255
CHAPTER 5 DEVICES
5
5.5 Index Register/Standard Device Register (Z)
5.5.1 Index Register (Z)
5.5 Index Register/Standard Device Register (Z)
5.5.1 Index Register (Z)
The index register is used for indirect specification (index modification) in programs. Index modification uses one point
of the index register.
The index register has 20 points (Z0 to Z19).
(1) Bit structure of the index register
One point of the index register consists of 16 bits, and data can be read or written in units of 16 bits.
Link register data are handled as signed data. In the case of the hexadecimal notation, 0000
H
to FFFF
H
can be stored.
However, because the most significant bit represents a sign bit, decimal values that can be specified are -32768 to 32767.
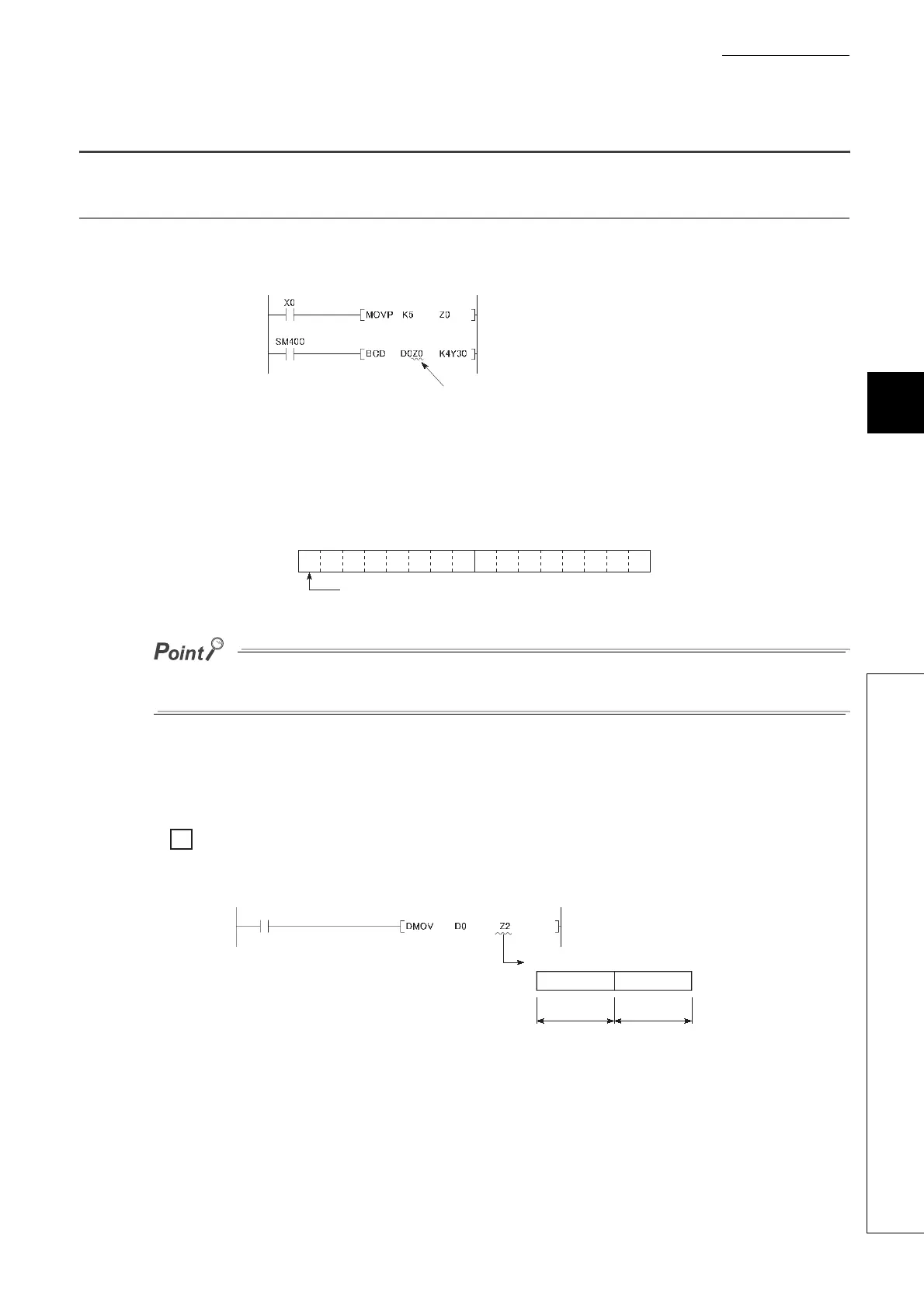
(2) Using in a 32-bit instruction
The processing target is Z
n
and Z
n+1
. The lower 16 bits correspond to the specified index register number (Z
n
),
and the higher 16 bits correspond to the specified index register number + 1.
When Z2 is specified in the DMOV instruction, Z2 represents the lower 16 bits and Z3 represents the
higher 16 bits.
(The most significant bit in a 32-bit structure is a sign bit.)
Specify the index register by one point
(16 bits).
Zn
b15
to
b0
The most significant bit is a sign bit.
Ex.
Ex.
Z3
Lower 16 bits Upper 16 bits
Z2
Processing target: Z2, Z3

 Loading...
Loading...











