7.1.6 Simple learning function
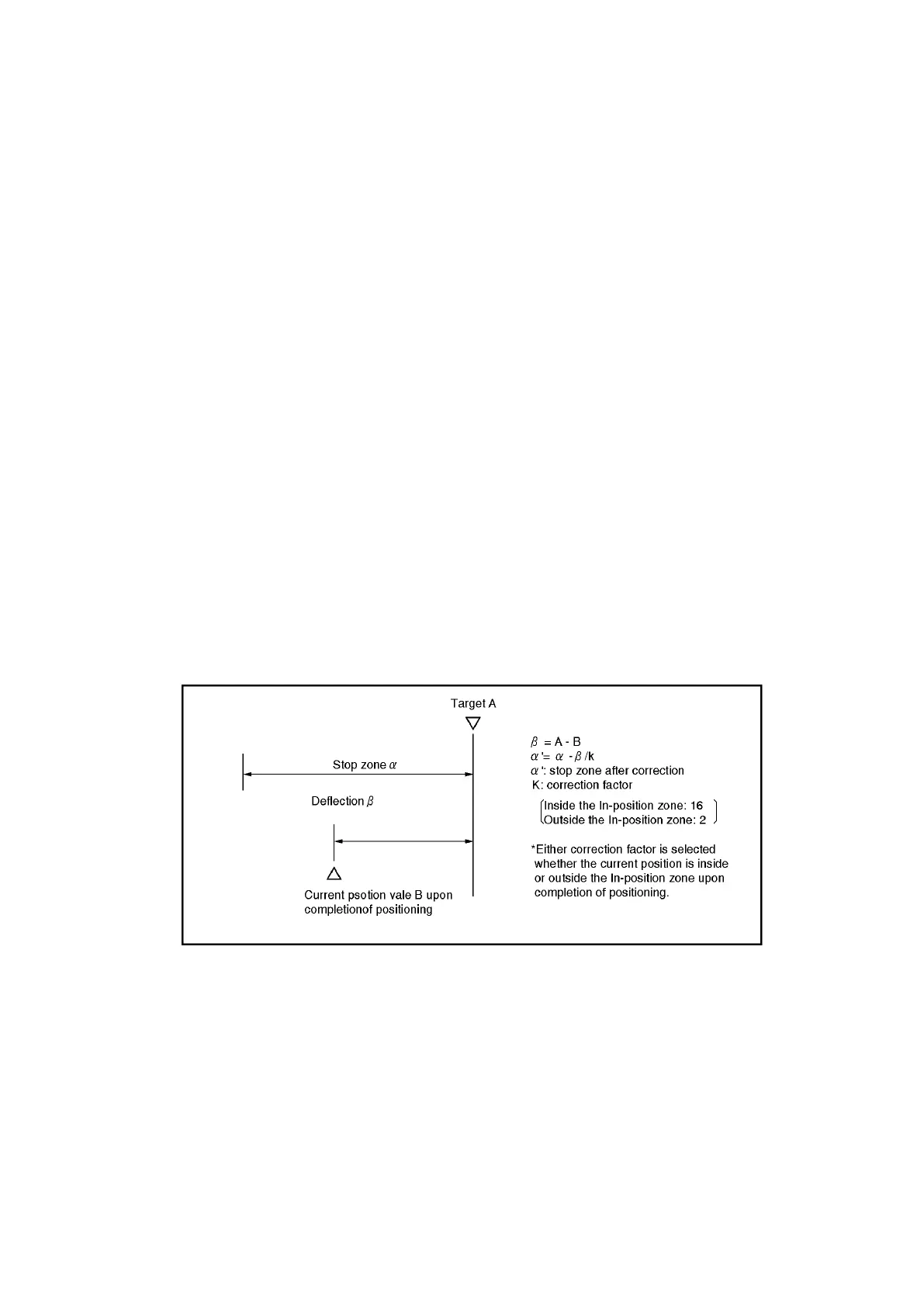
If a positional discrepancy occurs between the target position and the current position upon completion
of positioning, the discrepancy will be automatically corrected when the next positioning is carried out.
At this time, either the FWD stop zone or RVS stop zone is corrected depending on the positioning
direction. (The stop zone is not corrected when the positioning operation is started from inside the
travel amount which is executed by the ‘START from stop zone’ operation.)
This improves positioning repeatability and minimizes overrun. An error will occur when the stop
zone is not within the specified range upon completion of positioning.
Improved positioning due to this simple learning function is explained below.
(1) Setting the ‘stop zone’ parameter becomes easier.
The ‘stop zone’ parameter was conventionally set based on the predicated value. When using
the simple learning function, the stop zone is automatically corrected by simply setting any value
and repeating operation.
(2) ‘Stop zone’ does not need to be manually corrected as the brake becomes worn.
‘Stop zone’ is automatically corrected even for change in amount of brake slide due to wear.
(3) ‘Stop zone’ is not affected by load variation.
Load may vary due to travel in the reverse direction, such as the machine’s up/down motion and
trolley’s advance and retract motion. For the VS-212DN, two ‘stop zones’ are provided; one for
the FWD (forward) direction and one for the RVS (reverse) direction. Therefore, the simple
learning function effectively works even for load variation.
Note:
When power supply is interrupted, the learned stop zone is stored in the internal memory and
restored in the buffer memory when power is supplied next.
 Loading...
Loading...