204 IBM z13s Technical Guide
One-way algorithms are not strictly speaking cryptographic functions at all. They do not
use keys, and can only scramble data. They cannot de-scramble it. These algorithms are
used extensively within cryptographic procedures for digital signing and they tend to be
developed and governed by the same principles as cryptographic algorithms. One-way
algorithms are also known as
hash algorithms.
The most prominent one-way algorithms are the Secure Hash Algorithms (SHAs).
6.3 Cryptography on IBM z13s servers
In principle, cryptographic algorithms can run on processor hardware. But these workloads
are compute intensive, and the handling of secure keys also requires special hardware
protection. IBM z Systems offer several cryptographic hardware features that are specialized
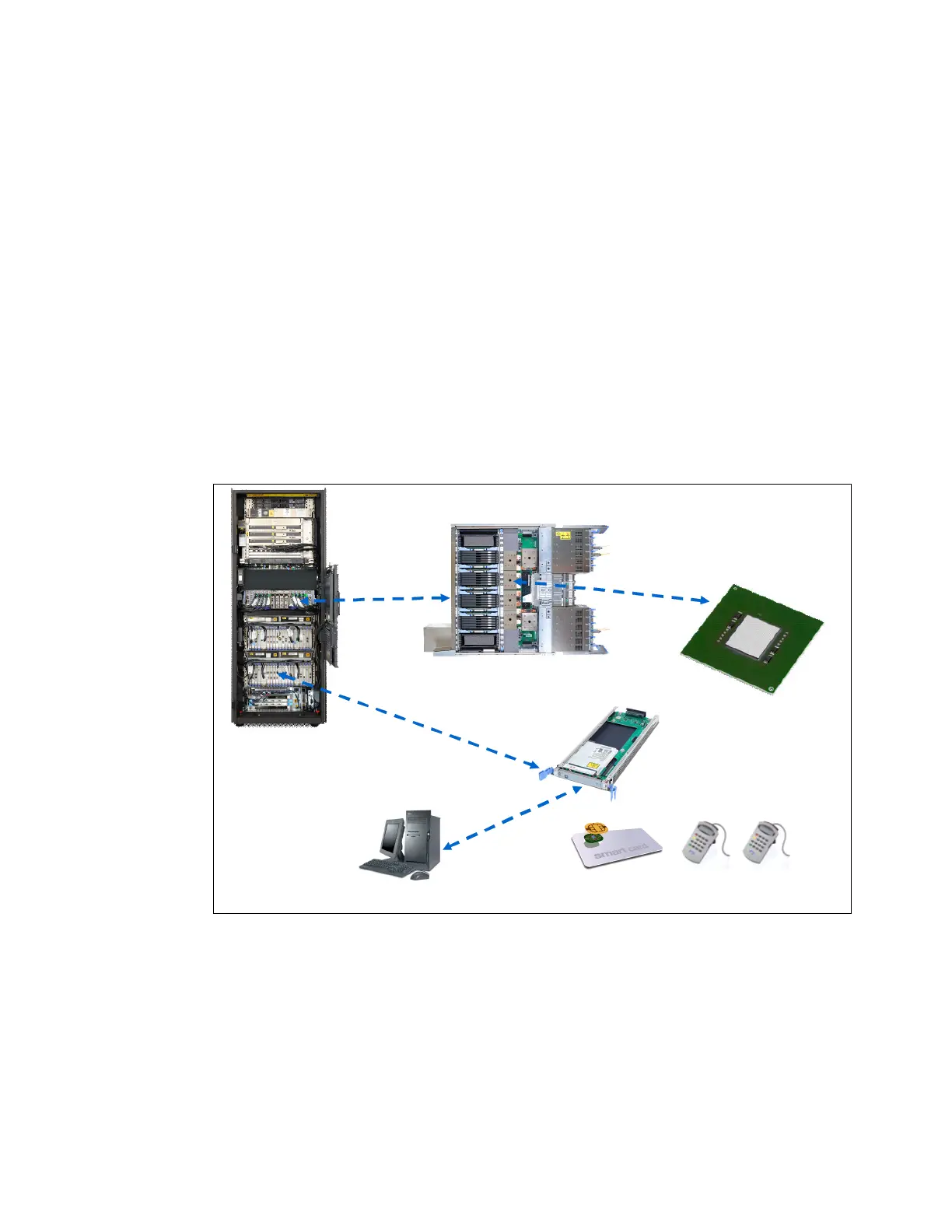
to meet the requirements for cryptographic workloads. Figure 6-2 shows the cryptographic
hardware that is supported on IBM z13s servers, and Table 6-1 on page 205 lists the
corresponding feature codes and describes the purpose of these hardware features. All these
features are described in more detail later in this chapter.
Figure 6-2 Cryptographic hardware supported on IBM z13s servers
Attached to every processor unit (PU) on a single chip module (SCM) in a central processor
complex (CPC) is a cryptographic coprocessor that can be used for cryptographic algorithms
using clear keys or protected keys. For more information, see 6.4, “CP Assist for
Cryptographic Functions” on page 207.
The Crypto Express5S card is an HSM placed in the PCIe I/O drawer of the z13s server. It
also supports cryptographic algorithms by using secret keys. This feature is described in
more detail in 6.5, “Crypto Express5S” on page 211.
CPC Drawer
Smart Cards
Crypto Express5S
Smart Card Readers
PU SCM
Each PU is
capable of
having the
CPACF
function
PCIe I/O
drawers
Trusted Key Entry
(TKE) workstation
TKE recommended for
management
of Crypto Express5S
and required for
EP11 mode

 Loading...
Loading...











