Overview of Interrupts
M30240 Group
Rev.1.00 Sep 24, 2003 Page 330 of 360
4.1 Overview of Interrupts
4.1.1 Type of Interrupts
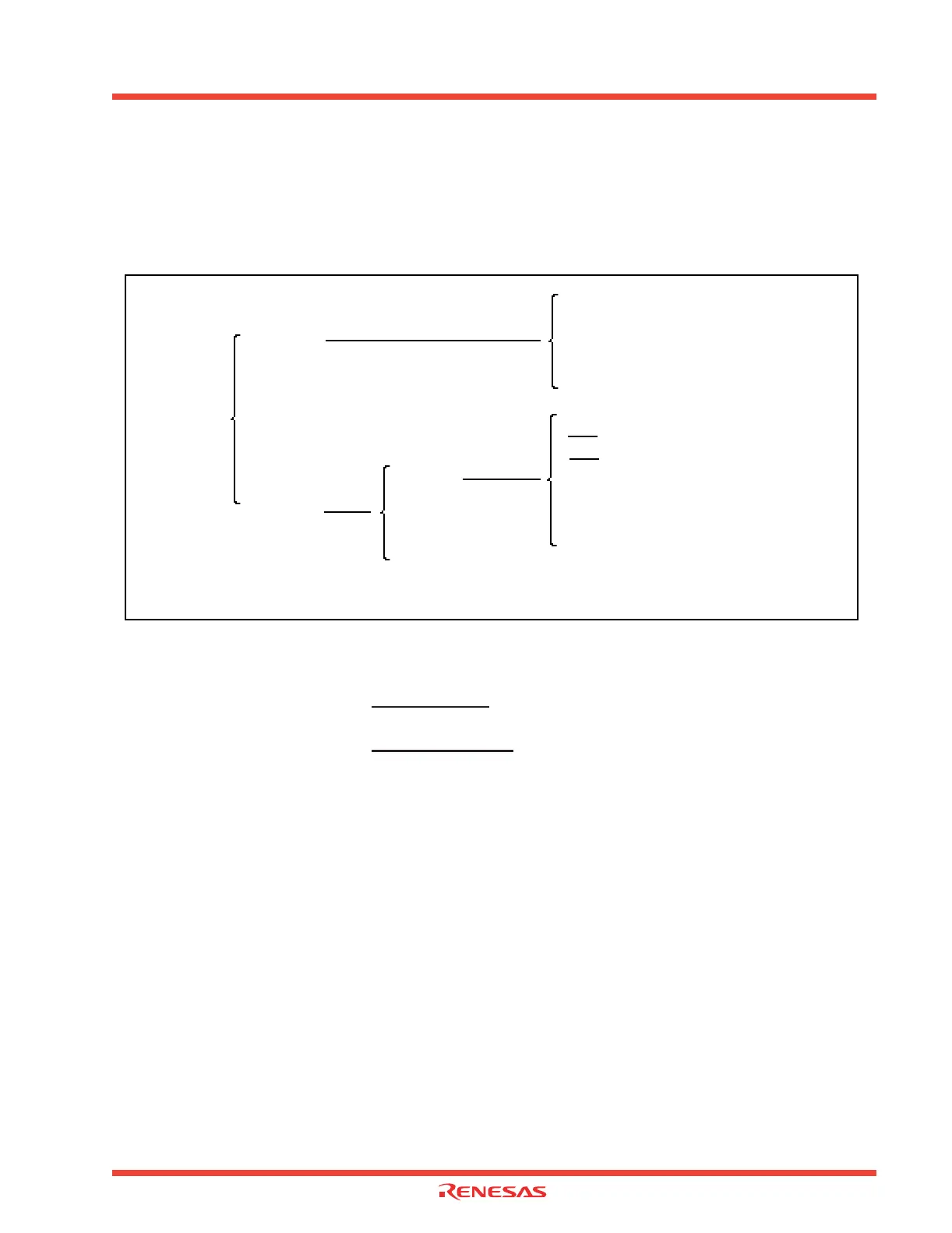
Figure 4.1 lists the types of interrupts.
Figure 4.1: Interrupt classification
• Maskable interrupt: An interrupt which can be enabled (disabled) by the interrupt enable flag
(I flag) or whose interrupt priority
can be changed by priority level.
• Non-maskable interrupt: An interrupt which cannot be enabled (disabled) by the interrupt enable flag
(I flag) or whose interrupt priority
cannot be changed by priority level.
4.1.1.1 Software Interrupts
A software interrupt occurs when executing certain instructions. Software interrupts are non-maskable
interrupts.
• Undefined instruction interrupt
An undefined instruction interrupt occurs when executing the UND instruction.
• Overflow interrupt
An overflow interrupt occurs when executing the INTO instruction with the overflow flag (O flag) set to
“1”. The following instructions can change the O flag when executed:
ABS, ADC, ADCF, ADD, CMP, DIV, DIVU, DIVX, NEG, RMPA, SBB, SHA, SUB
• BRK interrupt
A BRK interrupt occurs when executing the BRK instruction.
• INT interrupt
An INT interrupt occurs when assigning one of the software interrupt numbers 0 through 63 and exe-
cuting the INT instruction. Software interrupt numbers 0 through 31 are assigned to peripheral I/O in-
terrupts, so executing the INT instruction allows executing the same interrupt routine that a peripheral
I/O interrupt does.
Interrupt
Software
Hardware
Special
Peripheral I/O (Note)
Undefined instruction (UND instruction)
Overflow (INTO instruction)
BRK instruction
INT instruction
Reset
NMI
DBC
Watchdog timer
Single step
Address match
Note: Peripheral I/O interrupts are generated by the peripheral functions built into the microcomputer system.

 Loading...
Loading...











