Chapter 2. Central processor complex hardware components 55
2.4.2 Redundant array of independent memory
z13s servers use the RAIM technology. The RAIM design detects and recovers from failures
of DRAMs, sockets, memory channels, or DIMMs.
The RAIM design requires the addition of one memory channel that is dedicated for reliability,
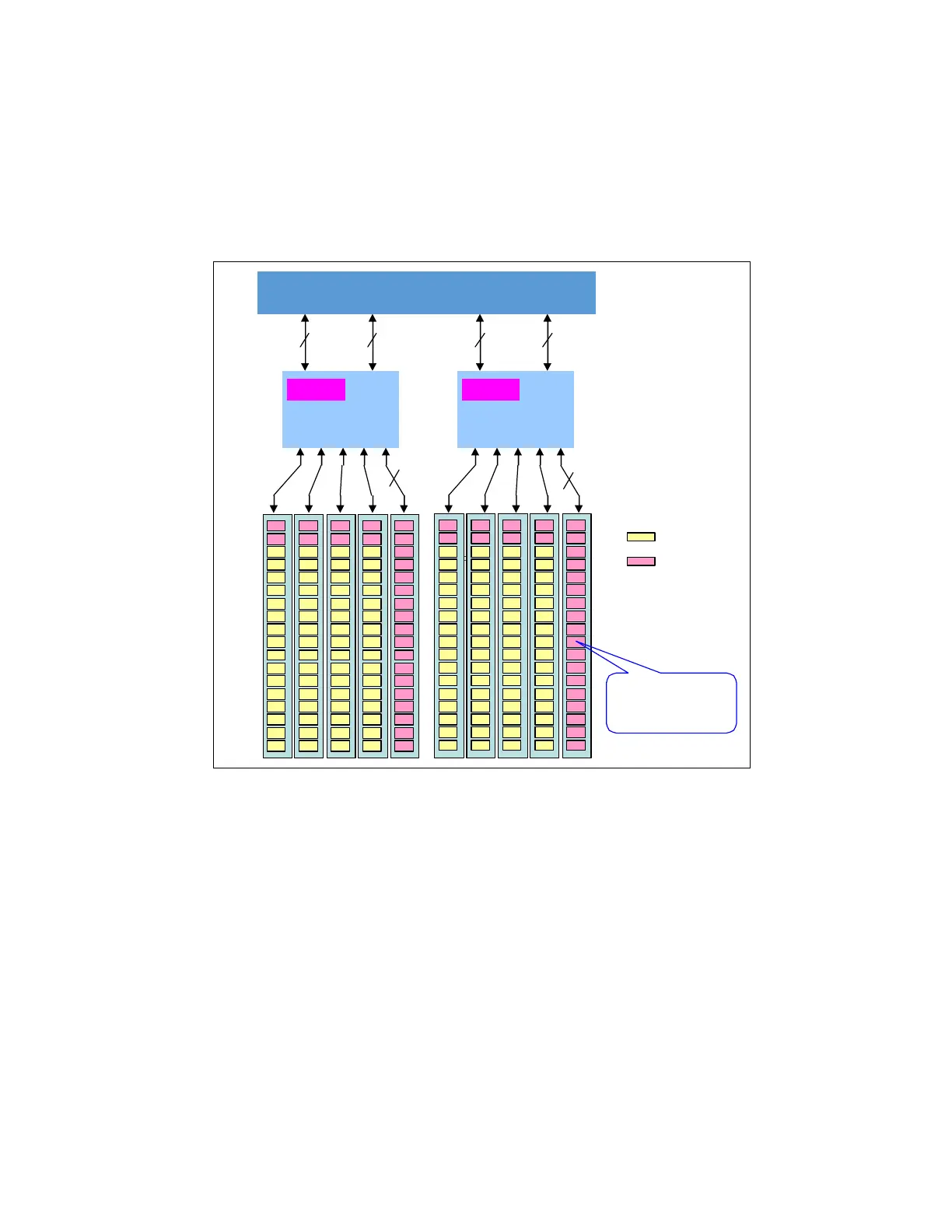
availability, and serviceability (RAS), as shown in Figure 2-18.
Figure 2-18 RAIM configuration per node
The parity of the four “data” DIMMs is stored in the DIMMs that are attached to the fifth
memory channel. Any failure in a memory component can be detected and corrected
dynamically. This system simplifies the memory subsystem design, while maintaining a fully
fault-tolerant RAIM design.
The RAIM design provides the following layers of memory recovery:
ECC with 90B/64B Reed Solomon code.
DRAM failure, with marking technology in which two DRAMs can be marked and no half
sparing is needed. A call for replacement occurs on the third DRAM failure.
Lane failure with CRC retry, data-lane sparing, and clock-RAIM with lane sparing.
DIMM failure with CRC retry, data-lane sparing, and clock-RAIM with lane sparing.
DIMM controller ASIC failure.
Channel failure.
DAT A
CHECK
DATA
CHECK
ECC
RAIM Parity
Level 4 Cache
Key Cache
MCU 0
Key Cache
MCU 1
Extra column
provides RAIM
function
16B
16B
16B
16B
2B
2B

 Loading...
Loading...











