548 IBM z13s Technical Guide
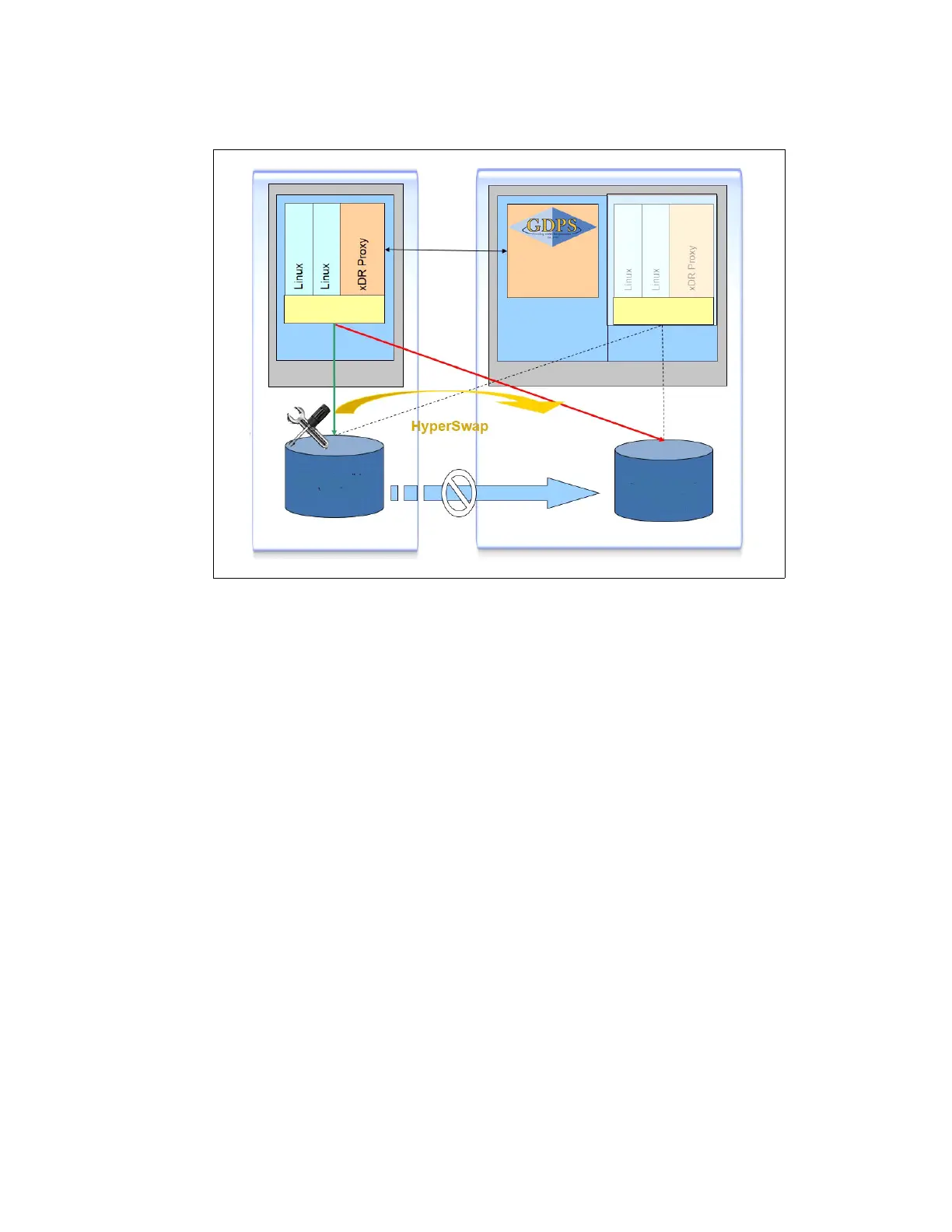
Figure I-4 shows the operation principle of a disk failover operation that uses HyperSwap.
Figure I-4 GDPS Storage failover
Without HyperSwap, the procedure to change the primary disk to the secondary can take up
to 2 hours, or even more, depending on the installation size. The procedures include shutting
down the systems, removing systems from clusters, and when applicable, reversing PPRC
(that is, suspending PPRC), and restarting the systems.
When using HyperSwap, disk swap takes seconds (for example, 6 seconds for 14 systems
and 10,000 volume pairs), and the systems remain active.
I.3.2 Unplanned disk outage
An unplanned HyperSwap is started automatically by GDPS when triggered by events that
indicate the failure of a primary disk device. HyperSwap events can include the following
events:
Hard failure triggers:
– I/O errors
– Boxed devices
– Control unit failures
– Loss of all channel paths
Soft failures, such as I/O response time triggers
Again, without HyperSwap, this process can take more than an hour even when done
properly. The systems are quiesced, removed from the cluster, and restarted on the other
side. With HyperSwap, the same operation can take seconds.
z/VM
z/VM
GDPS
Appliance
PPRC
z Systems z Systems
LPAR
LPAR
LPAR
z/VM + Linux
disks
(primary)
z/VM + Linux
disks
(secondary)
Site 1
Site 2

 Loading...
Loading...











