Key-Input Interrupt
M30240 Group
Rev.1.00 Sep 24, 2003 Page 271 of 360
2.11 Key-Input Interrupt
2.11.1 Overview
A Key-input interrupt occurs when a falling edge is input to any pin of Ports P0 or P1. The following is
an overview of the key-input interrupt:
2.11.1.1 Enable/Disable
The key-input interrupt can be enabled and disabled using the key-input interrupt register. The key-input
interrupt is affected by the interrupt priority level (IPL) and the interrupt enable flag (I flag).
2.11.1.2 Occurrence timing
With key-input interrupt enabled, Ports P0 and P1, which are set to input, become key-input interrupt
pins (KI0
through KI15). A key-input interrupt occurs when a falling edge is input to a key-input interrupt
pin. At this moment, the level of other key-input interrupt pins must be “H”. No interrupt occurs when the
level of other key-input interrupt pins is “L”.
2.11.1.3 How to determine a key-input interrupt
A key-input interrupt occurs when a falling edge is input to one of 16 pins, but each pin has the same
vector address.
Therefore, read the input level of the pins on Ports P0 and P1 in the key-input interrupt routine to
determine the interrupted pin.
2.11.1.4 Related registers
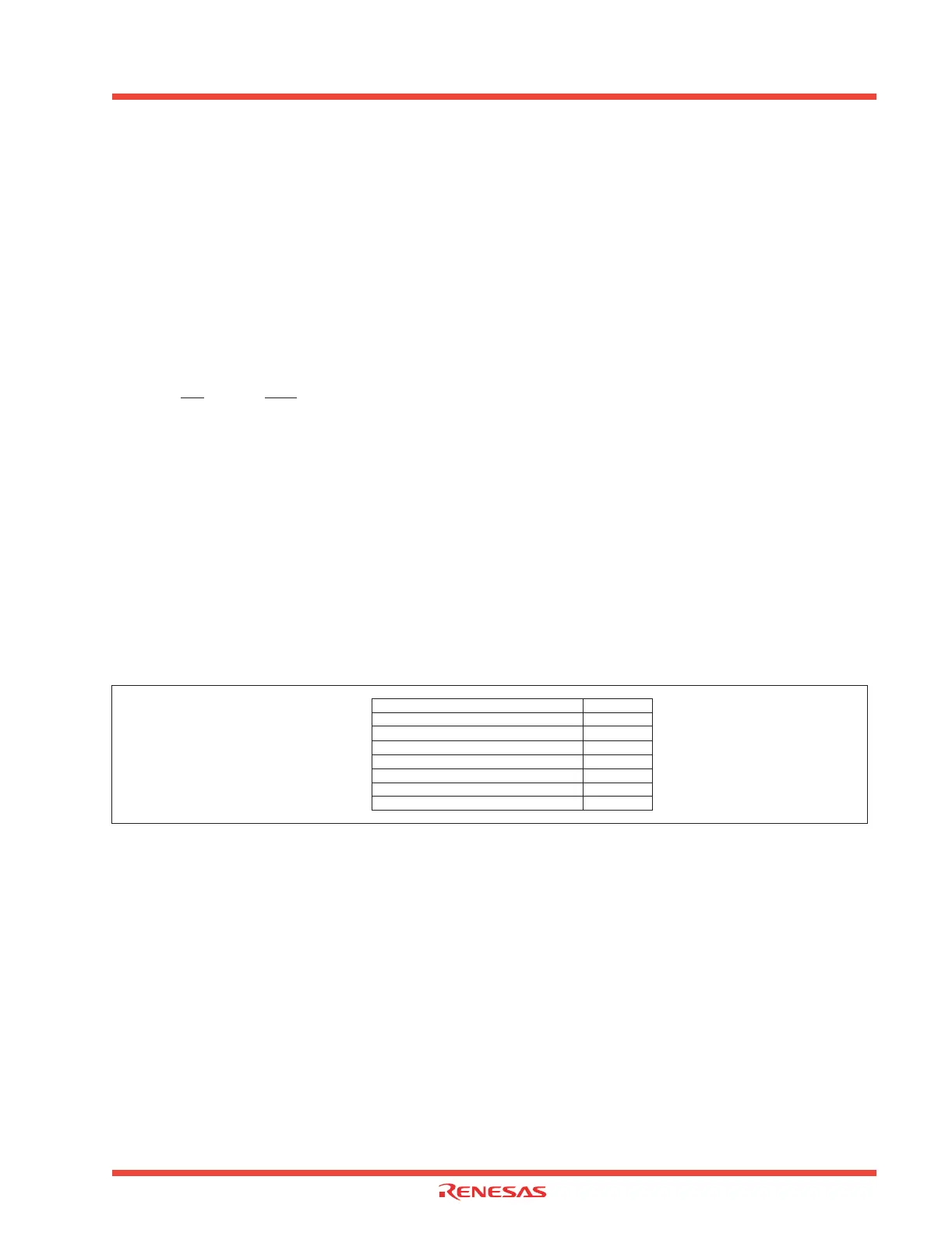
Figure 2.119 shows the memory map of key-input interrupt-related registers, and Figure 2.120 shows
key-input interrupt-related registers.
Figure 2.119: Memory map of key-input interrupt-related registers
004D
16
Key-input interrupt control register KUPIC
03E0
16
Port 0 P0
03E1
16
Port 1 P1
03E2
16
Port 0 direction register PD0
03E3
16
Port 1 direction register PD1
03FC
16
Pull-up control register 0 PUR0

 Loading...
Loading...











