A-D Converter
M30240 Group
Rev.1.00 Sep 24, 2003 Page 250 of 360
2.6.5 A-D Converter Errors
2.6.5.1 Absolute accuracy
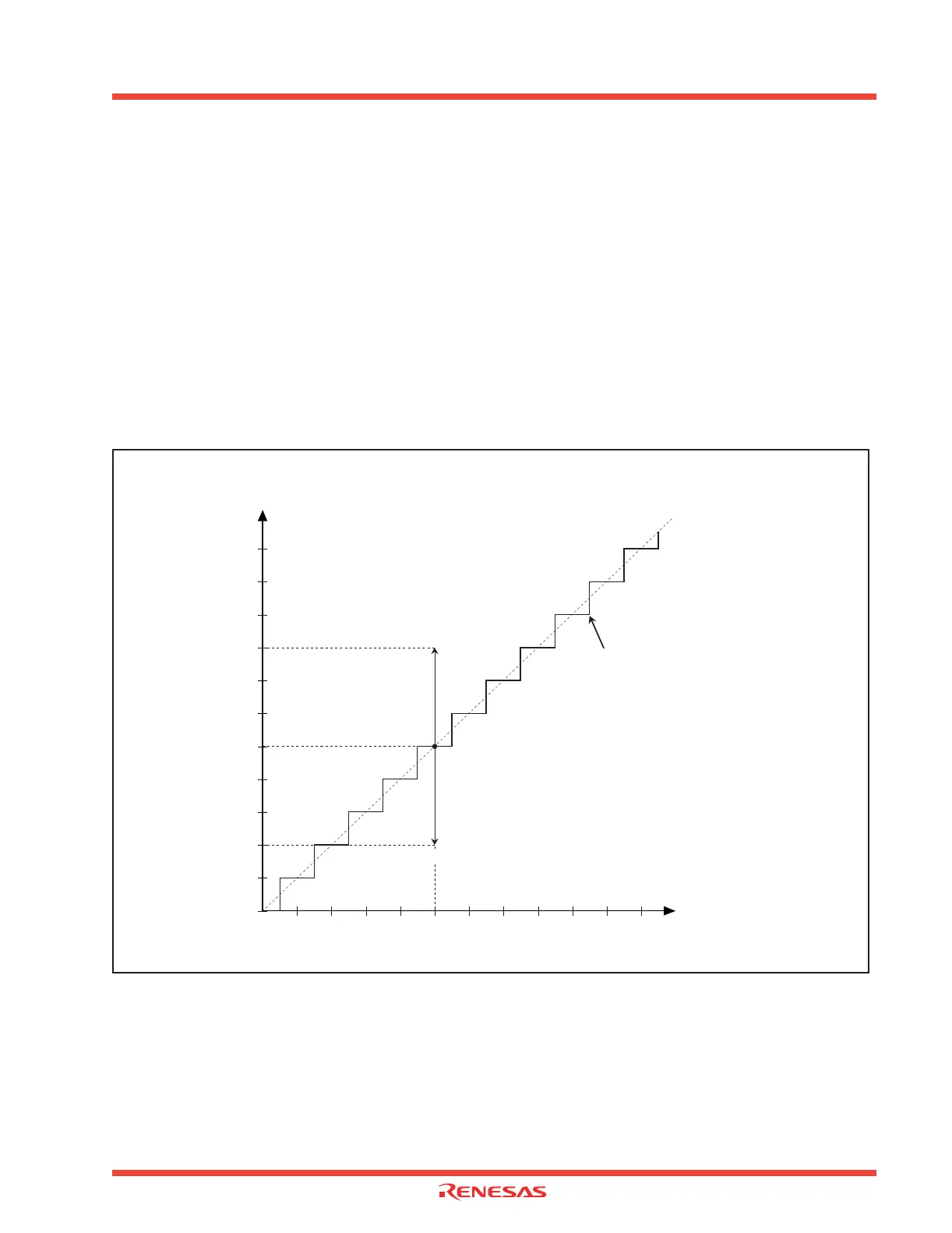
Absolute accuracy is the difference between output code based on the theoretical A-D conversion
characteristics, and actual A-D conversion result. When measuring absolute accuracy, the voltage at
the middle point of the width of analog input voltage (1-LSB width), that can meet the expectation of
outputting an equal code based on the theoretical A-D conversion characteristics, is used as an analog
input voltage. For example, if 10-bit resolution is used and if VREF (reference voltage) = 5.12 V, then 1-
LSB width becomes 5 mV, and 0 mV, 5 mV, 10 mV, 15 mV, 20 mV, etc. are used as analog input
voltages. See Figure 2.96. If analog input voltage is 25 mV, "absolute accuracy = ± 3LSB” refers to the
fact that actual A-D conversion falls on a range from 002
16
to 008
16
though an output code, 005
16
, can
be expected from the theoretical A-D conversion characteristics. Zero error and full-scale error are
included in absolute accuracy.
Also, all the output codes for analog input voltage between V
REF and AVcc becomes “3FF
16
”.
Figure 2.96: Absolute accuracy (10-bit resolution)
000
16
001
16
002
16
003
16
004
16
005
16
006
16
0
Analog input voltage (mV)
Theoretical A-D conversion
characteristic
510152025303540455055
007
16
008
16
009
16
00A
16
00B
16
+3LSB
–3LSB
Output code
result of A-D conversion)

 Loading...
Loading...











