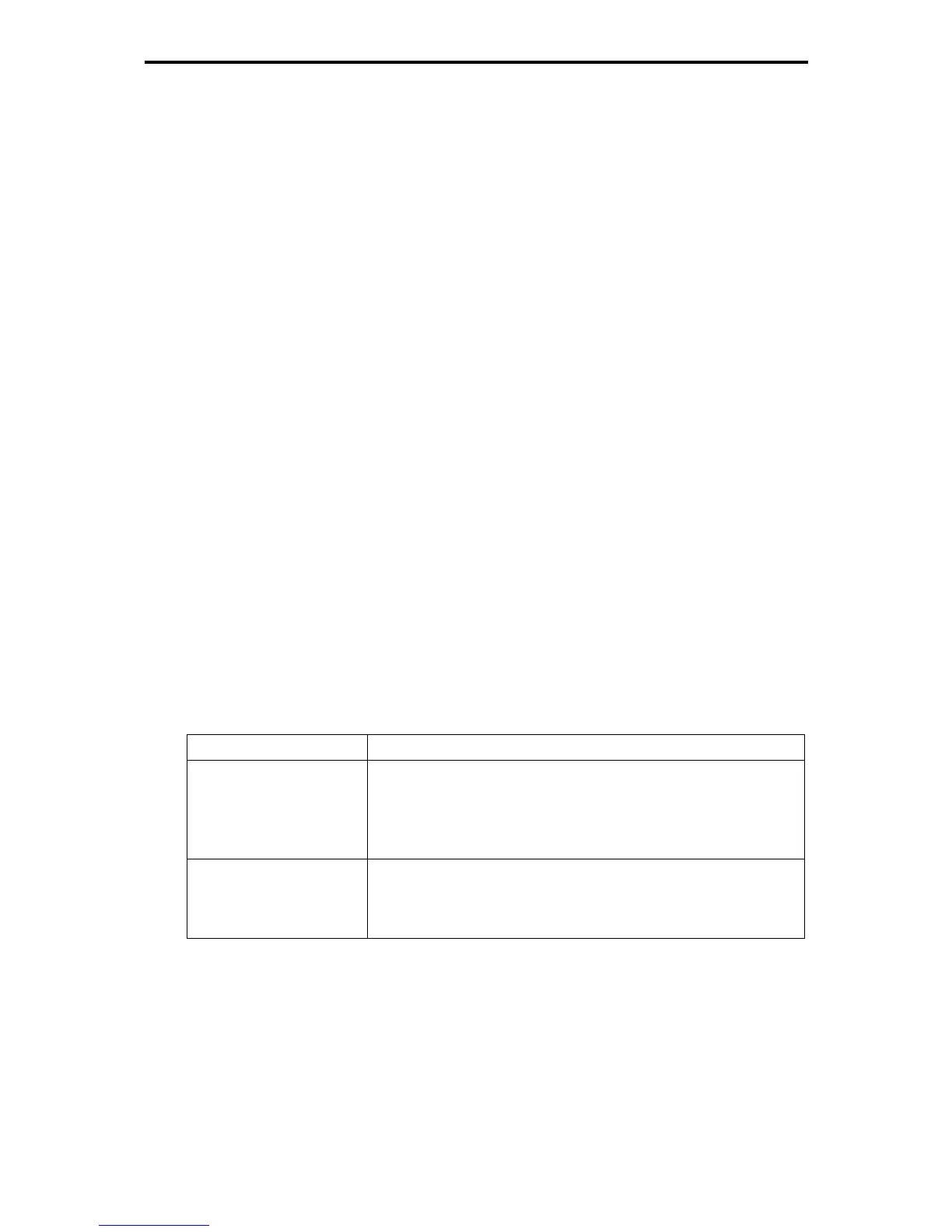
Table 1.6-7
Problem Measures
An earth leakage circuit
breaker (with overcurrent
protection function) that is
connected to the input
(primary) side has tripped.
1) Decrease the carrier frequency.
2) Make the wires between the inverter and motor shorter.
3) Make the current sensitivity of the earth leakage circuit breaker larger.
4) Use an earth leakage circuit breaker that features measures against
the high frequency current component (Fuji SG and EG series).
An external thermal relay
has malfunctioned.
1) Decrease the carrier frequency.
2) Increase the setting current of the thermal relay.
3) Use the electronic thermal overload protection built in the inverter,
instead of the external thermal relay.
Selecting inverter capacity
(1) To drive a general-purpose motor, select an inverter according to the nominal applied motor rating
listed in the standard specifications table. When high starting torque is required or quick acceleration
or deceleration is required, select an inverter with one rank higher capacity than the standard.
(2) Special motors may have larger rated current than general-purpose ones. In such a case, select an
inverter that meets the following condition: Inverter rated current > Motor rated current

 Loading...
Loading...











