Power Supply Specification Guidelines Intel® Server Board S2600CW Family TPS
126 Revision 2.4
10.2.2.4 AC Line Dropout/Holdup
An AC line dropout is defined as that when the AC input drops to 0VAC at any phase of the AC
line for any length of time. During an AC dropout, the power supply meets dynamic voltage
regulation requirements. An AC line dropout of any duration does not cause tripping of
control signals or protection circuits. If the AC dropout lasts longer than the holdup time, the
power supply recovers and meets all turn on requirements. The power supply meets the AC
dropout requirement over rated AC voltages and frequencies. A dropout of the AC line for any
duration does not cause damage to the power supply.
Table 46. AC Line Holdup Time
10.2.2.4.1 AC Line 12VSB Holdup
The 12VSB output voltage stays in regulation under its full load (static or dynamic) during an
AC dropout of 70ms min (=12VSB holdup time) whether the power supply is in ON or OFF
state (PSON asserted or de-asserted).
10.2.2.5 AC Line Fuse
The power supply has one line fused in the single line fuse on the line (Hot) wire of the AC
input. The line fusing is acceptable for all safety agency requirements. The input is a slow blow
type. AC inrush current does not cause the AC line fuse to blow under any conditions. All
protection circuits in the power supply does not cause the AC fuse to blow unless a
component in the power supply has failed. This includes DC output load short conditions.
10.2.2.6 AC Line Transient Specification
AC line transient conditions are defined as “sag” and “surge” conditions. “Sag” conditions are
also commonly referred to as “brownout”; these conditions are defined as the AC line voltage
drops below nominal voltage conditions. “Surge” is defined to refer to conditions when the AC
line voltage rises above nominal voltage.
The power supply meets the requirements under the following AC line sag and surge
conditions.
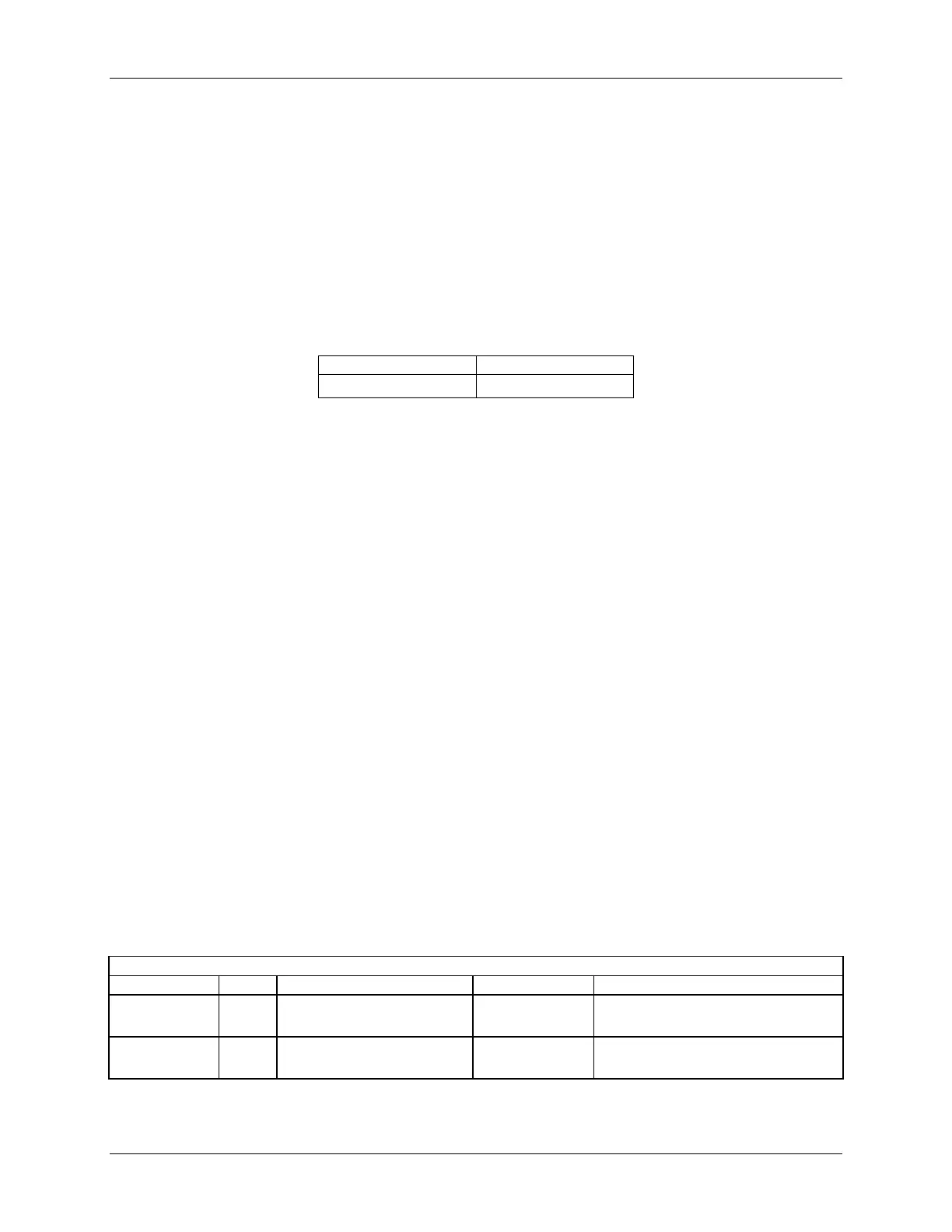
Table 47. AC Line Sag Transient Performance
AC Line Sag (10sec interval between each sagging)
cycle
Nominal AC Voltage ranges
No loss of function or performance
Nominal AC Voltage ranges
Loss of function acceptable, self
recoverable

 Loading...
Loading...