CRC Calculation Circuit
M30240 Group
Rev.1.00 Sep 24, 2003 Page 264 of 360
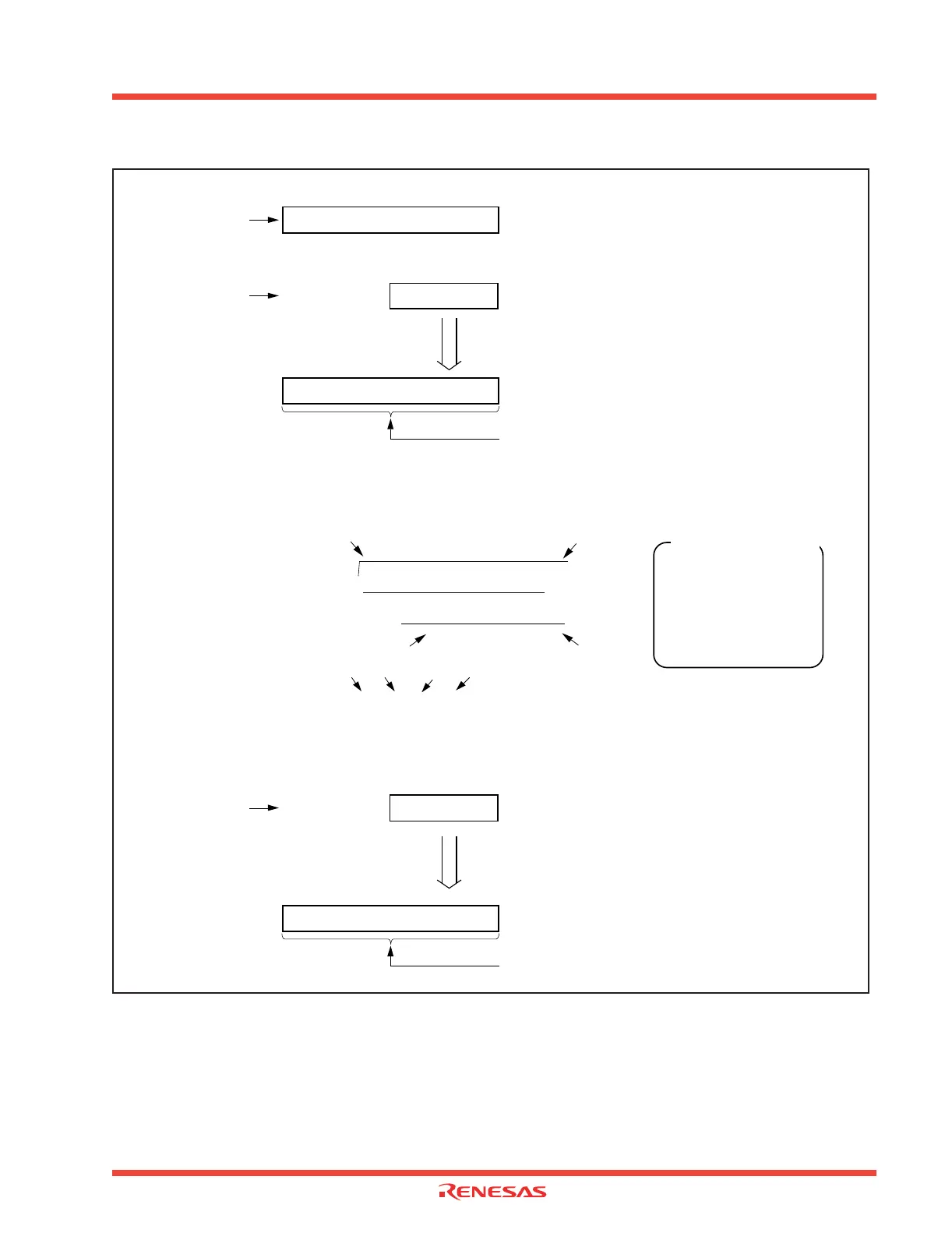
Figure 2.109: Operation of CRC Calculation Circuit
b15 b0
(1) Setting 000016
CRC data register CRCD
[03BD
16, 03BC16]
b0b7
b15
b0
(2) Setting 0116
CRC input register CRCIN
[03BE
16]
2 cycles
After CRC calculation is complete
CRC data register CRCD
[03BD
16, 03BC16]
1189
16
Stores CRC code
b0b7
b15 b0
(3) Setting 2316
CRC input register CRCIN
[03BE
16]
After CRC calculation is complete
CRC data register CRCD
[03BD
16, 03BC16]
0A41
16
Stores CRC code
The code resulting from sending 01
16 in LSB first mode is (1000 0000). Thus the CRC code in the generating polynomial,
(X
16
+ X
12
+ X
5
+ 1), becomes the remainder resulting from dividing (1000 0000) X
16
by (1 0001 0000 0010 0001) in
conformity with the modulo-2 operation.
Thus the CRC code becomes (1001 0001 1000 1000). Since the operation is in LSB first mode, the (1001 0001 1000 1000)
corresponds to 1189
16 in hexadecimal notation. If the CRC operation in MSB first mode is necessary in the CRC operation
circuit built in the M16C, switch between the LSB side and the MSB side of the input-holding bits, and carry out the CRC
operation. Also switch between the MSB and LSB of the result as stored in CRC data.
1 0001 0000 0010 0001
1000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
1000 1000 0001 0000 1
1000 0001 0000 1000 0
1000 1000 0001 0000 1
1001 0001 1000 1000
1000 1000
LSB
MSB
LSB MSB
98 1 1
Modulo-2 operation is
operation that complies
with the law given below.
0 + 0 = 0
0 + 1 = 1
1 + 0 = 1
1 + 1 = 0
-1 = 1

 Loading...
Loading...











