Troubleshooting – ZP Oxygen Analyzer Troubleshooting 5-89
FlexFit – Linkageless Control – Revision 1.0
PREFERRED
UTILITIES MFG CORPORATION
TT
RR
OO
UU
BB
LL
EE
SS
HH
OO
OO
TT
II
NN
GG
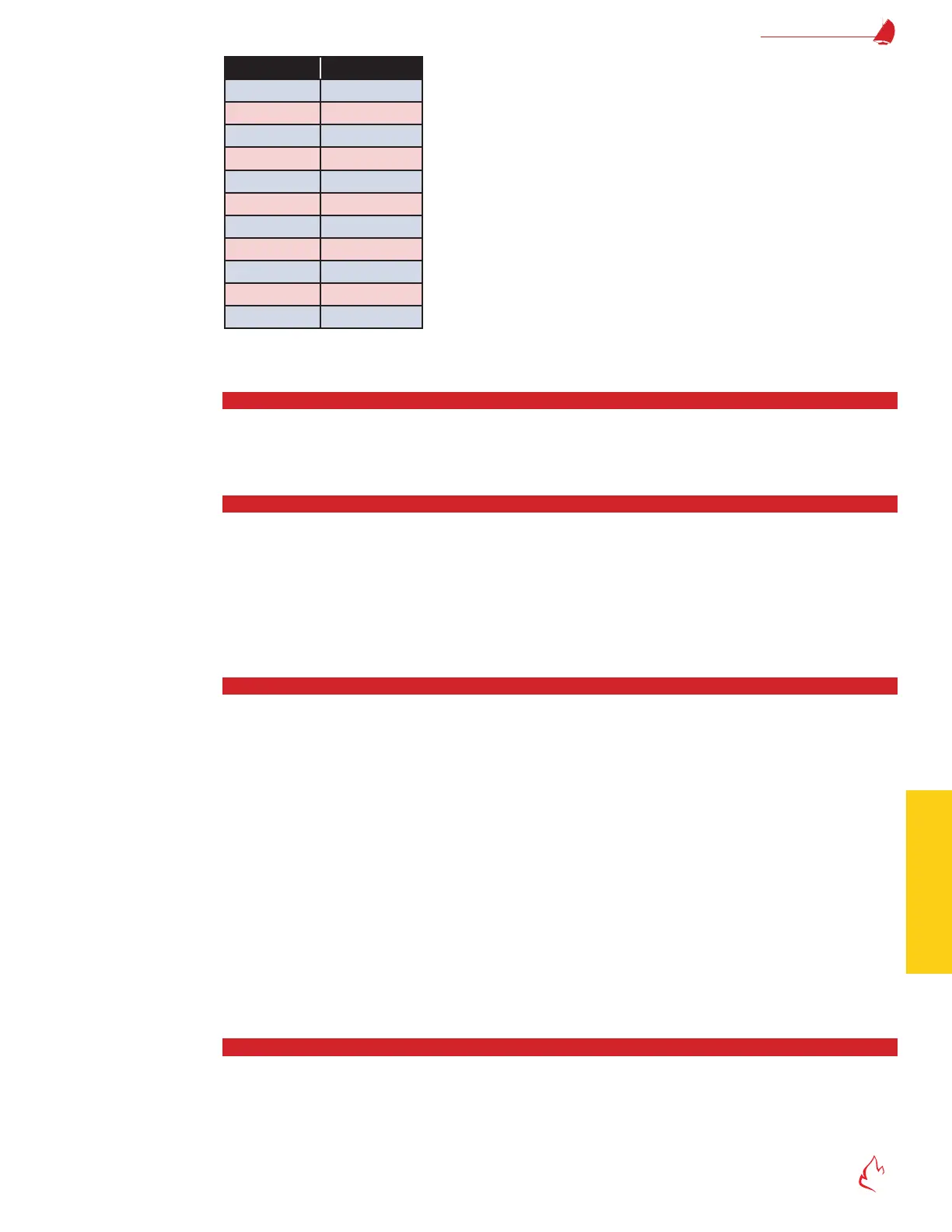
% Oxygen Cell mV
16.0 5.569
17.0 4.233
18.0 2.973
19.0 1.782
20.0 0.651
20.6 0.0
21.0 -0.4238
22.0 -1.449
23.0 -2.428
24.0 -3.366
25.0 -4.266
Table 5 – 3 Cell mV Vs. % Oxygen
Slow Response Time
• Check for excessive dirt on the detector lter or inside the probe.
• As the cell approaches the end of its life, the cell impedance increases toward 1100 ohms, and the cell response time
becomes longer.
Reading is Lower than Expected
• See "ZP Wet Measurement Vs. Dry Measurement".
• Check for CO or combustibles in the ue gas. CO or combustibles will oxidize on the internal surface of the cell. This
consumes the oxygen locally within the detector and causes a low reading.
• Check with certied calibration gas.
• Check to see if the lter is dirty or blocked.
• Check for detector leaks.
Reading is Higher than Expected
It is important to remember that the cell makes a differential measurement. That is, the cell compares the unknown oxygen
percentage in the ue gas against the known oxygen percentage in the ambient air inside the cell. Ambient air is typically 20.6%
oxygen; however, it can range from 19.5% to 20.9% as relative humidity and temperature change.
If the ue gas duct is pressurized and a duct leak allows ue gas to enter the detector head, the ambient oxygen percentage
can be substantially lower. Combustible gases in the ambient air will consume the oxygen on the surface of the cell and will lower the
percent oxygen in the ambient air inside the cell. If the ambient oxygen percentage inside the cell is low, a zirconia cell will sense a
lower differential and will cause the analyzer to indicate a higher oxygen level than is in the ue gas.
If the ceramic cell is dropped and cracks, the measured ue gas and ambient air will intermingle, and the oxygen percentage
on both sides of the cell will equalize. A zirconia cell will sense a lower differential and will cause the analyzer to indicate a higher
oxygen level than is in the ue gas.
• See "ZP Wet Measurement Vs. Dry Measurement".
• Check with certied calibration gas.
• Verify that the calibration gas port and tubing are plugged or closed during operation to prevent inltration of air.
• Check to see if the lter is dirty or blocked.
• Check for detector leaks.
• Check the AC line voltage; it must be 60 Hz and greater than 102 volts.
• Check the AC line voltage for excessive electrical noise.
 Loading...
Loading...