442 IBM z13s Technical Guide
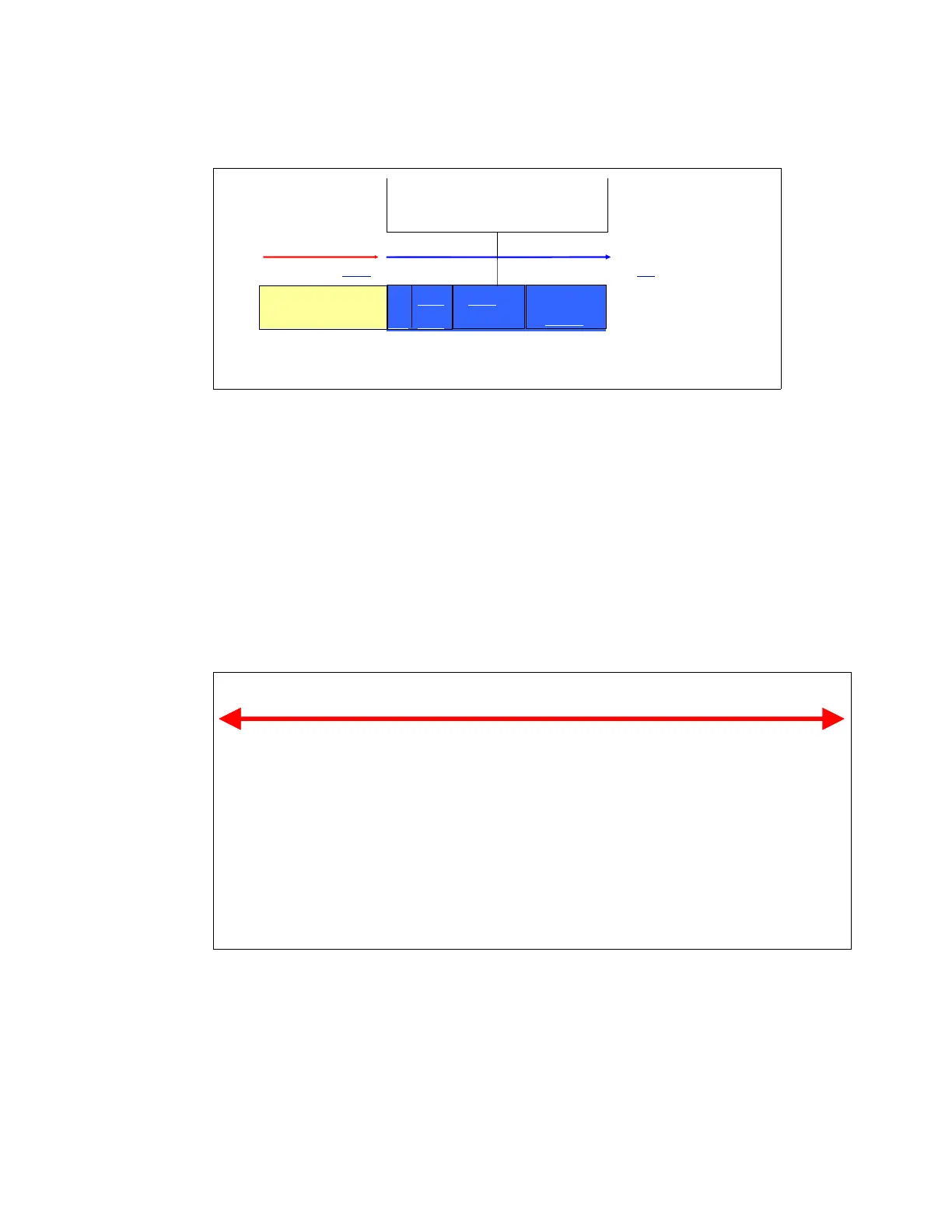
RNI reflects the distribution and latency of sourcing data from shared caches and memory, as
shown in Figure 12-3.
Figure 12-3 Relative Nest Intensity
Many factors influence the performance of a workload. However, usually what these factors
are influencing is the RNI of the workload. The interaction of all these factors results in a net
RNI for the workload, which in turn directly relates to the performance of the workload.
These factors are tendencies rather than absolutes. For example, a workload might have a
low I/O rate, intensive processor use, and a high locality of reference, which all suggest a low
RNI. But it might be competing with many other applications within the same LPAR and many
other LPARs on the processor, which tend to create a higher RNI. It is the net effect of the
interaction of all these factors that determines the RNI.
The traditional factors that were used to categorize workloads in the past are listed along with
their RNI tendency in Figure 12-4.
Figure 12-4 The traditional factors that were used to categorize workloads
Little can be done to affect most of these factors. An application type is whatever is necessary
to do the job. The data reference pattern and processor usage tend to be inherent to the
nature of the application. The LPAR configuration and application mix are mostly a function of
what must be supported on a system. The I/O rate can be influenced somewhat through
buffer pool tuning.
However, one factor,
software configuration tuning, is often overlooked but can have a direct
effect on RNI. This term refers to the number of address spaces (such as CICS
L1
The “Nest”
L2LP
L4LP
L2RP
L4RP
MEMP
Microprocessor Design
Memory Hierarchy or Nest
How Often?
L1MP
How intensely this part of the
architecture is utilized
L3P
RNI
How Far?
Low Relative Nest Intensity High
Batch Application Type Transactional
Low IO Rate High
Single Application Mix Many
Intensive CPU Usage Light
Low Dispatch Rate High
High locality Data Reference Pattern Diverse
Simple LPAR Configuration Complex
Extensive Software Configuration Tuning Limited
Low Relative Nest Intensity High
Batch Application Type Transactional
Low IO Rate High
Single Application Mix Many
Intensive CPU Usage Light
Low Dispatch Rate High
High locality Data Reference Pattern Diverse
Simple LPAR Configuration Complex
Extensive Software Configuration Tuning Limited

 Loading...
Loading...











