Reset
M30240 Group
Rev.1.00 Sep 24, 2003 Page 21 of 360
1.2.5 Reset
There are two types of resets: hardware and software. In both cases, operation is the same after the
reset.
1.2.5.1 Hardware reset
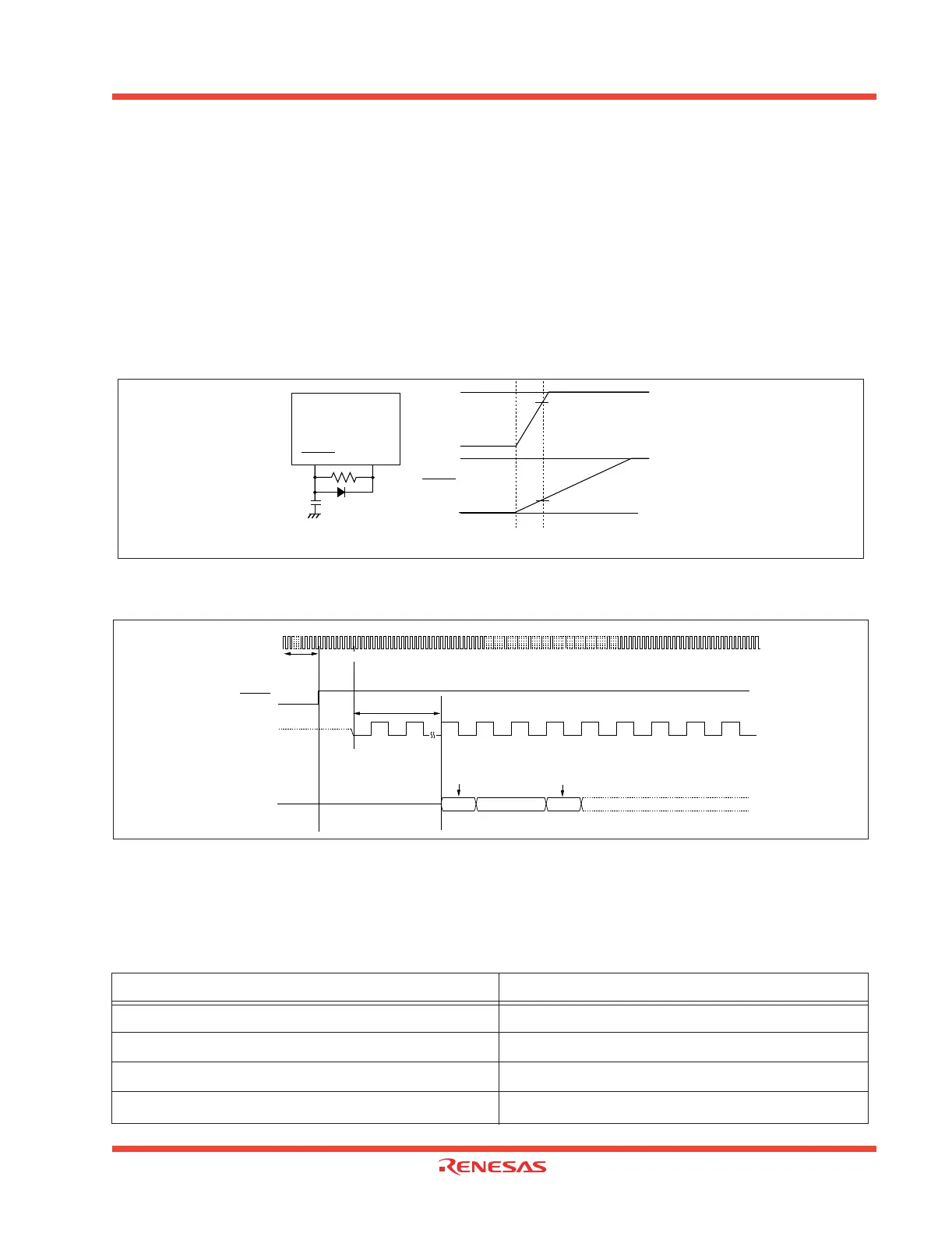
When the supply voltage is within the range where operation is guaranteed, a reset is effected by hold-
ing the reset pin level “L” (0.2Vcc max.) for at least 20 f(X
IN) cycles. When the reset pin level is then
returned to the “H” level while main clock is stable, the reset status is cancelled and program execution
resumes from the address in the reset vector table.
Figure 1.9 shows an example of a reset circuit. Figure 1.10 shows the reset sequence.
.
Figure 1.9: Reset circuit
Figure 1.10: Reset sequence
When the RESET pin level = “L”, all ports change to input mode (floating.) Table 1.4 shows the status
of the other pins while the RESET pin level is “L”.
Table 1.4: Pin status when RESET pin level is “L”
Pin name Status
P0 Input port (floating)
P1 Input port (floating)
P2, P3 Input port (floating)
P6, P7, P8
0
to P8
4
, P8
6
, P8
7
, P10
Input port (floating)
RESET
V
CC
0.8V
RESET
V
CC
0V
0V
5V
5V
4.0V
Example when V
CC
= 5V
Address
Content of reset vector
Internal clock Φ
24 cycles
FFFFE
16
X
IN
RESET
FFFFC
16
At least 20 cycles are needed
Internal clock
Φ

 Loading...
Loading...











