Intel® Server Board S2600CW Functional Architecture Intel® Server Board S2600CW Family TPS
26 Revision 2.4
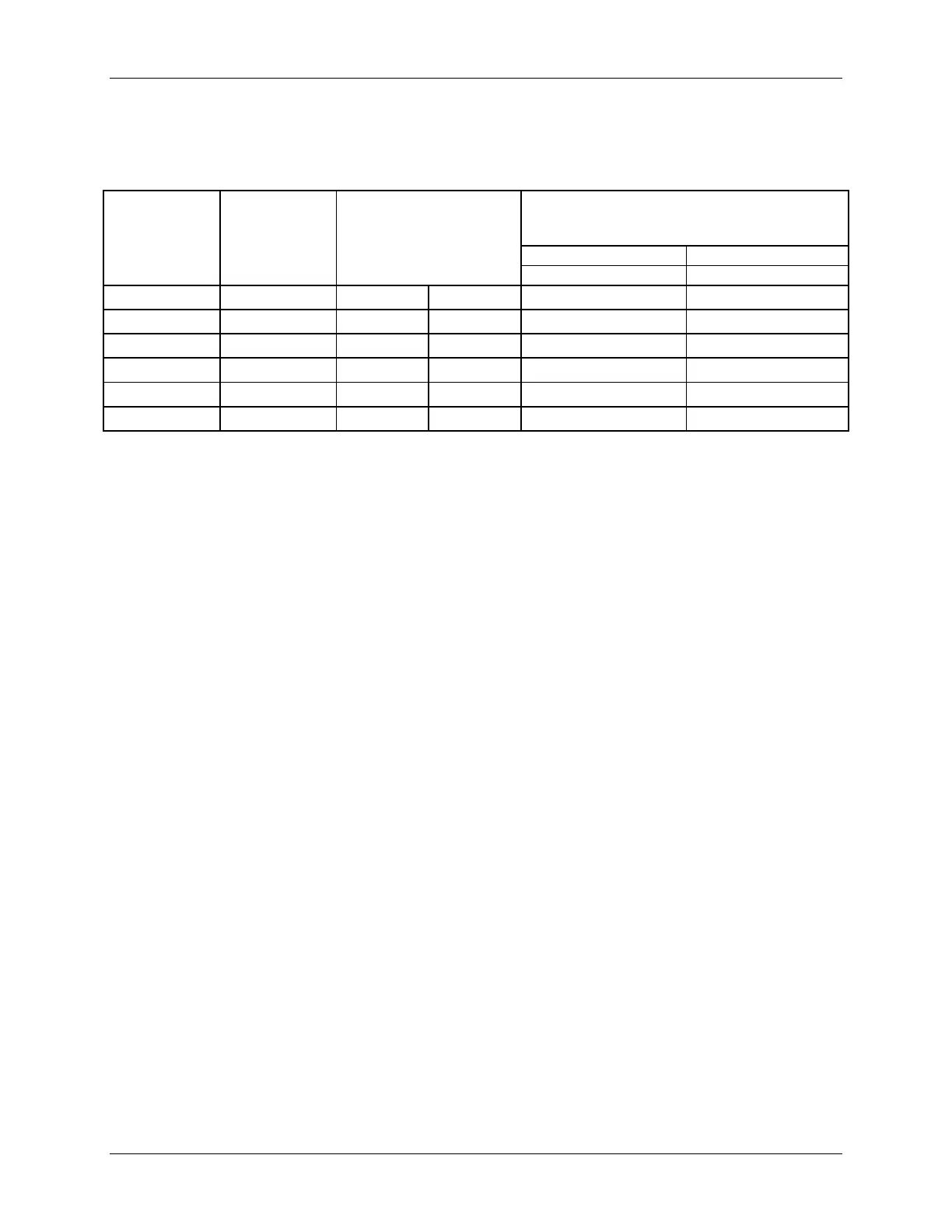
Table 4. DDR4 RDIMM & LRDIMM Support with Intel Xeon E5-2600 V4
Ranks Per
DIMM and Data
Width
Speed (MT/s) and Voltage Validated by
Slot per Channel (SPC) and DIMM Per Channel
(DPC)
3.3.2 Memory Population Rules
Each installed processor provides four channels of memory. On the Intel
®
Server Board
S2600CW each memory channel supports two memory slots, for a total possible 16
DIMMs installed.
System memory is organized into physical slots on DDR4 memory channels that
belong to processor sockets.
The memory channels from processor socket 1 are identified as Channel A, B, C and D.
The memory channels from processor socket 2 are identified as Channel E, F, G and H.
Each memory slot on the server board is identified by channel, and slot number within
that channel. For example, DIMM_A1 is the first slot on Channel A on processor 1;
DIMM_E1 is the first DIMM socket on Channel E on processor 2.
The memory slots associated with a given processor are unavailable if the
corresponding processor socket is not populated.
A processor may be installed without populating the associated memory slots
provided a second processor is installed with associated memory. In this case, the
memory is shared by the processors. However, the platform suffers performance
degradation and latency due to the remote memory.
Processor sockets are self-contained and autonomous. However, all memory
subsystem support (such as Memory RAS and Error Management) in the BIOS setup is
applied commonly across processor sockets.
The BLUE memory slots on the server board identify the first memory slot for a given
memory channel.
DIMM population rules require that DIMMs within a channel be populated starting with the
BLUE DIMM slot or DIMM farthest from the processor in a “fill-farthest” approach. In addition,
 Loading...
Loading...