App. A Advantageous Use of Inverters (Notes on Electrical Noise)
A-7
App.
(3) Anti-noise devices
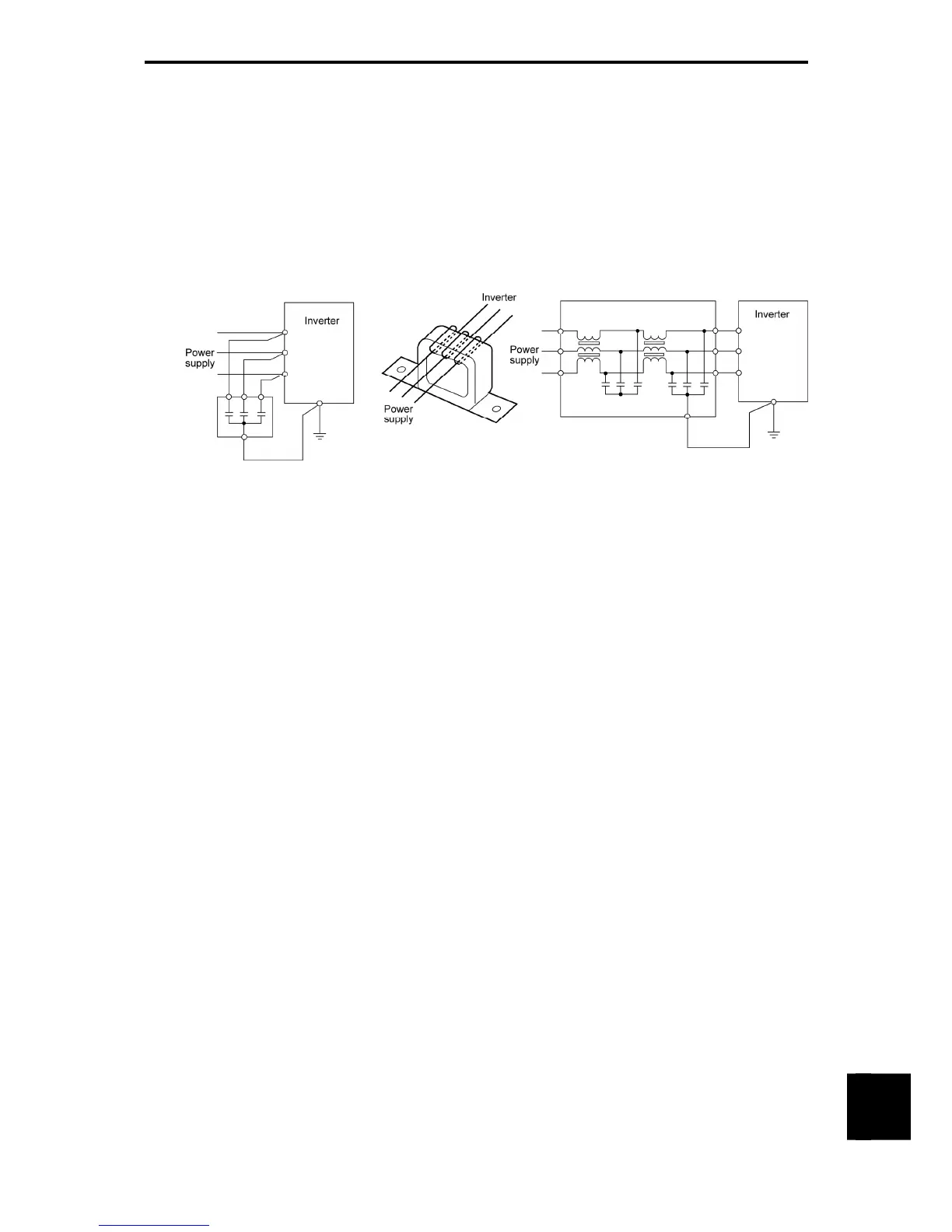
To reduce the noise propagated through the electrical circuits and the noise radiated from the main circuit
wiring to the air, a line filter and insulated transformer should be used (refer to Figure A-10).
Line filters are available in these types; the simplified type such as a capacitive filter to be connected in
parallel to the power supply line and an inductive filter to be connected in series to the power supply line
and the orthodox type such as an LC filter to meet radio noise regulations. Use them according to the
targeted effect for reducing noise. Insulated transformers include general insulated transformers and
shielded transformers, among others, each of which offers a different effect to prevent noise propagation.
(a) Capacitive filter (b) Inductive filter (c) LC filter for input
(Zero-phase reactor)
Figure A-10 Various Filters and their Connection
(4) Noise prevention measures at the receiving side
It is important to strengthen the noise immunity of those electronic devices installed in the same control
panel as the inverter or located near an inverter. Line filters and shielded or twisted shielded wires are used
to block the penetration of noise in the control circuit lines of these devices. The following treatments are
also implemented.
1. Lower the circuit impedance by connecting capacitors or resistors to the input and output terminals of
the signal circuit in parallel.
2. Increase the circuit impedance for noise by inserting choke coils in series in the signal circuit or passing
signal lines through ferrite core beads.
It is also effective to widen the signal base lines (0 V line) or grounding lines.
(5) Others
The level of generating/propagating noise will change with the carrier frequency of the inverter. The higher
the carrier frequency, the higher the noise level.
In an inverter whose carrier frequency can be changed, lowering the carrier frequency can reduce the
generation of electrical noise and result in a good balance with the audible noise of the motor under driving
conditions.

 Loading...
Loading...











