Watchdog Timer
M30240 Group
Rev.1.00 Sep 24, 2003 Page 265 of 360
2.9 Watchdog Timer
2.9.1 Overview
The Watchdog timer can detect a runaway program using its 15-bit timer prescaler. The following is an
overview of the Watchdog timer.
2.9.1.1 Start procedure
After reset, the Watchdog timer is stopped. Writing to the Watchdog timer start register initializes the
Watchdog timer to 7FFF
16
and causes it to start performing a down count. The Watchdog timer, once
started operating, cannot be stopped by any means other than the stop conditions shown below.
2.9.1.2 Stop conditions
The Watchdog timer stops in any one of the following states:
(a) Period in which the CPU is in a stopped state
(b) Period in which the CPU is in a waiting state
2.9.1.3 Initialization
The Watchdog timer is initialized to 7FFF
16
and begins a down count in the cases given below.
(a) When the Watchdog timer writes to the Watchdog timer start register while a count is in progress
(b) When the Watchdog timer underflows
2.9.1.4 Runaway detection
When the Watchdog timer underflows, a Watchdog timer interrupt occurs. In writing a program, write to
the Watchdog timer start register before the Watchdog timer underflows. The Watchdog timer interrupt
occurs regardless of the status of the interrupt enable flag (I flag). In processing a Watchdog timer
interrupt, set the software reset bit to “1” to reset software.
2.9.1.5 Cycle
The Watchdog timer cycle varies depending on the internal clock Φ and the frequency division ratio of
the prescaler selected. See Table 2.39.
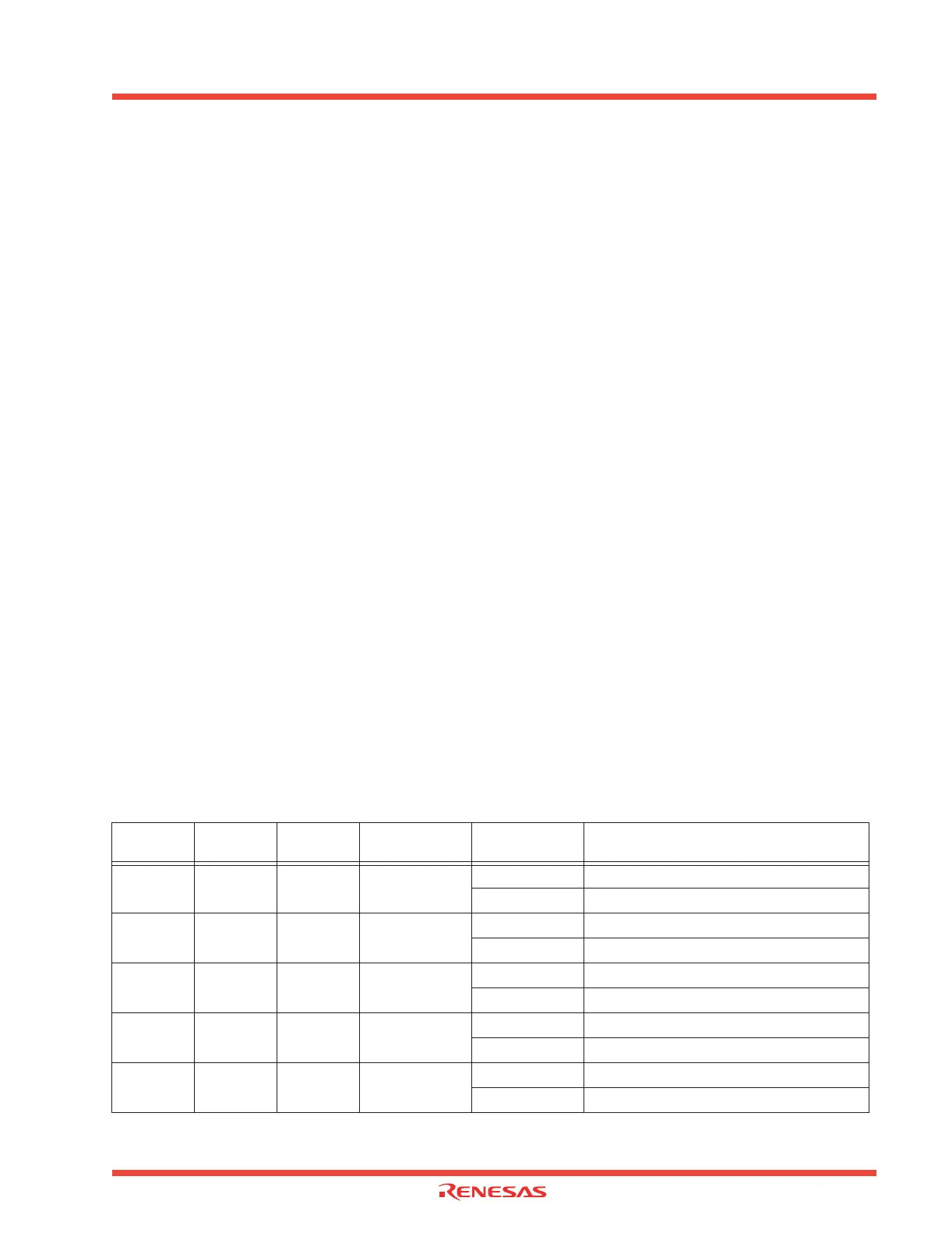
Table 2.41: Watchdog timer periodic table f(X
IN) = 12MHz
CM06 CM17 CM16
Internal
clock Φ
WDC7 Period
0 0 0 12MHz
0 Approx. 43.7ms
1 Approx. 349.5ms
0016MHz
0 Approx. 87.4ms
1 Approx. 699.1ms
0103MHz
0 Approx. 174.8ms
1 Approx. 1.40s
0 1 1 0.75MHz
0 Approx. 699.1ms
1 Approx. 5.59s
1 Invalid Invalid 1.5MHz
0 Approx. 349.5ms
1 Approx. 2.80s

 Loading...
Loading...











