I-26 Applications Guide Model 6485 Picoammeter Instruction Manual
The function of the detector is to develop a secondary current proportional to the current
of the primary ion beam, without interfering with the primary beam. The basic operation
of most detectors is similar; an ion from the primary beam strikes the detector and a sec-
ondary ion is generated, isolated from the primary ion stream. This current is then mea-
sured and used to control the intensity of the beam.
The secondary currents generated by the detectors are very low, and require a high degree
of accuracy and measurement repeatability. Currents as low as 5 or 6pA are not uncom-
mon; therefore, the measurement device must be capable of achieving resolutions below
1pA.
The Keithley Model 6485 Picoammeter is ideal for this application because it offers a
wide selection of range settings spanning from 20mA to 2nA. This will result in 5-1/2
digit resolution ranging from 100nA to 10fA. Numerous ranges, and fine measurement
granularity, will meet all current requirements for this application, as well as provide addi-
tional sensitivity for future development needs.
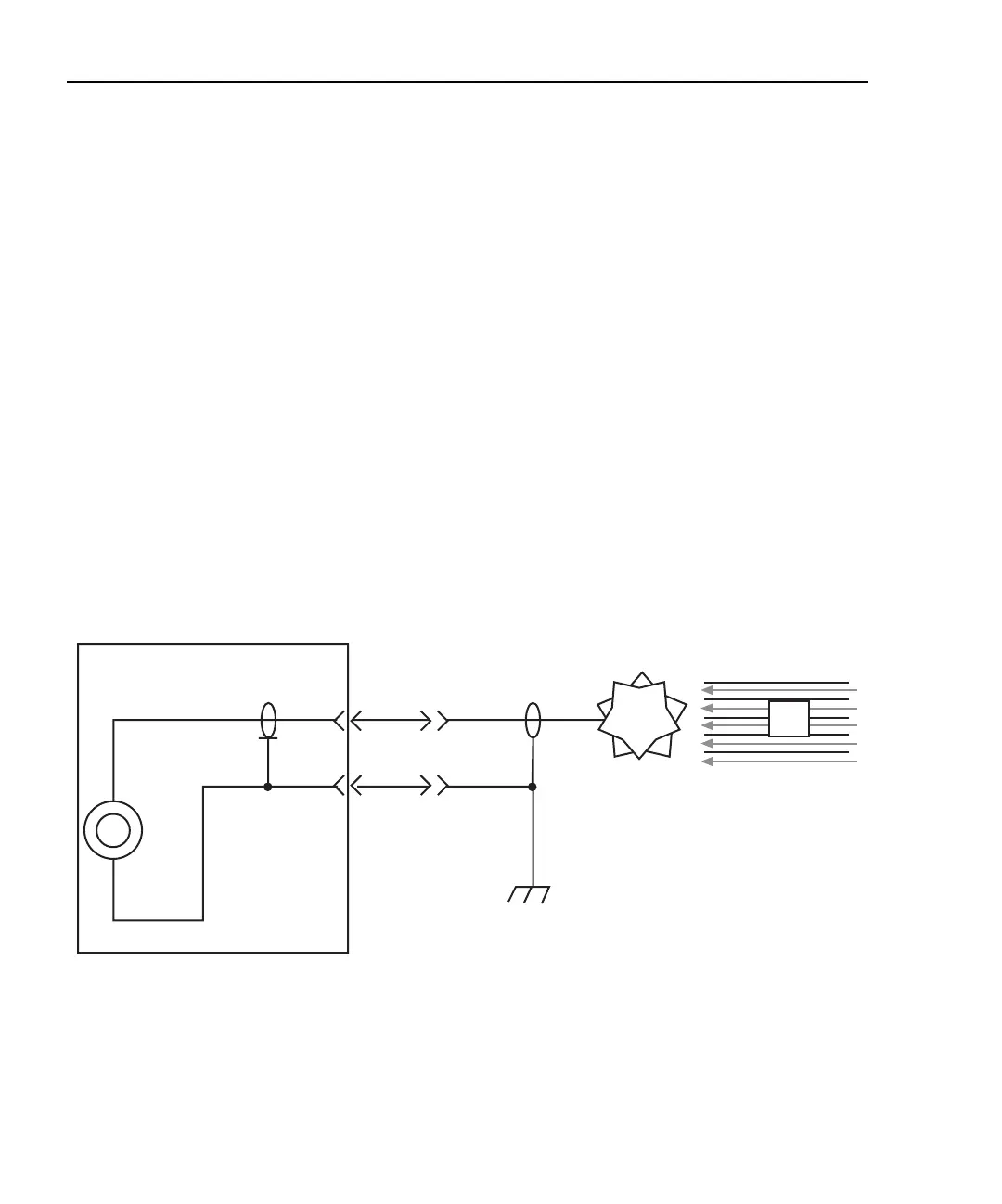
Signal connections to the picoammeter are made using the BNC connector mounted on the
rear panel. If the source on the ions is biased off ground, then the ion detector will most
likely be at ground potential. A simple coaxial vacuum feedthrough can be used to make
the connection between the detector and the picoammeter. See Figure I-24.
Figure I-24
Focused Ion Beam signal connections
Using switching systems to measure multiple current sources
Refer to “External trigger example,” page 7-13.
6485
Picoammeter
Ion
Detector
Ion
Beam
I
m
Coaxial Vacuum
Feedthrough

 Loading...
Loading...